Table of Contents
Introduction
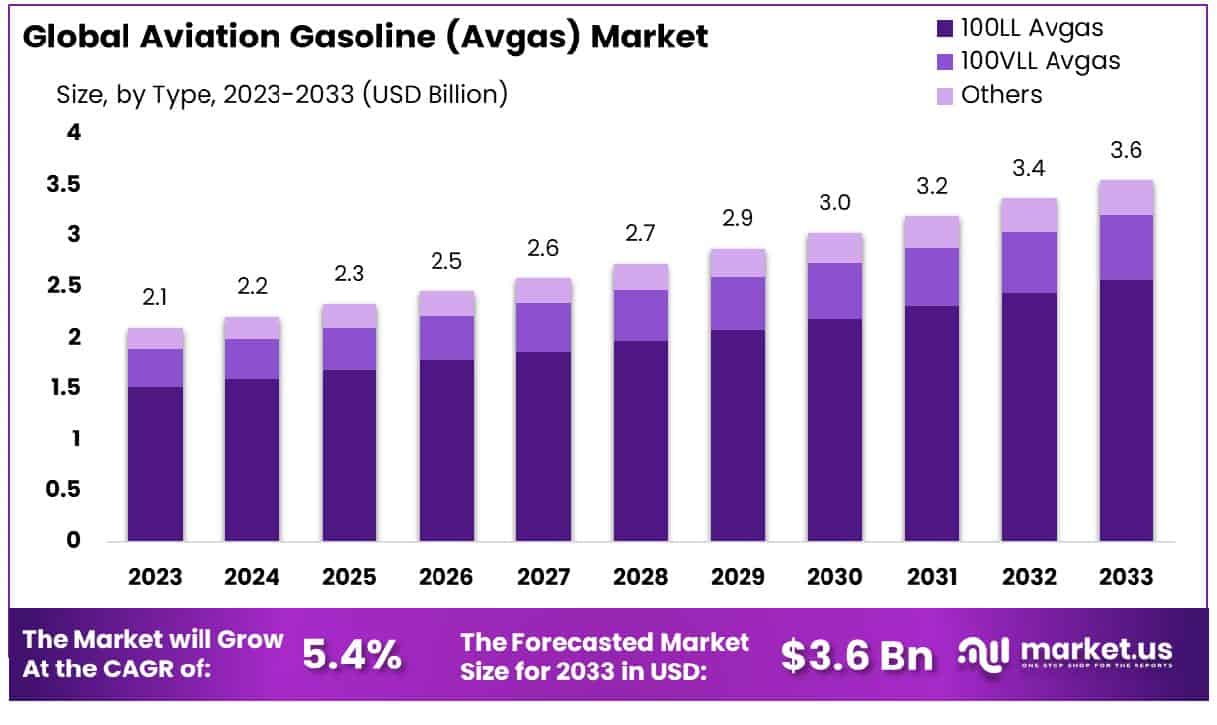
The Global Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) Market, valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2023, is projected to expand to approximately USD 3.6 billion by 2033, demonstrating a steady Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2024 to 2033. This growth is driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for general aviation aircraft and the escalating number of flight training schools worldwide. However, the market faces challenges such as stringent environmental regulations to reduce carbon emissions and the rising adoption of alternative fuels.
Recently, the industry has seen significant developments, such as advancements in fuel composition to enhance efficiency and reduce ecological impact. These innovations are pivotal in addressing the environmental concerns associated with Avgas emissions. Despite these challenges, the consistent demand for aviation gasoline underscores its indispensable role in the aviation industry, particularly for small aircraft and training planes, which rely exclusively on this type of fuel.
ExxonMobil Corporation has been proactive in expanding its global footprint through strategic partnerships and enhancing its supply chain capabilities for Avgas. Recently, ExxonMobil announced a significant investment to upgrade its facilities, which is expected to increase Avgas production by 20%. This development not only boosts production capacity but also improves the efficiency and environmental profile of Avgas offerings.
Shell Aviation has introduced a new formulation of Avgas that reduces emissions and improves engine efficiency. Launched in early 2023, this product has been adopted by several flight training academies, demonstrating a positive reception from the market. Shell Aviation’s commitment to innovation is evident in its continuous research and development efforts, aimed at meeting the stringent environmental standards facing the industry.
Chevron Corporation recently completed a merger with a regional fuel producer, aiming to expand its distribution network in the Asia-Pacific region. This strategic move, finalized in late 2022, is expected to enhance Chevron’s market penetration and improve its logistical operations, thereby securing a more robust position in the burgeoning aviation market in Asia.
