Table of Contents
Introduction
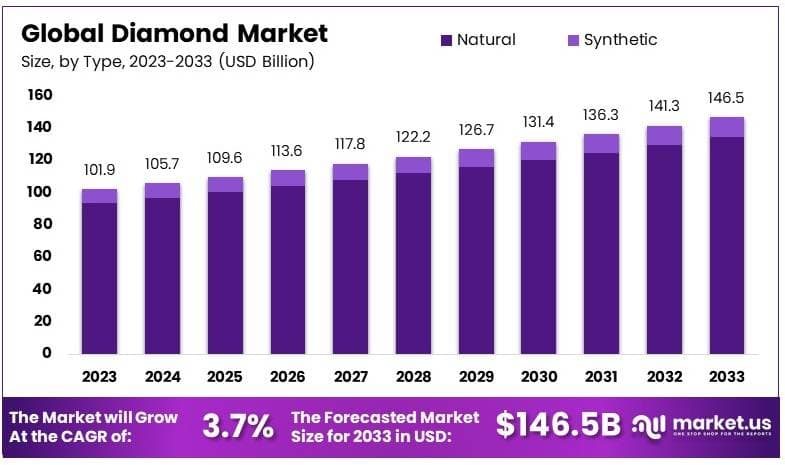
The Global Diamond Market is projected to expand from USD 101.9 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 146.5 billion by 2033, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
Diamond, a crystalline form of carbon, is one of the hardest known substances on Earth and is highly valued for its exceptional optical and physical properties. As both a gemstone and an industrial material, diamonds are primarily known for their aesthetic appeal in jewelry, where their brilliance and durability symbolize luxury and prestige.
However, beyond its ornamental uses, diamond has diverse industrial applications due to its unmatched hardness, thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it indispensable in sectors like construction, electronics, and healthcare. This versatility enhances diamond’s value as both a commercial and industrial asset.
The diamond market encompasses the extraction, processing, trading, and sales of natural and synthetic diamonds, primarily serving industries like jewelry, electronics, and precision cutting tools. This global market is complex and highly segmented, with two primary divisions: natural diamonds, mined from the earth, and synthetic diamonds, manufactured through high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes.
The market involves a multi-tiered supply chain including mining companies, wholesalers, jewelers, and retailers, with a strong emphasis on transparency and sustainability due to growing consumer and regulatory pressures. Over recent years, the rise of synthetic diamonds and shifting consumer preferences have reshaped traditional market dynamics, presenting both challenges and opportunities across the value chain.
Several factors contribute to the growth of the diamond market, among which increasing consumer disposable income and the expanding middle class, particularly in emerging economies, are primary drivers. Rising demand for luxury goods and investments in premium gemstones underpin the growth in the jewelry segment, while the growing acceptance and technological advancements in synthetic diamonds fuel demand in the industrial segment.
In addition, the emergence of blockchain technology has enhanced transparency in the diamond supply chain, helping to mitigate issues related to conflict diamonds and appealing to ethically conscious consumers. The rising demand for industrial diamonds, especially in electronics and precision cutting industries, further bolsters market expansion.
Demand in the diamond market is dual-faceted, driven both by consumer and industrial segments. The consumer side remains largely dominated by demand for jewelry, with significant contributions from markets in the U.S., China, and India, which together account for a considerable portion of global sales. Notably, millennial and Gen Z consumers are shaping new demand patterns, often prioritizing ethical sourcing and environmental impact, thus increasingly favoring lab-grown diamonds.
On the industrial front, demand is propelled by the need for high-performance materials in electronics, construction, and medical applications, with synthetic diamonds in particular seeing steady demand due to their consistent quality, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specialized uses.
The diamond market presents various opportunities, particularly through technological innovation and evolving consumer preferences. The lab-grown diamond sector, for example, holds significant growth potential due to its ethical appeal and cost advantages, appealing to younger, environmentally conscious demographics. Additionally, expanding applications in high-tech sectors—such as semiconductors, quantum computing, and thermal management solutions—highlight new avenues for industrial diamonds, particularly synthetic varieties.
