Table of Contents
Introduction
The ethylene oxide market is poised for steady expansion, with projections indicating a growth from USD 34.6 billion in 2023 to USD 49.8 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% over the forecast period. This growth trajectory can be attributed to several factors, including the rising demand for ethylene oxide derivatives such as ethylene glycol, widely used in antifreeze formulations and polyester production. However, the market faces significant challenges, notably the stringent regulatory environment concerning ethylene oxide due to its potential health hazards, which necessitates rigorous handling and processing standards.
Recent developments in this sector highlight technological advancements to improve the efficiency and safety of ethylene oxide production processes, which are critical in maintaining market competitiveness and addressing environmental and safety regulations. These dynamics underscore the complex interplay of drivers and barriers influencing the market landscape for ethylene oxide.
BASF, a leading chemical company, has recently increased its production capacity for ethylene oxide, demonstrating a proactive approach to meet the rising global demand, particularly for derivative products like ethylene glycol. This expansion is aimed at enhancing their supply chain efficiency and addressing the needs of diverse industries including automotive and textiles.
SABIC, another major player in the market, has focused on strategic partnerships to optimize its production process for ethylene oxide. By integrating advanced technological methods, SABIC aims to improve the yield and quality of its ethylene oxide, ensuring it remains competitive in a market increasingly driven by stringent environmental regulations.
Indorama Ventures Public Company Ltd. has made significant headway through acquisitions that expand its footprint in the ethylene oxide market. These acquisitions not only increase their production capacity but also enhance their ability to serve a broader range of industrial applications, from consumer goods to industrial solvents.
India Glycols Ltd., focusing on sustainable practices, has innovated in the development of bio-based ethylene oxide, tapping into the growing trend towards sustainability. Their approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also positions them favorably in markets increasingly regulated against chemical pollutants.
DowDupont has leveraged its extensive R&D capabilities to launch new, high-efficiency ethylene oxide catalysts that promise to reduce energy consumption and increase production rates. These developments are crucial as companies face pressure to lower operational costs and minimize environmental impact while maintaining high output levels.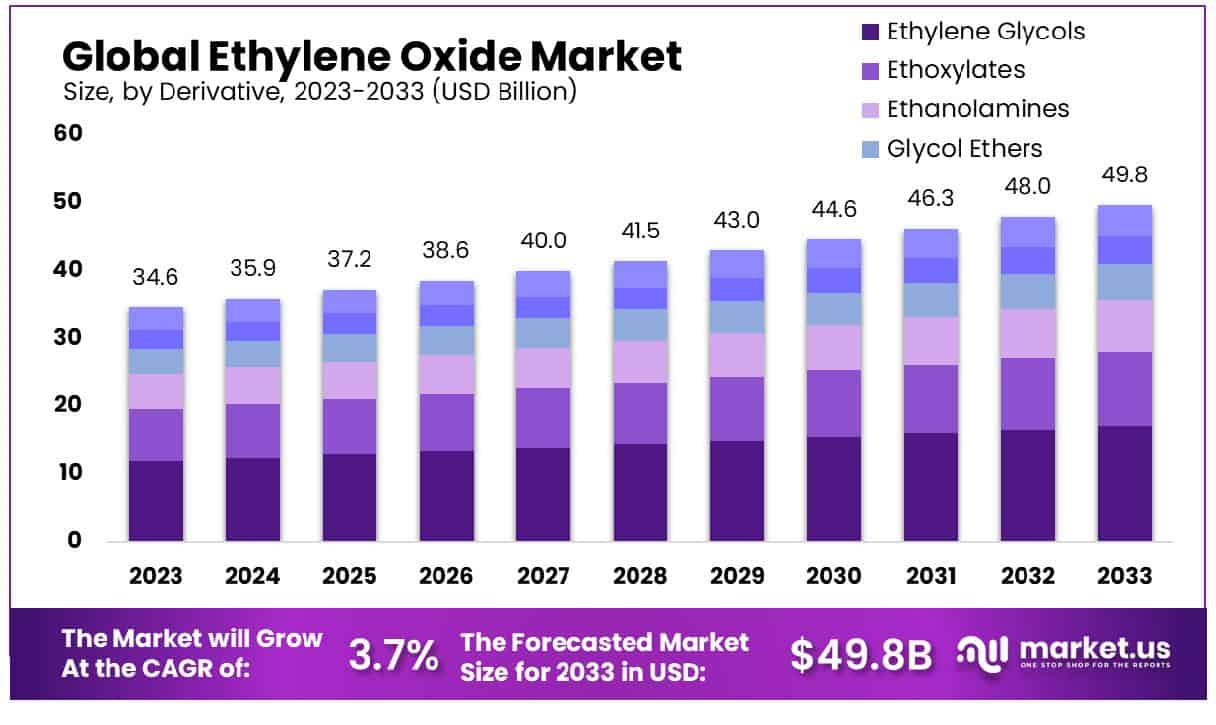
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Global Ethylene Oxide Market is projected to grow from USD 34.6 billion in 2023 to USD 49.8 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 3.7%.
