Table of Contents
Introduction
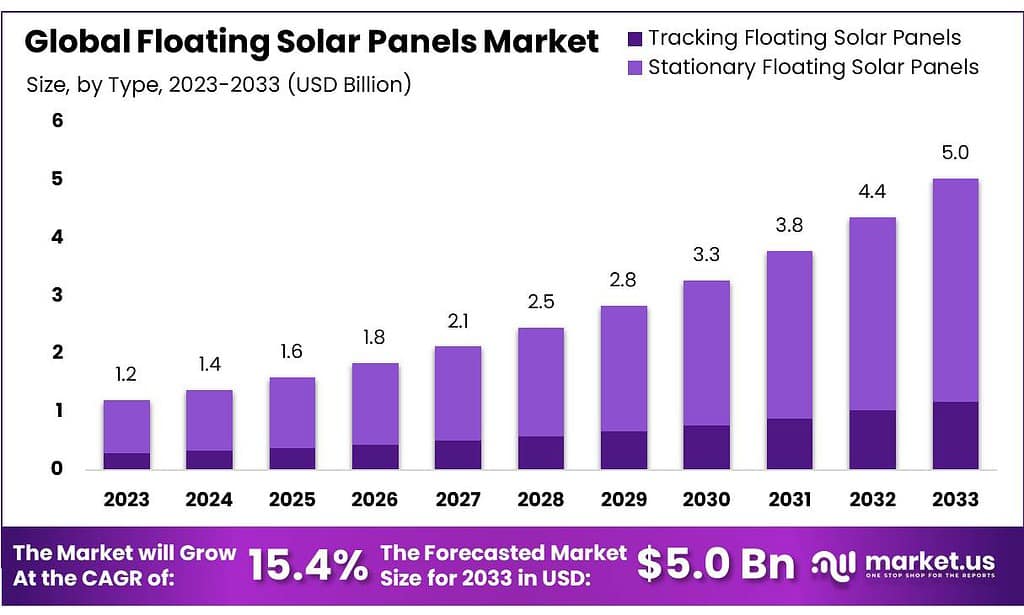
The global floating solar panels market is projected to expand from USD 1.2 billion in 2023 to around USD 5.0 billion by 2033, marking a robust CAGR of 15.4% during the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to a variety of factors including increasing demand for renewable energy sources, innovations in PV technology, and the scarcity of land for traditional solar farms which makes floating solar panels a viable alternative.
Challenges in the market involve high initial installation costs and the technological demands of operating in aquatic environments which can increase maintenance needs compared to land-based systems. Recent developments have seen significant advancements in project implementation and technology
For instance, large scale projects such as the hybrid hydro-floating solar power project initiated by the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand which aims to enhance energy efficiency while optimizing land use. Moreover, North America’s largest floating solar array was recently commissioned on the Canoe Brook Reservoir in New Jersey, showcasing a major step forward in utilizing underused water bodies for clean energy production.
Moreover, market dynamics are influenced by legislative support such as the US government’s introduction of the Power Our Reservoirs Act, which supports the research and deployment of floating solar technologies to safeguard water resources and bolster renewable energy production.
Additionally, the market’s competitive landscape features key players like Kyocera Corporation, Trina Solar, and JA Solar, which are heavily investing in research and development to push the boundaries of floating solar technology.
Recent developments in the floating solar panels market have showcased significant activity from major companies such as Kyocera Corporation, Ciel & Terre International, and SPG Solar, Inc., reflecting a trend of strategic advancements through construction projects, technological enhancements, and market expansion efforts.
Kyocera Corporation, in collaboration with Century Tokyo Leasing and Ciel & Terre International, has embarked on constructing what is slated to be the world’s largest floating solar power plant.
This project utilizes Ciel & Terre’s Hydrelio floating solar platforms and is part of a broader strategy by Kyocera to capitalize on Japan’s abundant water surfaces for solar power generation, addressing land scarcity issues. This venture not only enhances their production capacity but also supports Japan’s renewable energy goals by optimizing underutilized water bodies for power generation.
Ciel & Terre International has been actively expanding its operations and technological footprint, with recent reports indicating ongoing development of major projects aimed at bolstering their position in the global market.
Their involvement with Kyocera in the large-scale Japanese project highlights their role not only as equipment providers but also as key technical advisors, utilizing their patented floating platform technologies which are noted for their durability and environmental benefits.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: Expected to reach USD 5.0 billion by 2033 from USD 1.2 billion in 2023, with a CAGR of 15.4%.
