Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Agricultural and Food Production Output Across Major Nations
- Food And Nutrition Consumption Statistics
- Global Food And Nutrition Consumption – By Product Group
- Ideal Nutrition Intake Requirements and Guidelines
- Ideal Intake of Essential Nutrients
- Global Food Energy Intake
- Calorie Consumption – By Nation
- Basic Facts Related to Hunger and Nutrition
- Global Hunger Index (GHI) Score
- Malnutrition and Undernutrition Statistics
- Global Obesity Statistics
- Food Security Statistics
- Food Prices and Its Impact on Nutrition
- Environmental Impact
- Latest Food and Nutrition Trends
Introduction
According to Food And Nutrition Statistics, Understanding food and nutrition is crucial for maintaining health.
Macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provide energy and support bodily functions. While micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals are essential for various physiological processes.
Adequate hydration is also vital. Dietary guidelines advocate for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting added sugars, sodium, and saturated fats.
Nutritional labeling helps individuals make informed choices about packaged foods. A balanced diet not only reduces the risk of chronic diseases but also enhances energy levels and overall well-being.
Special considerations must be taken for specific populations and medical conditions. By grasping these fundamentals, individuals can make healthier dietary choices and improve their quality of life.
Editor’s Choice
- The global dietary supplements market size is expected to be worth around USD 306 billion by 2033, from USD 156 billion in 2023. Growing at a CAGR of 7.0% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
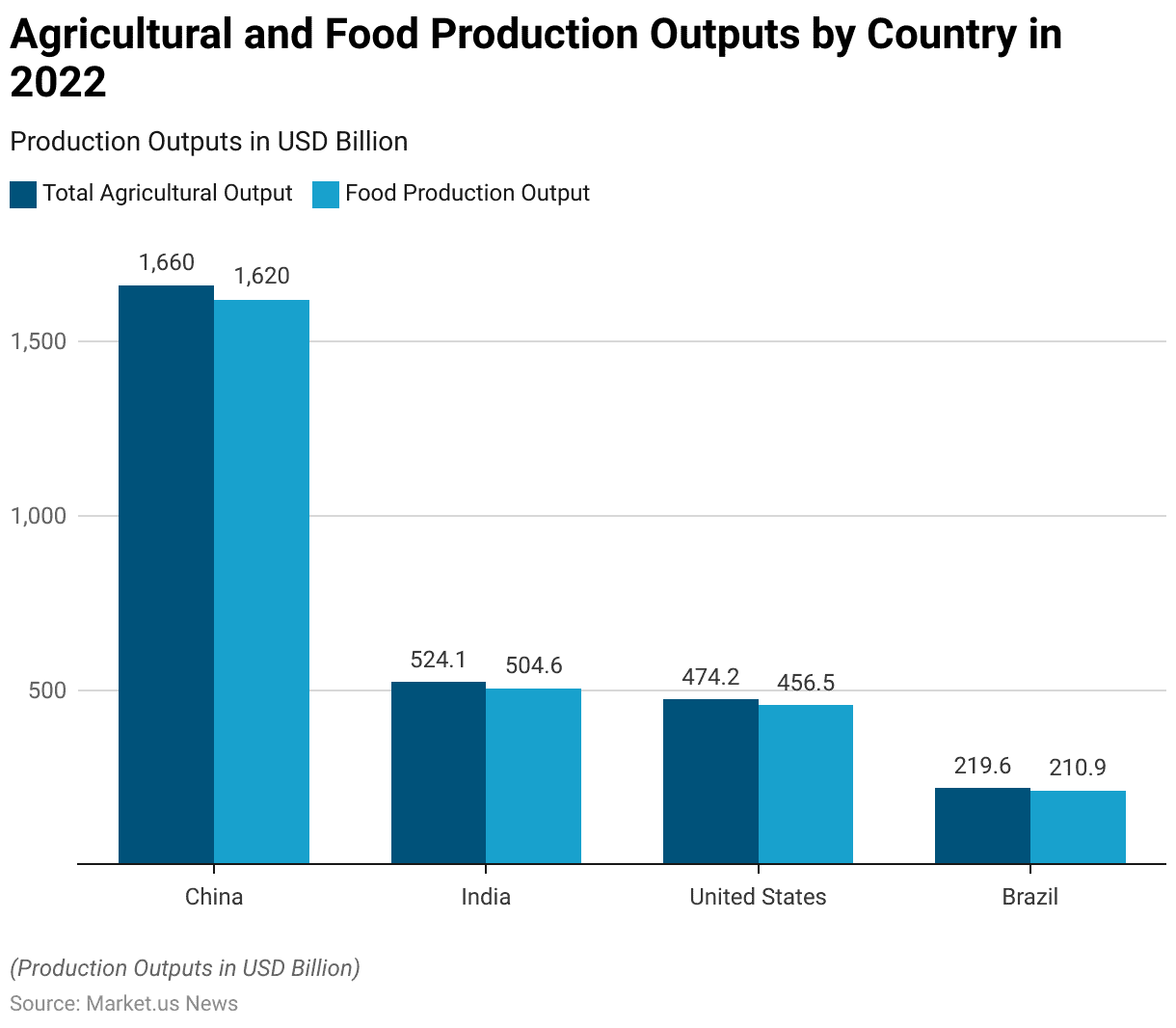
- In 2022, China maintained its position as the foremost agricultural powerhouse globally, boasting an impressive annual output worth $1.66 trillion. With $1.62 trillion dedicated to food production.