BP Plc has been focusing on securing new contracts with commercial airlines for their Avgas supply. In 2023, BP successfully signed agreements with three major airlines, expected to increase their Avgas sales volume by 15% annually. These agreements not only bolster BP’s market position but also enhance its stability in the highly competitive aviation fuel market.
Phillips 66 Company has been awarded a grant to develop a sustainable alternative to traditional Avgas. This funding, received in mid-2023, supports Phillips 66’s initiative towards creating a more environmentally friendly aviation fuel. The company is set to begin trials in 2024, with the potential to revolutionize the market by offering a green alternative that meets regulatory standards and customer expectations.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Global Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) Market size is expected to be worth around USD 3.6 Billion by 2033, From USD 2.1 Billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- North America holds 44.6% of the USD 0.9 billion Avgas market.
- By Type: 100LL Avgas dominates the market, holding a 72.3% share.
- By Aircraft Type: Piston Engine Aircraft constitute 63.5% of the aviation fuel market.
- By Application: Private applications lead to Avgas usage, accounting for 60.3% of demand.
Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) Market Statistics
- The aviation sector creates 13.9% of the emissions from transport, making it the second biggest source of transport GHG emissions after road transport.
- AVGAS 100LL, also known as Aviation Gasoline 100 Low Lead, is a specialized type of aviation fuel used in piston-powered aircraft.
- The executive actions are intended to promote the production and use of billions of gallons of sustainable fuel that will result in a 20% reduction in aviation emissions by 2030.
- Currently, aviation represents approximately 11% of U.S. transportation-related emissions.
- Jet fuel might reach 12,000 Wh/kg, while batteries today are 250 Wh/kg and will at best reach 1,250 Wh/kg
- Jet A freezing point is -40°C, while Jet A1 freezes at -47°. The lower freezing point of Jet A1 makes it more suitable for international long-haul flights, particularly the ones on polar routes.
- Year-over-year changes in fuel consumption and cost for July 2023 include an 8.4% increase in domestic fuel consumption, 26.4% decrease in domestic fuel cost, and 32.1% decrease in cost per gallon.
- Most fossil jet fuels have an aromatics level of around 20%.
- Considering that jet fuel represents 40% of the total operating costs Indian airlines have, the higher jet fuel price meant a big hit for the industry.
- SAF potentially can reduce lifecycle greenhouse gas (GHG) by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuel and is considered pivotal to achieving the aviation industry’s goal of a 50% net reduction in CO2 emissions in 2050.
- Additional supply at a competitive price is critical to achieving industry sustainability goals, to reach a production capacity of 3 billion gallons by 2030.
- Three carriers expect fuel prices to rise in the third quarter, with predictions ranging from $2.70 to $3.25 per gallon.
- Jet fuel prices in the US rose by over 2% from June to July.
- The findings show carriers used 1.678 billion gallons of fuel during the month. The performance is 5% above the month prior, where 1.597 billion gallons.
- Total fuel expenditure in July resulted in $4.16 billion, up 7.4% from the previous month, where the total was $3.87 billion. Compared to July 2019, expenditure increased by 25.1%.
- June 2023 recorded $3.87 billion in total fuel costs for airlines.
- Aviation accounts for 12% of CO2 emissions from transportation and 2% of all CO2 emissions globally.
- 160 million gallons of SAF were consumed in 2023 – a drop in the bucket of the 90 billion gallons of conventional fuel consumed globally that year.
- The percentage of occurrence of bacterial aviation fuel–-utilizers were less than 1.0% of the heterotrophic populations, while the fungal degraders were between 2.547 and 16.053%.
- TotalEnergies’ SAF allows up to 90% reduction of C02 emissions, over its entire lifecycle analysis, compared to its fossil equivalent. The SAF used for these flights is blended up to a 50% rate with Jet A1.
Emerging Trends
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF): There is a growing interest in sustainable aviation fuels that can be blended with traditional Avgas to reduce carbon emissions without compromising engine performance. This trend is driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations aimed at curbing aviation-related emissions. Major players in the market are actively researching and developing SAF solutions that are compatible with existing aircraft engines, indicating a potential shift towards greener alternatives in the coming years.
- Technological Innovations in Fuel Efficiency: Advances in chemical engineering have led to the development of more efficient and cleaner-burning Avgas formulations. These innovations not only improve the environmental footprint of aviation fuel but also enhance engine efficiency and performance. As fuel efficiency remains a critical factor for cost management in aviation, these improved formulations are gaining traction.
- Expansion of General Aviation in Emerging Markets: The expansion of general aviation sectors in emerging markets, such as China and India, is increasing the demand for Avgas. As these regions develop their aviation infrastructure and increase accessibility to flight training and recreational flying, the demand for specialized aviation gasoline is expected to rise significantly. This trend is driving investments in fuel supply chains and distribution networks to cater to the growing markets.