- Asia-Pacific holds 43.1% of the Ethylene Oxide Market, valued at USD 14.9 billion.
- By Derivative: Ethylene Glycols dominate the derivatives segment at 34.5%, essential for various applications.
- By End-user Industry: The automotive industry, the largest end-user, constitutes 34.2% of market demand.
- By Function: Sterilizing agents lead functions, representing 57.2% due to essential medical uses
Ethylene Oxide in Medical Sterilization
- Ethylene oxide is currently the only way to sterilize medical devices that can’t be exposed to steam. It’s used to sanitize 20 billion devices in the U.S. per year, such as pacemakers, catheters, and ventilators, and is also used to sterilize spices.
- As the agency notes, there only are 86 commercial sterilization facilities in the U.S. using EtO and those 86 facilities are responsible for sterilizing about 20 billion items annually, including various types of tubing, heart valves, surgical kits, pacemakers, syringes, and catheters.
- In fact, more than 50% of medical devices are sterilized using Ethylene Oxide to better protect them.
- IgE-mediated anaphylaxis mediated by ethylene oxide has been published in patients regularly undergoing hemodialysis and approximately 10% of such patients have been found to have IgE antibodies to ethylene oxide.
- In 2015, after a study of 24 catheters, ANSM (the French agency for the Safety of Health Products) found that not all manufacturers complied scrupulously with the protocol since 60 % of the medical devices analyzed exceeded the recommended standards.
Environmental and Health Impact of Ethylene Oxide
- The hope is to reduce ethylene oxide emissions by 80%, which the agency said is part of the Biden administration’s Cancer Moonshot and its commitment to securing environmental justice and protecting public health.
- Mortality from cancer among workers exposed to ethylene oxide (EtO) has been studied in 10 distinct cohorts that include about 29,800 workers and 2540 deaths.
- Industrial ethylene oxide emissions have already fallen nationwide by over 80% since 2002.
- The facility captures 100 percent of all fugitive ethylene oxide emissions within the facility.
- The facility reduces ethylene oxide emissions to the atmosphere from each exhaust point by at least 99.9 percent or 0.2 parts per million.
Ethylene Oxide Production and Industrial Incidents
- The only producer of ethylene oxide in Spain with an installed capacity of 140,000 tonnes per year and 50% of this production is destined for the manufacture of glycol, one of the main raw materials for the production of PET polymers.
- The first explosion occurred between 18:40 and 19:00 and affected an ethylene oxide tank of the company. The second one affected a transformation station of the same company.
- Ethylene oxide production reached 20 million tonnes globally in 2009, making it the 14th most-produced organic chemical.
- Dow Chemical Company was the largest producer in 2006, with an output of 3 to 3.5 million tonnes.
- BASF’s production was reported at 1.175 million tonnes in 2008-2009, highlighting its significant role in the market.
Emerging Trends
- Increased Demand in Healthcare Applications: With the global health sector expanding, the demand for sterilization products has surged. Ethylene oxide plays a vital role due to its effectiveness in sterilizing medical instruments and supplies that cannot withstand high-temperature steam sterilization. This trend is expected to persist as health services expand worldwide, particularly in developing regions.
- Regulatory Impact: Ethylene oxide is under stringent regulatory scrutiny due to its potential health risks, including its classification as a human carcinogen. In regions like the United States and the European Union, strict regulations govern its usage and emissions. Companies in the industry are increasingly investing in technologies to reduce emissions and improve safety, which may increase operational costs but are essential for compliance and maintaining market access.
- Technological Advancements for Safer Use: Innovation in application technology is a prominent trend. New methods that reduce the risk associated with ethylene oxide sterilization, including better containment and abatement systems, are being developed. These advancements are crucial for industry players to sustain their operational licenses and public trust.