- In 2022, bread and cereal products led to food consumption with 645.27 million metric tons, followed by vegetables at 513.94 million metric tons.
- In 2018, Ireland led the world in average daily dietary energy consumption per capita, with an intake of 16,520 kilojoules.
- Bahrain led with the highest average daily calorie intake in 2021, where individuals consumed 4,012 kilocalories per day.
- Global hunger showed little change from 2021 to 2022 but remained significantly higher than pre-COVID-19 levels. Affecting approximately 9.2% of the global population in 2022 compared to 7.9% in 2019.
- In 2022, around 390 million adults globally were underweight, while a staggering 2.5 billion were overweight, with 890 million classified as obese.
- In 2021, the share of the population that could not afford a healthy diet remained alarmingly high in several countries. Madagascar led with 97.8% of its population unable to afford a healthy diet, up from 97.1% in 2020.

Agricultural and Food Production Output Across Major Nations
- In 2022, China maintained its position as the foremost agricultural powerhouse globally. Boasting an impressive annual output worth $1.66 trillion, with $1.62 trillion dedicated to food production.
- Following closely, India, the world’s most populous nation, secured the second spot with an agricultural output valued at $524.1 billion, of which $504.6 billion was attributed to food.
- Despite a significantly smaller agricultural workforce compared to China and India. The United States clinched the third position with an output of $474.2 billion, $456.5 billion of which contributed to food production.