The push for sustainable practices, coupled with advances in supply chain transparency through blockchain and AI, provides companies with the opportunity to strengthen their competitive edge by aligning with market trends in sustainability and responsible sourcing.
Key Takeaways
- The diamond market was valued at USD 101.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 146.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 3.7%.
- Natural diamonds led the type segment in 2023, capturing 93.8% market share, driven by strong demand within luxury jewelry markets.
- Jewelry and ornaments dominated the application segment in 2023, accounting for 91.5% of market share, fueled by the rising global consumption of luxury goods.
- North America was the leading region in 2023, holding a 52.6% share of the market, valued at USD 53.6 billion, attributed to a high concentration of luxury consumers.
Diamond Statistics
- The 59.6-carat Pink Star diamond sold for a record $71.2 million.
- India polishes over 90% of the world’s diamonds by volume.
- The U.S. leads in diamond jewelry sales, with over 40% of the market.
- Lab-grown diamonds represent around 2% of the global diamond market.
- A one-carat diamond engagement ring averages $5,000 in 2023.
- Online channels account for over 30% of diamond sales.
- Millennials make up 45% of diamond buyers in the U.S.
- China is the second-largest market, with a 15% share.
- The Kimberley Process certifies 99.8% of rough diamonds to prevent conflict stones.
- The diamond industry employs over 10 million people globally.
- Average mined rough diamonds are between 1-2 carats.
- Mining yields about 1 carat per ton of ore.
- Diamond mines last about 20-30 years on average.
- A 10-carat diamond costs $10,000 to $2 million, based on quality.
- Roughly 85% of cut diamonds go to jewelry; the rest serve industry.
- India imports over 15% of the world’s rough diamonds.
- Polishing yields 40-60% of rough diamond weight.
- U.S. prices for a 1-carat diamond range from $4,000 to $18,000.
- The first diamond engagement ring was gifted in 1477.
- Diamonds in jewelry are usually recut or reset every 20-25 years.
- Around 80% of diamonds are unsuitable for jewelry and used in industry.
- Global diamond reserves stand at around 1.3 billion carats.
- Diamonds were discovered in India over 2,000 years ago.
- The U.S. holds over 50% of diamond jewelry demand; China has 12.2%.
- Round-cut diamonds are the top choice, making up nearly 50% of U.S. sales.
- The Cullinan Diamond, at 3,106.75 carats, is the largest ever found.
- Lab-grown diamond production grew 25% in 2023.
- Lab-grown diamonds cost around 70% less than natural ones.
- Engagement rings make up 20% of diamond jewelry sales.
- Average spending on engagement rings in the U.S. was $5,800 in 2023
Emerging Trends
- Growing Demand for Ethical and Sustainable Diamonds: With consumers prioritizing transparency and ethical sourcing, the diamond industry is increasingly adopting initiatives like blockchain-based traceability. AI and blockchain technologies enable customers to verify the origin of diamonds, ensuring they meet ethical standards. Companies are leveraging certifications such as the Responsible Jewellery Council’s Chain of Custody, which is becoming crucial for attracting socially conscious buyers.
- Rise of Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs): Lab-grown diamonds continue to gain popularity, especially among younger demographics seeking affordability and sustainability. These diamonds, which offer the same physical characteristics as natural ones at a lower cost, are becoming mainstream in the U.S. market. However, many consumers still value natural diamonds for their unique origin and perceived higher long-term value, making natural diamonds appealing as luxury items with emotional and financial resonance.
- Personalization and Unique Diamond Cuts: Consumers are increasingly seeking personalized jewelry, favoring unique shapes and custom features that reflect individuality. Demand for non-traditional cuts, such as elongated ovals and hexagons, is growing, alongside rustic, minimally processed diamonds like salt-and-pepper stones. These “imperfect” diamonds, with visible inclusions, have carved out a unique niche for those desiring a more distinctive look, diverging from the traditional perfect clarity aesthetic.
