Table of Contents
Introduction
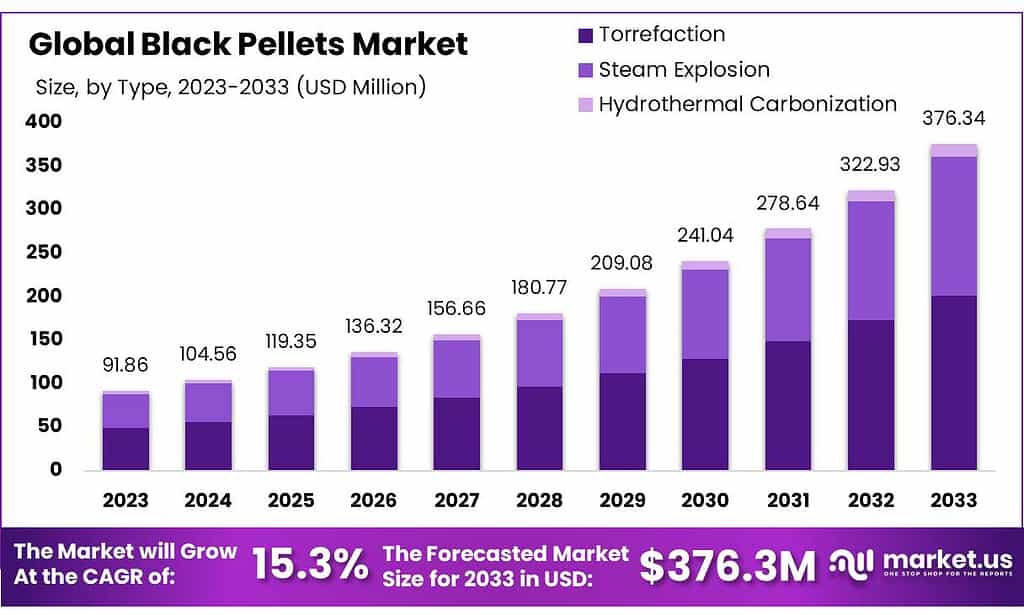
The global Black Pellets Market is positioned for robust growth, with the market size expected to expand from USD 91.86 million in 2023 to approximately USD 376.34 million by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.3% over the forecast period. This impressive growth is driven by several factors, including increasing demand for renewable energy, advancements in biomass technology, and stringent environmental regulations.
Growth in this market is driven by increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly energy solutions. The rising awareness of environmental issues has spurred interest in black pellets, which serve as a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels. For example, in 2023, wood chips were the most preferred feedstock, holding 45.2% of the market share due to their availability and sustainability.
The power generation sector, which accounted for 56.1% of the market share in 2023, is the largest application area for black pellets. This sector benefits from the efficiency and reliability of black pellets in generating electricity, thereby supporting the transition towards greener energy sources.
However, the market faces several challenges. The initial cost of adopting black pellets is relatively high, which can be a barrier to widespread adoption. Additionally, the market’s reliance on government policies and trends introduces a degree of uncertainty. Changes in regulations regarding renewable energy and carbon emissions could impact market stability.
Recent developments in the black pellets market include significant investments by leading companies such as Zilkha Biomass Energy and Blackwood Technology in expanding production capacities and enhancing distribution networks. These companies are also focusing on research and development to improve the efficiency of the torrefaction process, which is crucial for producing high-quality black pellets.
Arbaflame, renowned for its innovative approach in the black pellet sector, has focused on perfecting pellet production to serve the power generation market. Their specialized pellets are designed to replace coal, providing a more sustainable and cleaner energy alternative.
Airex Energy Inc., based in Canada, has been active in commercializing its biomass torrefaction technology. Their process transforms biomass into biochar, a stable form of carbon that can be used as a substitute for coal. Airex Energy’s focus remains on enhancing the environmental credentials of black pellets and promoting their use across various energy-intensive industries.
Key Takeaways
- The global black pellets market was valued at USD 91.86 Million in 2023.
- The global black pellets market is projected to reach USD 376.34 Million by 2033.
- Among black pellet types, the torrefaction type held the majority of the revenue share at 53.6%.
- Based on feedstock types, wood residue accounted for the largest market share with 64.3%.
- Among applications, heat generation accounted for the majority of the black pellets market share at 54.9%.
- Based on end-user, the residential sector dominated the market with a share of 44.5%.
- The European Union’s renewable energy directive mandates that 32% of the energy consumed in the EU should come from renewable sources by 2030, driving demand for black pellets.
Black Pellets Statistics
- The addition of water (20%) and shorter drying time (4 hours) resulted in pellets with higher moisture content (3.34%), better heat conduction, and particle arrangement, leading to increased density and energy density.