- Regulatory and Safety Standards: There is an ongoing trend towards tighter safety and quality standards for aviation fuels, including Avgas. Regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing more rigorous testing and certification processes for Avgas to ensure safety and reliability in aviation operations. This trend emphasizes the importance of high-quality fuel production and has led to improvements in refining processes and quality control measures.
- Price Volatility and Supply Chain Resilience: The Avgas market is experiencing fluctuations in pricing due to global economic factors and geopolitical tensions that affect oil and gas supply chains. This volatility prompts a trend toward building more resilient supply chains to ensure stable Avgas availability and pricing for the aviation industry. Companies are diversifying their sourcing strategies and enhancing storage capabilities to mitigate these risks.
Use Cases
- General Aviation: Avgas is predominantly used in general aviation for piston-engine powered aircraft. These include small private planes, training aircraft, and vintage warbirds. The general aviation sector relies heavily on Avgas due to its high octane rating which is essential for the high-compression engines used in these aircraft. General aviation accounts for approximately 70% of the total Avgas consumption globally.
- Flight Training Schools: Flight training academies are significant consumers of Avgas. These schools use single-engine planes extensively for training purposes, which predominantly operate on Avgas. With the increasing number of pilot certifications—rising by an average of 3% annually—flight schools’ demand for Avgas continues to grow to meet the training needs.
- Agricultural Aviation: Avgas is also used in agricultural aviation, particularly in crop dusting and aerial application of pesticides and fertilizers. The specific requirements for low-altitude flying and maneuverability make Avgas-powered aircraft ideal for this purpose. This segment utilizes about 10% of the global Avgas supply, with expectations of growth in regions expanding their agricultural capabilities.
- Emergency Services: Aviation Gasoline is crucial for emergency and rescue operations, including air ambulances and firefighting. These services often use light aircraft that require Avgas for their operations, due to the fuel’s reliability and the aircraft’s agility. The segment is projected to see a growth in Avgas demand by 5% annually, driven by increasing global emphasis on rapid response and disaster readiness.
- Recreational Flying: Recreational flying is another area where Avgas is extensively used. Enthusiasts and hobbyists who fly vintage and sport aircraft rely on Avgas for its performance qualities. This segment, while smaller in volume compared to others, is seeing a resurgence as economic conditions improve and interest in personal and recreational flying grows.
Key Players Analysis
ExxonMobil is actively involved in the Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) sector, particularly focusing on Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) production. Recently, they’ve made strides by producing SAF at their Gravenchon refinery in France, aiming to produce significant quantities to support the European Union’s CO2 reduction goals. This initiative is part of their broader strategy to deliver about 200,000 barrels per day of lower-emission fuels by 2030.
Shell Aviation actively supports the aviation sector by offering both conventional Avgas and innovative sustainable aviation fuels (SAF). They are leading initiatives to decarbonize air travel through agreements like the one with Delta to accelerate SAF usage at LAX, demonstrating a strong commitment to reducing aviation emissions. These efforts are part of Shell’s broader strategy to adapt aviation to more sustainable practices while continuing to meet global fuel needs.
Chevron Corporation is making significant strides in the Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) sector, particularly focusing on sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). They have established a commitment to reduce carbon intensity by advancing SAF technologies, including partnerships and investments to scale up production capabilities. Chevron’s efforts include joining the Clean Skies for Tomorrow coalition, aiming to make SAF account for 10% of global jet fuel by 2030. Additionally, Chevron has partnered with companies like Gevo to produce SAF from inedible corn and other feedstocks, underlining their strategy to provide lower-carbon alternatives in aviation.
BP Plc is actively enhancing its portfolio in the Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) sector, primarily through sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). The company is focusing on significant expansion in SAF production, targeting about 100,000 barrels per day by 2030 through strategic global projects. BP emphasizes producing high-quality Avgas specifically for aviation, ensuring safety and reliability in spark ignition aviation piston engines. This commitment is part of BP’s broader strategy to reduce carbon emissions in aviation and support the industry’s transition to lower-carbon alternatives.
Phillips 66 Company has been actively involved in the aviation gasoline (Avgas) sector, particularly focusing on the development of unleaded Avgas. The company, in collaboration with Afton Chemical, has been working on an unleaded Avgas alternative known as 100M under the FAA’s Piston Engine Aviation Fuels Initiative (PAFI). However, their testing has been paused due to issues encountered during durability testing. Despite these challenges, Phillips 66 remains committed to reducing lead in aviation fuel and is exploring other viable alternatives to continue its efforts in this area.