- Product Types: Stationary panels, holding over 76.5% market share, offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness; tracking panels optimize energy capture by up to 25%.
- Technology Dominance: Thin film technology, capturing over 50.2% market share, favored for lightweight and cost-effectiveness.
- Capacity Preference: Above 15 MW capacity dominates with over 71.1% market share, favored for utility-scale projects.
- Regional Analysis: Asia Pacific leads with 68.5% market share, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for renewable energy.
Floating Solar Panels Statistics
- After conducting the study the floating solar system was able to gain 2.06% power gain over ground-mounted PV panels. The performance ratio of the floating solar system was comparatively better (89.6%) compared to the ground-mounted PV system (87.79%).
- Research indicates that floating solar panels could generate up to 1,302 terawatt-hours (TWh) annually if deployed on 10% of the surface area of nearly 68,000 lakes and reservoirs worldwide.
- Ethiopia could generate 129% of their current energy demands and Rwanda 237% of their current energy demands from these systems alone.
- A study by the World Bank estimated that floating solar panels could generate 2,100 GW globally.
- The cooling effect of water helps maintain the panels’ temperature, increasing their efficiency by 5-15% compared to land-based panels.
- On average, floating solar installations in the UK might cost £1,200-£1,500 per kW, compared to ground-mounted systems costing £900-£1,200 per kW.
- One of Europe’s largest floating solar panel installations is in the Queen Elizabeth II Reservoir in London. It comprises 23,000 solar panels, generating enough electricity to power 1,800 homes annually.
- China leads the world in floating solar installations.
- China’s largest floating solar farm is located in Huainan, Anhui Province, and has a capacity of 150 MW.
- Europe shows promise, too. Finland could produce 17% of its electricity via floating solar, with Sweden and Denmark close behind at 16%.
- Five countries – Benin, Ethiopia, Kiribati, Rwanda, and Papua New Guinea – could meet all electricity needs from floating solar.
- The floating solar market may reach £1.8 billion by 2026, expanding 43% annually from 2019-2026.
- Others, such as Bolivia and Tonga, could satisfy a significant portion, 87% and 92%, respectively.
- Many African, Caribbean, South American, and Central Asian nations could satisfy 40-70% of demand.
- By 2050, the Netherlands will install 25 gigawatt peak (GWp) of floating solar power on inland waters and 45 GWp at sea.
- Deploying floating solar panels on just 1% of global reservoirs could produce 404 gigawatts peak (GWp) of clean energy.
- According to SEIA, since the 2000s, the annual solar power has witnessed a growth rate of approximately 42%.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the floating solar panels market indicate significant technological and strategic advancements, driven by global needs for sustainable and efficient energy solutions. One notable trend is the rise of floating photovoltaic systems (FPV) or “floatovoltaics,” which are expected to establish a new global market, reaching 4.8 gigawatts of deployment by 2026.
These systems are particularly appealing in areas with land-use constraints, as they can be installed on bodies of water, reducing the need for valuable land space while leveraging the cooling effects of water to enhance solar panel efficiency.
Another key trend is the integration of floating solar with tracking technologies. Tracking systems allow solar panels to follow the sun’s trajectory, thereby maximizing energy capture.
Recent innovations in this area include horizontal single-axis tracking systems (HSAT), which have been adapted for floating installations. These innovations promise up to 40% increased energy production, part of which is derived from the natural cooling effect of water.
Additionally, the synergy between floating solar and hydropower is emerging as a potent solution, especially in regions with existing hydropower infrastructure. This hybrid approach leverages existing grid connections and infrastructure, which can significantly reduce installation and operational costs, while also increasing energy output and grid stability.
Use Cases
- Utility-Scale Power Generation: Floating solar panels are increasingly used in large-scale installations on reservoirs and lakes to generate substantial amounts of electricity without consuming valuable land. These systems are particularly prevalent in countries with high land use constraints such as Japan, India, and South Korea.
- Water Conservation: By covering significant surface areas of reservoirs, floating solar panels help reduce water evaporation. Studies suggest that covering 30% of the world’s reservoirs could save approximately 106 cubic kilometers of water annually, which is close to the annual water usage of about 300 million people.
- Enhanced Efficiency through Cooling: The water beneath the solar panels provides a cooling effect, which helps improve the efficiency of the panels. This cooling leads to a higher electricity output compared to land-based systems, which can suffer from overheating.