- Black pellets exhibited excellent durability (>98%) regardless of moisture content and drying time, indicating strong particle bonding.
- Charcoal fines, bound with rice starch, offer a promising alternative for residential heating, especially the T3 treatment (20% moisture content, 4 hours drying), meeting desirable properties for use and commercialization.
- The country is the ninth largest rice producer in the world, with an estimated annual national intake of 11.5 million tons.
- Pellet size range 0.8 to 3.5 mm with ±0.1 mm absolute accuracy.
- Force measuring range up to 250 cN with ±2 cN absolute accuracy.
- Black pellets can thus replace fossil coal up to 100% in smaller units and up to 70% in larger units.
- Black pellets are cheaper to ship than white pellets. This is due to the higher wet and dry durability of black pellets, as well as the fact that they hold about 15% more energy per ton and have 15% higher bulk density than white pellets.
- That gives savings of approximately 30% with black pellets compared to white pellets just in shipping, regardless of prevailing fuel prices.
- Idemitsu is planning to increase its black pellet output to 300,000 t/yr within three years after the start-up of the first plant. Its final target is 3mn t/yr by 2030,
- Black pellets were produced using two proportions of water (10 or 20%) and a drying time of 4 or 6 hours.
- The addition of water allowed for better heat conduction and particle arrangement, producing pellets with a durability greater than 98%.
- Brazil stands out on the world stage for being the largest producer and consumer of charcoal, accounting for 12% of world production.
- Carbon black, a fine powdery material obtained by the incomplete combustion or thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons, contains 90–99% carbon, where the rest is mostly hydrogen and oxygen.
- Carbon black has various applications depending on its grade, but more than 92% of the global production is used in the rubber industry, especially in tire production.
- The total CO2 emissions for power generation in a 50 MW using black pellets and coal amounted to 16.27 and 272.10 kton/y, respectively.
- Copenhagen Biomass Merchants (CM Biomass) was also set to add about 420,000 t/yr of wood pellet production capacity in the US in 2023, with 150,000 t/yr of this already commissioned in the first half of the year in Jackson, Alabama.
- US producer Enviva was evaluating a potential deferral of up to 12 months to 2026 of the 1.1mn t/yr Bond plant, Mississippi, “in light of ongoing liquidity management initiatives”.
- Enviva, the world’s largest industrial wood pellet producer, owns and operates 10 plants with a combined production capacity of about 6.2mn t/yr.
- Canadian pellet producer Prairie Clean Energy aims to raise its production of flax pellets to at least 150,000 t/yr by 2026 using untapped agricultural residues in the US and Canada.
- In 2018, global crude steel production was approx. 1.8 gigatonnes while its direct CO2 emissions stood at 2 gigatonnes (2017), representing 23.5% of all direct industrial emissions.
- The indoor stored steam exploded wood pellets on the surface of the pile only exhibited a 3% decrease in durability after twenty months in storage.
- In the summer period with high relative humidity and temperature, the durability of pellets sampled from the surface of the pile dropped from 92 to 22% after three months in storage with a durability of 10% measured after nine months in storage.
- The large-scale use of biomass worldwide in decarbonizing power generation is predicted to grow to meet the EU 2030 emissions targets of 40% below 1990 levels and the renewables target of providing at least 27% of EU’s energy requirements.
Emerging Trends
- Technological Innovations: Advanced torrefaction processes are enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of black pellet production. These technologies allow for the controlled heating of biomass in the absence of oxygen, improving the energy density and water resistance of the final product. Furthermore, the integration of automation and digital technologies in production processes is streamlining operations, from feedstock handling to pellet packaging, improving both the quality and environmental footprint of black pellets.
- Environmental Benefits: Black pellets are gaining traction due to their eco-friendly characteristics. They are produced from organic waste materials like wood residues, reducing reliance on finite resources and lowering greenhouse gas emissions during both production and combustion. Additionally, their combustion produces fewer pollutants compared to traditional fossil fuels, contributing to better air quality and aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
- Regulatory Support: The market is also influenced by regulatory frameworks that promote safety, quality, and sustainability in the production and use of black pellets. Governments worldwide are updating these regulations to support the growing shift towards renewable energy sources, ensuring that black pellets meet stringent environmental standards.
- Cost Efficiency: There’s a focus on making black pellet production more cost-effective. This involves optimizing raw material use, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing the overall supply chain efficiency. Such cost reductions are vital for making black pellets a competitive alternative to traditional energy sources.
- Global Market Expansion: The demand for black pellets is rising globally, with significant growth opportunities in both developed and emerging markets. In regions like Asia-Pacific and Europe, the push for renewable energy and reduction of carbon emissions is driving the adoption of black pellets in various applications, from power generation to residential heating.