TotalEnergies is intensively involved in the aviation sector, particularly focusing on the production and supply of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF). The company has established strategic partnerships, such as with Airbus and Safran, to enhance SAF development and significantly reduce CO2 emissions from aviation. These efforts align with their ambition to achieve net carbon neutrality by 2050. TotalEnergies is increasing SAF production capacity at its facilities, like the Grandpuits site, to meet rising industry demand and regulatory requirements for higher SAF blends in aviation fuel.
Air BP, a division of BP, is actively involved in the aviation gasoline (Avgas) sector, focusing on both unleaded and sustainable options. They provide high-quality Avgas designed for safe and reliable operation in spark ignition aviation piston engines. Notably, Air BP has initiated trials of unleaded Avgas (91UL) at Goodwood Aerodrome and continues to supply Avgas 100LL while exploring sustainable alternatives. These efforts are part of Air BP’s broader commitment to meeting evolving fuel requirements and enhancing environmental sustainability in aviation.
FBO Partners is actively involved in providing essential services in the aviation gasoline (Avgas) sector, particularly focusing on the storage and distribution of Avgas to general aviation. They operate facilities that offer secure hangar and parking options for various aircraft, ensuring safe and reliable Avgas supply. Additionally, they support the transition to unleaded Avgas, reflecting a commitment to sustainability and adapting to changing industry standards. Their involvement in the aviation industry is complemented by their expertise in real estate and FBO management, which aids in efficiently managing Avgas supplies and services at their locations.
Avfuel Corporation, headquartered in Ann Arbor, Michigan, is a prominent supplier in the aviation gasoline sector, especially known for unleaded avgas. The company has been instrumental in distributing the G100UL avgas, a high-octane unleaded fuel approved by the FAA, reflecting its commitment to innovation and environmental sustainability in aviation fuels.
Eastern Aviation Fuels, a prominent supplier in the Avgas sector, specializes in distributing high-quality aviation gasoline. The company is known for its focus on delivering 100LL avgas, which meets stringent performance requirements for piston engine aircraft. Their commitment ensures reliable and safe engine performance, catering extensively to the general aviation community across various operational needs.
Pinnacle Petroleum is a key player in the aviation gasoline (Avgas) sector, focusing on providing high-quality Avgas to various markets. They are recognized for their significant role in distributing Avgas which is essential for powering piston-engine aircraft, thereby supporting the aviation industry’s operational needs across North America.
World Fuel Services Corporation is a key provider in the aviation gasoline (Avgas) sector, recognized for delivering reliable and high-quality Avgas alongside other aviation fuels. They focus on integrated fuel supply solutions, ensuring operational efficiency and support for global fixed base operators (FBOs). Their expertise extends to logistics, technical services, and a comprehensive supply chain that enhances the efficiency of aviation operations worldwide.
AvGas LLC is actively involved in the Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) sector, particularly recognized in the industry-wide transition towards unleaded avgas. The company is part of the Piston Aviation Fuels Initiative (PAFI), which collaborates with the FAA to evaluate and potentially certify new unleaded avgas formulations that meet high octane requirements without the use of lead. This initiative reflects a significant effort to address environmental concerns and regulatory pressures regarding lead emissions from aviation fuels.
Q8 Aviation, a subsidiary of Kuwait Petroleum International, is a major player in the aviation fuel sector, particularly known for supplying jet fuel. It ensures a secure and efficient fuel supply from production to delivery, serving over 70 international and regional airports across 21 countries, including some of Europe’s busiest airports. The company’s extensive network and commitment to quality, safety, and technical excellence make it a key supplier for over 200 of the world’s major airlines. Q8 Aviation also engages in sustainable practices by integrating Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) into its offerings.
Gazprom Neft Aviation has not been directly linked to specific activities in the aviation gasoline (Avgas) sector. The company is primarily known for its involvement in the production and supply of jet fuel and has been actively involved in the development of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). Their efforts are focused on reducing the environmental impact of aviation fuels, which include collaborations with major Russian airlines to develop and implement SAF solutions.
Conclusion
The market for Aviation Gasoline (Avgas) continues to demonstrate a critical role in the aviation industry, particularly for small aircraft and piston-engine planes. Despite facing challenges from environmental regulations and the rising interest in alternative fuels, the demand for Avgas remains robust, supported by its essential use in general aviation. Market stability is currently maintained by consistent demand among key user groups, including flight training schools and hobbyist pilots.
Looking forward, the Avgas market is expected to experience gradual growth, influenced by factors such as technological advancements in fuel formulations and potential regulatory changes. Stakeholders in the industry should monitor these developments closely to adapt strategies that align with evolving market dynamics and regulatory environments.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