- Growth in Developing Economies: The market for ethylene oxide is expanding significantly in developing countries, driven by growth in industries such as textiles, detergents, and personal care products. The increase in disposable income in these regions supports the demand for a broad range of consumer goods, indirectly boosting the ethylene oxide market.
- Sustainable and Safer Alternatives: There is a growing interest in finding alternatives to ethylene oxide, especially for sterilization, due to the associated health and environmental risks. Research into safer and more sustainable chemicals that can offer similar benefits without drawbacks is gaining traction. This could potentially disrupt the market if viable alternatives are commercialized on a large scale.
Use Cases
- Sterilization of Medical Devices and Supplies: Ethylene oxide is predominantly used to sterilize approximately 50% of all sterile medical devices in the U.S. The process involves exposing products to EO gas under controlled conditions to eliminate bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Given the precision and sensitivity of many medical devices that cannot withstand high temperatures, EO’s role is indispensable.
- Production of Ethylene Glycol: A significant portion of ethylene oxide produced globally, about 75%, is converted into ethylene glycol. This compound is crucial in the manufacture of automotive antifreeze, polyester fibers, and resins. Polyester fibers alone account for a substantial market share in the textile industry, supporting the production of clothing, upholstery, and other fabric-based products.
- Manufacture of Detergents and Surfactants: Ethylene oxide reacts with alcohols to produce ethoxylates, which are key components in household and industrial detergents. Approximately 10-15% of the global EO production is directed towards this application. These ethoxylates enhance the cleaning efficiency of detergents and are integral to formulations that require mildness to human skin and effective dirt removal.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: EO is used to produce ingredients like emulsifiers and solvents that are common in personal care products such as lotions, shampoos, and soaps. The market for EO in personal care is projected to grow, driven by increasing consumer spending on cosmetic products worldwide.
- Agricultural Chemicals: Ethylene oxide derivatives are also used in the production of certain fungicides, insecticides, and herbicides. This application taps into the agricultural sector, providing solutions to enhance crop protection, yield, and quality in farming operations.
- Food and Beverage Industry: While less common, EO is used for the pasteurization and sterilization of certain food items and spices. This application ensures that food products are safe for consumption without employing high-temperature processes that might alter the taste or nutritional content.
Major Challenges
- Environmental and Health Safety Concerns: Ethylene oxide is classified as a human carcinogen by international health organizations, raising serious concerns regarding its safety in industrial and healthcare applications. The long-term exposure risks associated with EO can lead to severe health issues, including lymphoma and breast cancer. These health risks necessitate stringent handling and containment measures, which increase operational costs.
- Regulatory Compliance and Restrictions: In response to the health risks, regulations governing the use of EO have become increasingly strict. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed rules to reduce EO emissions by 93% from certain facilities. Compliance with such regulations not only increases the cost of operations but also limits the scope of EO applications, forcing companies to invest in expensive abatement technologies.
- Market Volatility and Supply Chain Disruptions: The market for ethylene oxide is susceptible to price fluctuations due to its dependency on ethylene prices, which are closely tied to crude oil markets. For example, any geopolitical instability that impacts oil prices can directly affect EO costs. Additionally, EO production requires sophisticated infrastructure and careful logistics due to its highly reactive nature, making supply chain disruptions a frequent challenge.
- Public Perception and Community Pushback: Facilities producing or utilizing EO often face opposition from local communities due to the potential health risks associated with EO emissions. Community pushback can lead to delays in permit approvals, increased scrutiny from regulators, and even the shutdown of operations. This not only affects the operational feasibility but also impacts the reputation of the companies involved.
- Alternative Technologies and Substitutes: As health and environmental concerns grow, there is increasing research and investment into alternative sterilization methods and less hazardous chemicals that can replace EO in certain applications. For example, advancements in hydrogen peroxide-based sterilization and plasma sterilization technologies offer viable alternatives without the associated carcinogenic risks. The emergence of these technologies threatens to reduce EO’s market share in its key application areas.
- Technological and Innovation Gaps: While there is a pressing need for safer and more efficient EO usage technologies, the pace of innovation in this area is often outstripped by regulatory and market demands. Bridging this gap requires substantial R&D investments, which can be prohibitive for many firms, especially in a tightly regulated market.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Expanding Sterilization Needs in Emerging Markets: The global demand for medical sterilization is projected to grow, especially in emerging markets where healthcare sectors are expanding rapidly. The increase in medical facilities and health awareness in these regions presents a significant opportunity for EO usage. The global medical device sterilization market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2028, signifying a growing demand for EO sterilization processes.