Use Cases
- Power Generation: Black pellets serve as an effective replacement for fossil coal in power generation. Their high energy density and water-resistant properties allow them to be used directly in coal-fired power plants without significant modifications to existing infrastructure. This application not only supports the transition to renewable energy but also helps reduce carbon emissions significantly.
- Industrial Heating: Industries requiring high temperatures for processes, such as cement and steel manufacturing, can utilize black pellets due to their high combustion efficiency and energy content. This makes them a suitable, more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels for industrial heating applications.
- Residential Heating: In residential settings, black pellets can be used in pellet stoves and boilers to provide heating. They are an eco-friendlier alternative to heating oils or natural gas, offering a cleaner burning option and contributing to reduced household carbon footprints.
- Co-firing with Coal: Black pellets are particularly valuable in the co-firing market, where they are mixed with coal in power plants. This practice helps reduce the carbon footprint of these plants without necessitating complete infrastructural overhaul, providing a transitional solution towards full renewable energy use.
- Integrated Energy Systems: Some innovative approaches integrate black pellet production with combined heat and power (CHP) systems. These systems utilize the heat generated during the pellet production process for both the drying stages of pellet production and to provide additional energy outputs, such as electricity to the grid, optimizing energy use and enhancing the sustainability of the production process.
Major Challenges
- High Production Costs: One of the primary challenges is the high cost associated with producing black pellets. The torrefaction process, which involves heating biomass in the absence of oxygen to create black pellets, is energy-intensive and costly. This can make black pellets more expensive compared to traditional biomass fuels like white pellets or raw wood chips. The need for specialized equipment and technology further adds to the production costs, making it challenging for black pellets to compete with cheaper fossil fuels.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Establishing a stable supply chain for black pellets is another significant hurdle. The production of black pellets requires a consistent and reliable supply of biomass feedstock, such as agricultural residues or forestry by-products. However, fluctuations in the availability of these raw materials due to seasonal changes or market dynamics can disrupt production. Additionally, the transportation and storage of black pellets require careful management to maintain their quality, particularly their hydrophobic properties, which can add logistical challenges and costs.
- Limited Market Penetration: Despite their advantages, black pellets have struggled to gain widespread market penetration. Many industries and energy producers are hesitant to switch to black pellets due to the need for initial investments in equipment modifications and the higher upfront costs. Furthermore, the existing infrastructure for coal and white pellets is already well-established, creating a barrier to entry for black pellets, which are still seen as a niche product in many regions.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Rising Demand for Renewable Energy: As countries aim to reduce their carbon emissions and transition to renewable energy sources, black pellets offer a viable alternative to coal. Governments in regions like Europe, Asia, and North America are implementing stricter environmental regulations and offering incentives for renewable energy adoption. This creates a favorable environment for black pellets, which can be co-fired with coal in existing power plants, reducing carbon emissions without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: There is significant potential for black pellets in emerging markets, particularly in Asia. Countries like Japan and South Korea are increasingly adopting black pellets to meet their renewable energy goals. Additionally, Southeast Asian countries with abundant biomass resources, such as Vietnam and Indonesia, are becoming key producers and exporters of black pellets. The expansion of production facilities in these regions, supported by investments from companies like Idemitsu Kosan, highlights the growth potential in these markets.
- Technological Innovations: Advances in torrefaction technology are making black pellet production more efficient and cost-effective. Innovations that reduce energy consumption during production or allow for the use of a wider range of biomass feedstocks are expected to lower costs and enhance the competitiveness of black pellets. These technological improvements can help overcome some of the current barriers to adoption, such as high production costs, and open up new applications in various industries, from power generation to industrial heating.
- Sustainability Initiatives: As global businesses and governments intensify their focus on sustainability, the demand for carbon-neutral energy sources like black pellets is expected to grow. Companies are increasingly looking for ways to reduce their carbon footprints, and black pellets offer an effective solution for industries that rely heavily on energy, such as cement and steel production.
Key Players Analysis
Zilkha Biomass Energy LLC is a pioneer in the black pellets industry, offering a significant advancement with its water-resistant Zilkha Black® Pellet. These pellets are designed to handle like coal but burn cleaner, making them a sustainable alternative for coal-fired power plants looking to reduce their environmental impact. Zilkha’s technology not only enhances the pellets’ storage and handling characteristics but also their burning efficiency, positioning the company as a key player in the shift towards sustainable energy solutions.
Blackwood Technology B.V. specializes in the black pellets sector with its innovative FlashTor® technology, which significantly enhances the quality and efficiency of pellet production. This technology allows for the large-scale transformation of biomass into high-energy, water-resistant black pellets, serving as a cleaner, renewable alternative to coal. Blackwood’s recent expansions include supplying technology to new pellet plants in Thailand and ongoing collaborations to enhance torrefaction technology. Their pioneering work positions them strongly within the renewable energy market, pushing forward the adoption of black pellets in energy-intensive industries.