- Hybrid Systems with Hydropower: In regions with existing hydropower infrastructure, floating solar panels can be integrated to create hybrid systems. This combination allows for more consistent energy generation, leveraging solar power during the day and hydropower as needed, which is particularly useful in managing seasonal water flows and during periods of drought.
- Aquaculture Integration: Some regions are exploring the dual use of water bodies for both power generation and aquaculture, known as AquaPV. This approach allows for the colocation of renewable energy generation and food production, optimizing the use of water bodies while minimizing environmental impacts.
Major Challenges
- Environmental and Mechanical Concerns: Floating solar installations deal with aquatic environments that pose unique challenges such as corrosion, moisture, and the impact of salt and water currents, which require robust and weather-resistant materials. The technology must also handle shifts in water levels and withstand strong winds and waves without compromising structural integrity.
- High Capital Costs: The initial setup and development costs of floating solar systems are generally higher than those for ground-mounted systems. This includes costs for floating structures, specialized mooring systems, and protective coatings necessary to endure aquatic conditions.
- Maintenance and Accessibility: Regular maintenance and cleaning are more complex and costly, due to the difficulty in accessing systems on water. This challenge is exacerbated by the potential for biofouling and sediment accumulation on the floating structures and panels.
- Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles: Floating solar projects often face lengthy and complex permitting processes, especially in regions without established regulations for such installations. Navigating these bureaucratic procedures can lead to delays and uncertainties in project timelines.
- Grid Integration: Connecting floating solar systems to the main power grid can require additional infrastructure investments, particularly in remote locations or where existing grid connections are not near water bodies.
- Limited Suitable Locations: Not all water bodies are viable for floating solar installations due to factors such as depth, water quality, and existing usage for recreation or conservation, which may limit potential sites.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Technological Innovation: There’s a growing focus on integrating solar tracking technology with floating solar systems. This technology allows panels to maximize sunlight exposure by following the sun’s path, thereby enhancing energy efficiency. The adoption of tracking systems in floating solar arrays is expected to increase their energy generation efficiency significantly.
- Geographical Expansion: The Asia-Pacific region currently leads the floating solar panel market, primarily driven by countries like China, Japan, and India, which are rapidly deploying these systems to meet their burgeoning energy needs. This region is expected to maintain its dominance due to large-scale installations and favorable government policies. North America and Europe are also showing robust growth, with an increasing number of projects that integrate floating solar with hydropower systems, leveraging existing water infrastructure for enhanced energy output.
- Sector-Specific Applications: Floating solar technology is not just limited to large-scale utility projects but is also expanding into industrial and commercial sectors. These installations are tailored to meet the specific energy needs of industries and commercial entities located near water bodies, which helps reduce their reliance on conventional power sources and enhances sustainability.
- Investment and Cost Reduction: Investment in floating solar technology is growing, with significant reductions in the cost of solar panels and the development of more durable and efficient floating structures. These advancements are making floating solar a more attractive option for investors and are expected to drive further market expansion.
- Regulatory and Policy Support: Governments worldwide are increasingly supporting the adoption of renewable energy technologies, including floating solar panels, through incentives and regulatory support. This is expected to facilitate the faster deployment and integration of floating solar systems into national grids.
Key Players Analysis
Kyocera Corporation has been significantly expanding its presence in the floating solar panels sector. In 2023, the company, in collaboration with Century Tokyo Leasing and Ciel et Terre, announced plans to construct the world’s largest floating solar power plant. This project will further cement Kyocera’s role in the renewable energy market, demonstrating their commitment to innovative energy solutions and their capability to implement large-scale projects.
Ciel & Terre International has been instrumental in developing floating solar technologies, particularly noted for their Hydrelio system, which allows standard PV panels to be installed on large bodies of water. This technology is key to the company’s operations and partnerships, including significant collaborations with companies like Kyocera. Ciel & Terre’s focus on sustainable and efficient energy production is evident through their continuous involvement in extensive floating PV projects globally.
In 2023, SPG Solar, Inc. continues to develop its portfolio in the floating solar panels sector, though specific projects and achievements for this year are not detailed in readily available sources. The company has been recognized for its innovative approaches in the past and is likely maintaining its role in advancing floating solar technology.
Lanco Solar Energy Pvt. Ltd., a subsidiary of Lanco Infratech Limited, is a prominent player in India’s solar energy sector. Founded in 2008, Lanco Solar specializes in developing, constructing, and operating solar power plants. As of 2023, the company has managed to significantly increase its solar power project capacity, further establishing its commitment to renewable energy and sustainable practices. Lanco Solar is actively involved in various states across India, showcasing its extensive reach and influence in the renewable energy market.