- Digital Transformation and E-commerce Growth: Online diamond sales are expanding rapidly, predicted to reach nearly a quarter of the market. Brands are investing in digital experiences, from virtual try-on options to seamless payment systems. E-commerce allows companies to reach a global audience and adapt to the growing preference for online luxury purchases. This digital shift is crucial for engaging tech-savvy consumers and offering convenience without compromising authenticity.
- Price Stabilization Amid Supply Adjustments: After several years of volatility, the diamond market is gradually stabilizing. With production levels adjusting and demand recovering, prices for both rough and polished diamonds are showing signs of moderate recovery. Factors such as sanctions on Russian diamonds and lower-than-expected production levels are tightening supply, supporting price increases. This trend may present an opportunity for natural diamond stakeholders as they redefine value propositions amid evolving consumer preferences.
Top Use Cases
- Electronics and Heat Management: Diamonds’ exceptional thermal conductivity, approximately five times higher than copper, makes them ideal for high-performance electronics. In semiconductor technology, lab-grown diamonds are increasingly used as heat sinks, critical for cooling high-power devices and prolonging component life. Diamond substrates are being explored to support the future of microelectronics as computing needs continue to expand (annual market growth for lab diamonds in tech is projected at around 7-8%).
- Quantum Computing and Data Processing: Diamonds with nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers are at the forefront of quantum technology. These NV diamonds, which have unique electronic properties, serve as stable qubits for quantum computers and enhance data storage. This emerging field is expected to accelerate as diamonds offer a promising path for room-temperature quantum operations, potentially reducing cooling costs by 30-40% in quantum labs.
- Medical and Biomedical Applications: Nanodiamonds are being integrated into advanced medical applications due to their biocompatibility. They enhance drug delivery by carrying pharmaceuticals directly to target cells, improving treatment efficacy. Additionally, nanodiamonds reinforce materials used in tissue engineering, supporting the development of bone scaffolds and potentially increasing patient recovery rates by 20% in trials for regenerative medicine.
- Industrial Cutting and Drilling Tools: As the hardest known material, diamonds are invaluable in industrial applications, including mining, construction, and precision manufacturing. Diamond-tipped drills, saws, and cutting tools improve efficiency in cutting hard surfaces, such as concrete and metal, by over 50% compared to traditional tools. The demand for diamond-based industrial tools is expected to grow at a 5% CAGR, especially in automotive and aerospace sectors, as these industries require precise, durable tooling solutions.
- Blockchain for Diamond Traceability: The diamond industry is leveraging blockchain to ensure traceability, verifying each gem’s origin to meet ethical and environmental standards. This technology combats the circulation of conflict diamonds by providing an immutable record of a diamond’s journey from mine to market. Blockchain-based traceability enhances transparency and supports consumer trust in a market valued at approximately $80 billion annually. With blockchain, companies can ensure compliance and demonstrate responsible sourcing, increasingly critical to today’s socially conscious consumers
Major Challenges
- Competitive Pressure from Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds (LGDs) have increased market share significantly due to their lower prices often up to 70-80% cheaper than natural diamonds for similar carat weight and clarity. This affordability is particularly appealing to budget-conscious younger consumers. Consequently, LGDs have captured a substantial portion of lower and mid-market segments, which continues to affect demand for natural diamonds. This trend is projected to reduce the natural diamond market by nearly 50% in some consumer segments over the coming years.
- Economic Slowdown in Key Markets: Global economic uncertainty, especially in the U.S. and China—two of the largest diamond markets has curbed luxury spending. Rising inflation and an economic slowdown in China, where diamond sales dropped by 18% in 2023, have led consumers to prioritize savings over luxury purchases. In the U.S., high inflation and recession fears have similarly dampened consumer demand, creating a cautious market environment.