- Innovation in EO Sterilization Technology: Technological advancements that enhance the safety and efficiency of EO sterilization processes can open new markets and expand its applicability. Innovations that reduce EO concentrations or improve abatement systems can meet stricter regulatory standards and reduce operational risks, making EO sterilization more attractive to a broader array of industries, including food and cosmetic sterilization.
- Integration with Sustainable Practices: As industries are pushed towards adopting more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices, EO producers have the opportunity to innovate in ways that minimize environmental impact. Developing and implementing greener production techniques and recycling methods can not only reduce emissions but also improve the public perception of EO as a product.
- Value-added Products in the Supply Chain: The derivatives of EO, such as ethylene glycols, ethoxylates, and ethanolamines, are used across a wide range of industries including automotive, textiles, and agriculture. Increasing the value chain integration—where companies expand their operations into producing downstream products—can leverage EO’s base market to tap into higher-margin products. This integration allows for better control over raw material costs and improved market responsiveness.
- Partnerships and Collaborative Expansions: Forming strategic partnerships with healthcare providers and medical device manufacturers can open new avenues for growth. By collaborating directly with end users, EO producers can better understand market needs and tailor their offerings to meet specific industry requirements, thus enhancing market penetration and brand loyalty.
- Geographic Expansion: There is substantial growth potential in regions that are currently underserved by EO facilities. Setting up production and sterilization plants in these areas can reduce logistics costs and improve service delivery for local businesses, thereby increasing market share in untapped regions.
Key Players Analysis
BASF has significantly enhanced its production capacity in the ethylene oxide sector by expanding its operations at the Verbund site in Antwerp, Belgium. This strategic expansion, which involved an investment exceeding €500 million, added about 400,000 metric tons per year to their production capabilities. The expansion includes a new world-scale ethylene oxide plant and increased capacities for essential derivatives like alkoxylates, which are used in various applications, including detergents and automotive fluids.
SABIC is expanding its capabilities in the ethylene oxide sector through significant projects, including the construction of a new ethylene oxide/ethylene glycol (EO/EG) plant in Al-Jubail, Saudi Arabia. This initiative, which leverages advanced EO/EG technology licensed from Scientific Design Company, underscores SABIC’s commitment to enhancing its production capacity to meet growing market demands. The plant is part of a broader strategy to bolster SABIC’s presence in the global chemicals market, reflecting its forward-looking approach to embracing cutting-edge technologies and expanding its production base.
Indorama Ventures Public Company Ltd. has significantly expanded its footprint in the Ethylene Oxide sector by acquiring Old World Industries in Clear Lake, Texas, in 2012. This facility, renamed Indorama Ventures Oxide & Glycols, stands as one of North America’s largest reactors, boasting low fixed-costs and an exemplary environmental and safety record.
India Glycols Ltd., in collaboration with Clariant International, has established a joint venture named Clariant IGL Specialty Chemicals Private Limited, focusing on renewable ethylene oxide derivatives. This venture combines India Glycols’ expertise in renewable bio-ethylene oxide with Clariant’s strong presence in industrial and consumer specialties across multiple South Asian markets. This strategic partnership aims to lead in the green ethylene oxide sector by leveraging sustainable practices and innovative production capabilities.
Dow, following the DowDuPont merger, continues to enhance its production capabilities in the ethylene oxide (EO) sector. Recent expansions include their integrated world-scale ethylene production facilities in Texas. This strategic growth supports Dow’s broader aim to meet rising global demand for EO and its derivatives, crucial for various industrial applications, despite a temporary setback from a fire incident at their Louisiana site that caused a force majeure but is not expected to affect market supply significantly due to current low EO demand.
Huntsman International is expanding its ethylene oxide (EO) production by adding 250 million pounds per year to its existing one billion pounds at its Port Neches, Texas facility. This expansion aims to leverage North American ethane cost advantages and enhance the production of intermediates like surfactants and specialty chemicals.
LOTTE Chemical Corporation is significantly enhancing its production of ethylene oxide adduct (EOA) by investing approximately $211 million. This expansion at the Daesan plant in South Korea will increase EOA production capacity to 480,000 tons annually and will also raise the production of high-purity ethylene oxide (HPEO) to 250,000 tons. This initiative is part of LOTTE’s strategy to boost its specialty chemicals and eco-friendly materials portfolio.