Solaris Synergy Ltd. has continued to carve out a significant presence in the floating solar panels sector through 2023, focusing on enhancing the efficiency and viability of their floating photovoltaic systems. These systems are designed to be a sustainable alternative to land-based solar arrays, utilizing water bodies to generate renewable energy efficiently. Solaris Synergy’s innovative approach includes modular designs that can scale from several kilowatts to dozens of megawatts, making it adaptable to various project sizes and needs.
Sharp Corporation remains a significant player in the floating solar panel market, capitalizing on its expertise in photovoltaic technology to offer advanced solutions. Although specific project details or achievements in 2023 or 2024 are not widely detailed, the company’s ongoing involvement in this sector underscores its commitment to expanding renewable energy capacities and exploring innovative applications for solar technology on water surfaces.
Floating Power Plant A/S has made strides in 2023 by advancing their floating solar panels projects, focusing on integrating renewable energy solutions that capitalize on the synergy between wind and solar technologies. This innovative approach not only maximizes energy production but also leverages the natural cooling effect of water to increase the efficiency of the solar panels, showcasing a commitment to enhancing renewable energy capabilities in marine environments.
BayWa r.e. Renewable Energy GmbH has significantly expanded its floating solar panels portfolio, especially evident with the initiation of the construction of a 27.4 MWp floating PV plant on a Dutch lake in 2025. This project highlights BayWa r.e.’s ongoing commitment to pushing the boundaries of floating PV technology and its dedication to utilizing unconventional spaces for renewable energy production, thereby supporting the shift towards sustainable energy sources across Europe.
Ciel & Terre USA, a subsidiary of the French company Ciel & Terre International, has been actively expanding its operations in the floating solar panel sector across the United States. By 2023, the company had installed a notable 46 MWp through various projects and had more than 30 MWp lined up for completion in 2023 and 2024. Ciel & Terre USA is known for utilizing its patented Hydrelio technology, which allows standard photovoltaic panels to float on water bodies, thus conserving land and reducing water evaporation. This technology has seen widespread application across different climates and types of water bodies in the U.S., indicating robust adaptability and growth potential in the renewable energy sector.
Trina Solar Limited, another major player in the floating solar panel market, continues to influence the global market with significant projects and technological advancements. Although specific 2023 or 2024 projects were not detailed, the company’s ongoing contributions to the solar energy industry are marked by its consistent development and implementation of large-scale photovoltaic installations worldwide. Trina Solar is known for its commitment to innovation in the solar panel technology sphere, often leading initiatives that push the boundaries of how solar energy is harnessed and utilized.
SPG Energy Group’s specific activities in the floating solar panels sector for the years 2023 and 2024 were not prominently featured in the recent data available online. However, the company is recognized in the renewable energy industry for its contributions to solar power, often focusing on innovative solar solutions and sustainability projects. For updated and detailed information, direct sources from SPG Energy Group or industry-specific publications would be ideal.
Ocean Sun AS, on the other hand, has been actively expanding its innovative floating solar solutions. In 2024, Ocean Sun launched a significant project—a 2 MWp floating solar power system at Soneva Secret resort in the Maldives. This project, aimed at reducing the resort’s reliance on diesel generators, involves innovative solar rings and integrates solar energy with battery storage, set to be completed in early 2025. Additionally, Ocean Sun has completed a 270 kW off-grid floating PV system at a Spanish port in early 2024, showcasing their robust, low-cost solutions adaptable to various sea states and conditions. These projects underscore Ocean Sun’s commitment to leveraging floating solar technologies to address energy needs in diverse environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, floating solar panels represent a pivotal innovation in renewable energy technologies, offering a promising solution to global energy challenges. These systems efficiently utilize underused water surfaces, thereby preserving valuable land resources while simultaneously enhancing energy generation through the cooling effects of water. Despite facing challenges such as high initial costs, maintenance complexities, and environmental concerns, the market for floating solar panels is poised for substantial growth.
This is driven by technological advancements, increased environmental awareness, and supportive government policies worldwide. As the industry continues to innovate and overcome these hurdles, floating solar panels are expected to play an increasingly significant role in the global transition to sustainable energy sources, marking a critical step forward in harnessing solar power more effectively and responsibly.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