Bionet is a notable player in the black pellets sector, leveraging its capabilities to produce high-quality pellets from forestry waste. As part of the Gazprombank Group, one of the largest enterprises in Russia, Bionet has utilized its extensive resources to manufacture black pellets, which are known for their energy efficiency and environmental benefits. The company has focused on optimizing the use of waste materials to create a sustainable product that offers a viable alternative to conventional fossil fuels, contributing significantly to the renewable energy landscape.
Arbaflame is advancing the black pellets sector with its proprietary Arbacore pellets, designed for both full replacement and co-firing with coal in power plants. Using a steam explosion process, Arbaflame enhances the wood fibers’ breakdown, increasing pellet durability and energy content. This Norwegian firm’s innovative approach not only supports cleaner energy production but also facilitates a smoother transition from coal, aligning with global sustainability goals. Arbaflame’s significant investments and strategic collaborations aim to expand its impact and market presence globally .
Airex Energy Inc. is significantly impacting the black pellets sector with its innovative CarbonFX technology, transforming biomass into high-energy, environmentally friendly biocoal. Operating from Québec, Canada, Airex has recently bolstered its position through a CA$38 million funding round, indicating strong investor confidence and enabling further growth. This funding will support the expansion of their biochar production initiatives and other sustainable projects, emphasizing their commitment to renewable energy solutions and carbon reduction. Airex’s biocoal serves as a viable coal replacement, highlighting its potential in contributing to the global transition towards greener energy sources.
Bioendev has established itself as a significant player in the black pellets sector, utilizing its proprietary torrefaction technology developed from extensive research at Umeå University in Sweden. The company has made substantial progress with its largest torrefaction facility in Scandinavia, capable of producing 16,000 tons of black pellets annually. This production capacity highlights Bioendev’s commitment to transforming biomass into a sustainable and commercially viable energy source. Bioendev’s focus extends to enhancing the energy density and water resistance of black pellets, making them a more effective substitute for coal in various energy production settings. With several global patents, the company emphasizes high process control and the ability to deliver cost-effective torrefaction technology and facilities, which are appealing to industries looking to reduce their carbon footprint and transition from fossil fuels.
The Energy Research Centre of the Netherlands (ECN), now part of TNO since merging in 2018, has been a significant player in energy innovation, including the development of black pellets. ECN focuses on advancing sustainable energy technologies, which aligns with its work in the black pellets sector to provide cleaner energy alternatives. The organization has contributed to enhancing the properties and production processes of biomass pellets, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly. ECN’s efforts in this field support the transition to renewable energy sources by improving the functionality and economic viability of black pellets as a sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuels.
Thermogen Industries, a subsidiary of Cate Street Capital, has teamed up with Zilkha Biomass Energy to produce black pellets using Zilkha’s patented technology. This collaboration will enable Thermogen to manufacture over 300,000 tonnes annually of Zilkha’s water-resistant black pellets at its facility in Maine, USA. These black pellets, designed to handle like coal but offer a cleaner alternative, will help meet the increasing demand for renewable energy sources in coal-firing plants, enhancing supply and production capabilities in the renewable energy market.
Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. is actively expanding its role in the black pellets sector, particularly through the development of a large-scale commercial production plant for “Idemitsu Green Energy Pellets™” in Vietnam. This initiative marks a significant move towards reducing CO2 emissions from coal-fired boilers, highlighting the company’s commitment to sustainable energy solutions. Idemitsu plans to achieve an annual production capacity of 300,000 tons of these high-calorie, water-resistant black pellets within three years. These pellets can be co-fired with coal without requiring modifications to existing combustion equipment, which offers a practical solution for reducing carbon emissions in energy production. This effort is part of Idemitsu’s broader strategy to transition from traditional energy sources to more sustainable alternatives, supporting global environmental sustainability goals.
Conclusion
The black pellets market is poised for significant growth as global efforts to transition to renewable energy sources intensify. With their enhanced energy density, hydrophobic properties, and compatibility with existing coal infrastructure, black pellets present a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. The increasing adoption of these pellets for co-firing in coal power plants, particularly in Europe and Asia, highlights their growing importance in reducing carbon emissions and supporting sustainability goals.
Technological advancements in torrefaction and expanding production facilities in regions rich in biomass resources are further driving market expansion. However, challenges such as high production costs and supply chain complexities remain. Overall, black pellets represent a promising solution in the renewable energy landscape, with continued innovation and investment likely to overcome current hurdles and unlock further growth opportunities.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