Formosa Plastics Ltd. has significantly bolstered its operations in the ethylene oxide sector, particularly through its Mailiao Complex in Taiwan. This complex, operational since 1974, plays a pivotal role in Formosa’s production of key petrochemicals, including ethylene oxide. The facility forms part of Formosa’s broader strategy to expand and modernize its production capabilities, supporting the growth of mid-and downstream industries while emphasizing safety and environmental sustainability.
Royal Dutch Shell, now Shell plc, maintains a strong presence in the ethylene oxide market, particularly noted for its high-purity production that is crucial for various applications including polyester fibers and detergents. The company is actively expanding its capabilities, notably through a significant partnership with CNOOC in China, aiming to enhance ethylene oxide production capacity and embrace new, more efficient technologies.
Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) is expanding its footprint in the ethylene oxide market by establishing a new Mono Ethylene Glycol (MEG) plant at its Paradip Refinery. This initiative is part of IOC’s broader strategy to enhance its integration within the petrochemical sector, focusing on value maximization from its refinery operations. The new MEG plant is expected to significantly bolster the supply for industries such as textiles, enhancing self-sufficiency in domestic markets.
Akzo Nobel N.V. is advancing its presence in the ethylene oxide sector by developing a novel technology platform for producing ethylene amines from ethylene oxide. This technology is showcased at their demonstration plant in Sweden, which is designed to reduce raw material use and enhance cost and environmental efficiencies. The technology focuses on producing key amines like diethylenetriamine (DETA) and triethylenetetramine (TETA), which are crucial for applications like epoxy curing and oil field chemicals. Akzo Nobel views this as a game-changing advancement that could significantly impact the industry, underscoring their commitment to sustainable growth.
Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited has significantly expanded its involvement in the ethylene oxide sector through strategic acquisitions and the development of extensive production capacities globally. Notably, the company has acquired facilities in Texas, USA, that produce purified ethylene oxide and glycols, with one of the largest reactors in North America. Additionally, Indorama has enhanced its manufacturing capabilities in Ankleshwar, India, focusing on ethylene oxide derivatives for various industrial applications. These strategic moves underscore Indorama’s commitment to broadening its footprint and capabilities in the ethylene oxide market across multiple global locations.
LyondellBasell recently sold its Ethylene Oxide & Derivatives business, including a production facility in Bayport, Texas, to INEOS for $700 million. This strategic move allows LyondellBasell to focus on its core operations and strategic growth, reflecting its disciplined approach to value creation. The transaction includes high-quality ethylene oxide production capabilities and various derivatives, benefiting from access to cost-advantaged feedstocks and logistics networks. This acquisition is a significant expansion for INEOS into the U.S., complementing its existing European operations and enhancing its position in the global market.
Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd., a leader in chemical production, has significantly invested in the ethylene oxide sector. The company utilizes its ethylene oxide primarily for producing derivatives like ethylene glycol, which are essential in making polyester fibers and PET bottles. Their technological expertise allows for high-efficiency production processes that contribute to their broad market presence in various chemical sectors.
INEOS has recently bolstered its position in the ethylene oxide sector by acquiring LyondellBasell’s Ethylene Oxide and Derivatives business, including a significant facility in Bayport, Texas. This expansion enhances INEOS’s production capabilities in the U.S. and complements its existing operations in Europe, establishing the company as a leader in both regions for ethylene oxide and its derivatives.
Kazanorgsintez, a major Russian chemical producer, operates an extensive ethylene oxide production facility, integral to its diversified chemical production portfolio. The company uses ethylene oxide primarily for producing essential derivatives such as glycols and ethanolamines, which find widespread applications across various industries including textiles and antifreeze production.
Conclusion
Ethylene oxide (EO) continues to be an indispensable chemical in various critical sectors, notably in medical sterilization and as a precursor for numerous industrial compounds. Despite facing substantial challenges related to health, safety, and environmental regulations, EO presents significant growth opportunities. These include expanding market demands in emerging economies, advancements in sterilization technologies, and potential integrations within sustainable practices.
To capitalize on these opportunities, companies must navigate regulatory landscapes effectively, innovate in technology and process efficiencies, and consider strategic expansions both geographically and across the value chain. Successfully addressing these areas will be crucial for sustaining and enhancing the market position of ethylene oxide in the global chemical industry landscape.