- Sanctions on Russian Diamonds: With Russia supplying about 35% of the global rough diamond market, sanctions from the U.S., EU, and other countries have disrupted supply chains and reduced the availability of Russian diamonds. The U.S., the largest importer of finished diamonds, now restricts the import of Russian stones, pressuring manufacturers to find alternative sources. This restriction has contributed to price volatility and may lead to a shortfall in supply if further sanctions expand to include polished diamonds.
- High Production Costs and Decreasing Viable Mining Sites: Mining natural diamonds is increasingly costly due to the depletion of near-surface reserves, pushing companies to shift toward more expensive underground mining operations. It is estimated that global diamond production could decrease by 10-20% over the next decade, intensifying scarcity. However, maintaining viable operations as mines delve deeper and incur higher costs challenges the profitability of natural diamond mining, especially as LGD prices continue to undercut the market.
- Environmental and Social Governance (ESG) Pressures: The diamond industry faces mounting scrutiny over environmental and social impact. While natural diamond mining supports local economies in countries like Botswana, where mining revenues contribute to infrastructure and social services, it also raises concerns about environmental degradation. Additionally, LGDs are marketed as sustainable, though their energy-intensive production questions this claim. As a result, both sectors face pressure to meet high ESG standards, affecting operations, brand image, and long-term market positioning.
Top Opportunities
- Expansion of Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs): Lab-grown diamonds are set to capture a larger share of the market, especially in the U.S. and Asia, due to their affordability and sustainability appeal. With prices around 70-80% lower than natural diamonds, LGDs are particularly attractive to younger, budget-conscious consumers. The LGD market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8-10% through 2030 as demand for sustainable luxury continues to rise among eco-aware buyers, especially millennials and Gen Z.
- Digital Transformation and E-commerce Growth: The online diamond jewelry market is expanding rapidly and is expected to account for up to 25% of total diamond sales by 2025. This growth is fueled by advancements in virtual try-on technology, secure digital transactions, and an increasing preference for online shopping. Companies are investing in robust digital platforms to enhance the online shopping experience, appealing to a tech-savvy demographic looking for convenience and transparency in their purchases.
- Luxury Demand in Emerging Markets: The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing a rise in disposable income and a growing middle class with an affinity for luxury goods. As cultural interest in diamonds, particularly for engagement rings, grows, these markets offer substantial growth potential. China remains a leading consumer, and as disposable income rises in these regions, demand for both natural and synthetic diamonds in jewelry is expected to see a steady increase, contributing significantly to the industry’s growth.
- Industrial Applications of Synthetic Diamonds: Beyond jewelry, synthetic diamonds are gaining traction in industrial sectors due to their durability and thermal conductivity. These properties make synthetic diamonds ideal for use in electronics, cutting tools, and medical equipment. The industrial diamond market is expected to grow at a CAGR of about 4-5% through 2032 as sectors like electronics and construction increasingly adopt synthetic diamonds for specialized uses, offering high-margin revenue opportunities.
- Investment Appeal of Natural Diamonds: Natural diamonds are experiencing renewed interest as a form of alternative investment, particularly as inflation hedges and as symbols of lasting value. With a projected 10-20% decrease in operational mines by 2030, scarcity is expected to drive up the long-term value of natural diamonds. This investment appeal, coupled with the potential for portfolio diversification, positions natural diamonds as an attractive asset for high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors
Key Player Analysis
- De Beers Group: As one of the most recognized names in diamonds, De Beers has maintained a leading position for over a century, handling about 30% of the world’s rough diamond supply. Operating across Botswana, Canada, Namibia, and South Africa, the company is vertically integrated from mining to retail. In 2023, De Beers generated around $4 billion in revenue and continued investing in technology, notably through blockchain-based traceability solutions that enhance transparency in sourcing and retail, especially appealing to ethically conscious buyers.
- Anglo American plc: Anglo American, the parent company of De Beers, holds an 85% stake in the diamond giant, making diamonds a significant component of its diversified mining portfolio. In 2023, Anglo American’s revenue reached $30 billion, with the diamond segment accounting for 13% of its income. As a major player across multiple resources, Anglo American emphasizes sustainable practices, implementing environmental measures across all its mining sites, including those dedicated to diamond extraction, to address global sustainability standards and maintain community support.
- Lucara Diamond Corp.: Lucara Diamond Corp. is well-regarded for its high-value diamond finds, including notable discoveries from its Karowe mine in Botswana. This mine has produced some of the largest diamonds in recent years, including the 1,109-carat Lesedi La Rona. With an estimated $200 million in revenue in 2023, Lucara has focused on technological innovation, utilizing its blockchain-based platform, Clara, to streamline diamond sales directly between producers and buyers. This digital initiative has helped Lucara lead in transparent and traceable diamond sales.
- Gem Diamonds Limited: Specializing in high-quality diamonds, Gem Diamonds operates primarily from the Letšeng mine in Lesotho, known for producing large, high-value stones. In 2023, Gem Diamonds reported revenues of approximately $188 million, primarily from its high-carat, high-quality rough diamonds that consistently fetch premium prices. Gem Diamonds is committed to sustainable mining, with efforts to improve environmental stewardship and contribute to local community development, aligning with industry demands for responsible mining practices.
- Petra Diamonds: Petra Diamonds is a major mid-tier diamond producer with operations in South Africa and Tanzania, famous for high-quality stones from mines like Cullinan, known for rare blue diamonds. Petra generated around $450 million in revenue in 2023, focusing on operational efficiency and debt reduction to strengthen its financial position. The company is currently optimizing its mines to improve production output, an approach aimed at maintaining competitive pricing and operational sustainability in an evolving market
Recent Developments
- In June 2024, Noble Corporation plc (“Noble”) announced an agreement to acquire Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc. (“Diamond”) in a stock-plus-cash transaction. Diamond shareholders will receive 0.2316 shares of Noble and $5.65 per share in cash, reflecting an 11.4% premium to Diamond’s June 7 closing price. Upon completion, Diamond shareholders will own about 14.5% of Noble’s shares, solidifying Noble’s position in offshore drilling.
- In December 2024, Diamondback Energy, Inc. (“Diamondback”) and Endeavor Energy Resources, L.P. (“Endeavor”) announced a merger valued at $26 billion, including Endeavor’s net debt. This merger establishes a premier independent operator in the Permian Basin, enhancing Diamondback’s portfolio and creating efficiencies across operations.
- In 2023, De Beers Group expanded its Provenance Information program to include more Tracr platform participants in the diamond manufacturing process, increasing participation by 16% over 2022. This ensures that only diamonds traceable to De Beers mines and trading companies enter the program, strengthening transparency in the supply chain.
- In 2023, Pandora launched three new lab-grown diamond collections, bringing these offerings to Australia, Mexico, and Brazil. By expanding accessible and stylish diamond jewelry options, Pandora reinforces its mission to make diamonds part of everyday fashion for a wider audience worldwide.
Conclusion
The Diamond Market is poised for steady growth, driven by robust demand across both luxury and industrial sectors. Traditional natural diamonds continue to captivate high-end consumers, particularly in the U.S. and Asia, while lab-grown diamonds expand the market with an affordable, sustainable alternative, favored by younger, eco-conscious buyers. Enhanced transparency through blockchain and digital sales innovations are redefining consumer engagement and trust, particularly as brands appeal to ethically aware audiences.
In the industrial segment, synthetic diamonds’ unique properties are increasingly applied in technology, electronics, and medical fields, broadening the market’s scope and resilience. This dual demand, bolstered by evolving consumer values and advanced digital infrastructure, positions the diamond industry for sustainable expansion amidst an evolving global landscape