- Brazil secured the fourth position with an agricultural output worth $219.6 billion. With $210.9 billion allocated to food production.
Food And Nutrition Consumption Statistics
Global Per Capita Food And Nutrition Consumption Across Various Food Categories
- In 2018, global per capita food consumption demonstrated diverse dietary patterns across various food categories.
- Vegetables, other than tomatoes, topped the list with an average consumption of 107.9 kilograms per person.
- Milk followed as a significant component of diets worldwide, with a per capita consumption of 79.3 kilograms.
- Rice and wheat were also staple foods, consumed at 78.4 and 67 kilograms per person, respectively.
- Potatoes had a considerable presence in global diets, with a consumption rate of 32.9 kilograms per capita.
- Other fruits were consumed at 26.7 kilograms per person, while tomatoes specifically accounted for 21.2 kilograms per capita.
- Sugar was a notable part of the diet, with a consumption rate of 20.4 kilograms per person. Closely followed by fish and seafood at 20.2 kilograms.
- Maize rounded out the list with an average consumption of 18.8 kilograms per person.
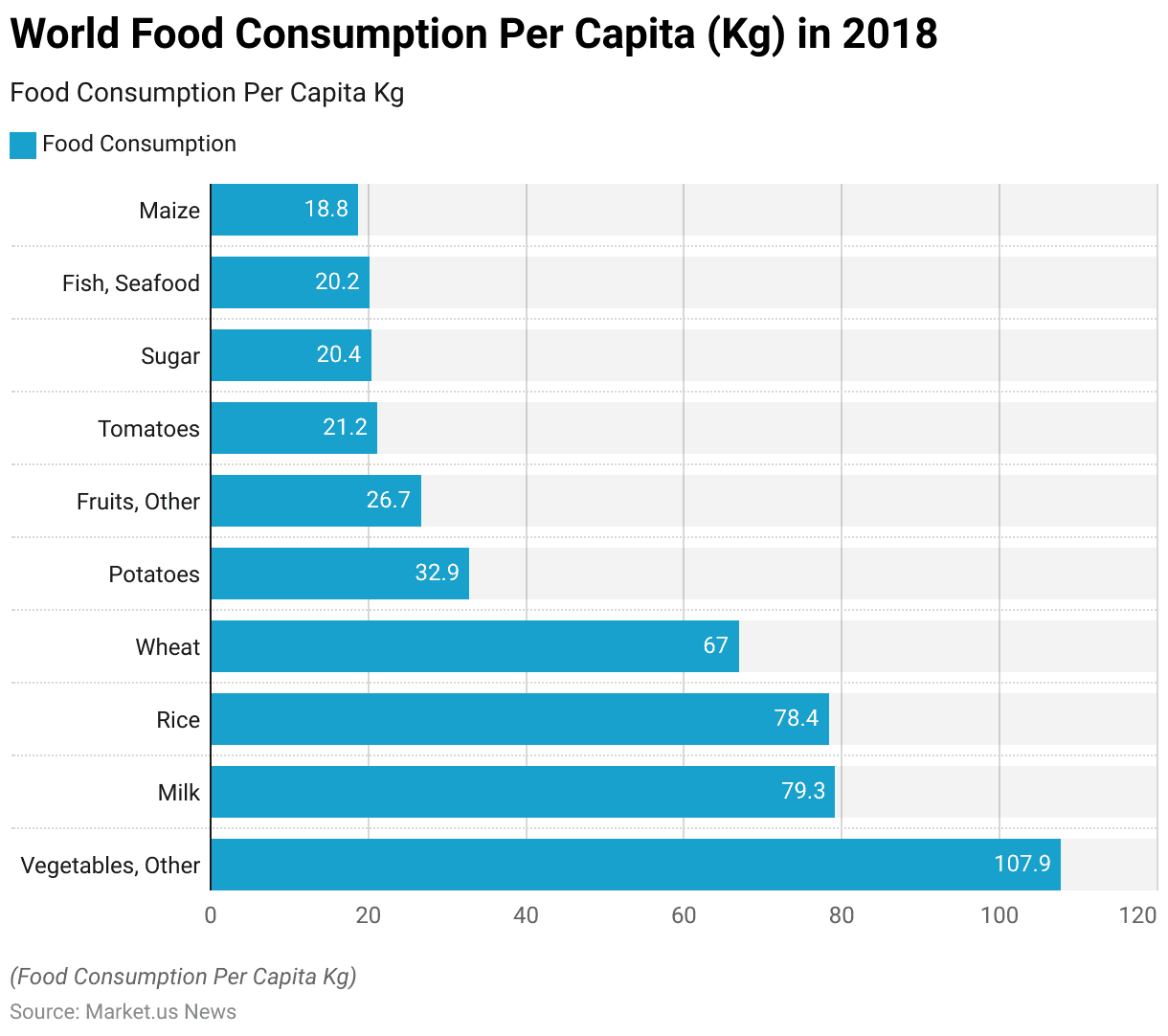
Global Food And Nutrition Consumption – By Product Group
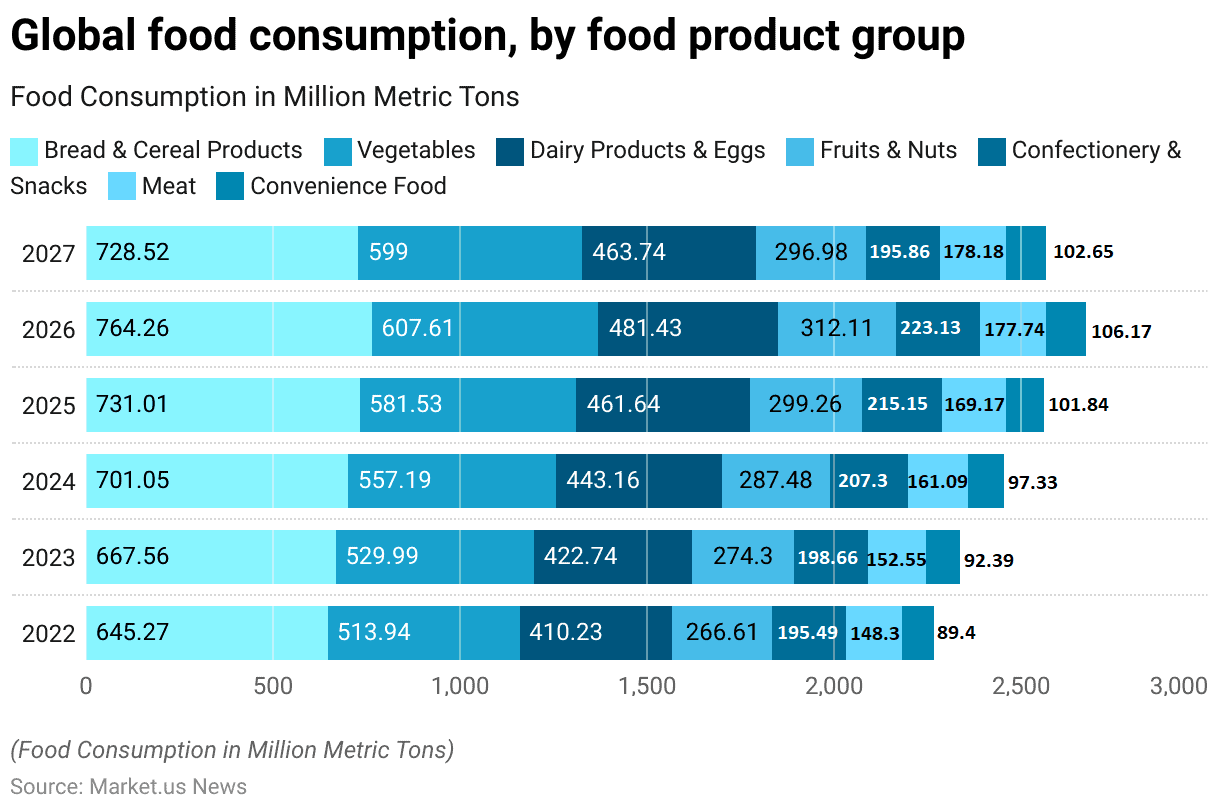
- Global food consumption across various food product groups has shown notable trends from 2022 to 2027. In 2022, bread and cereal products led consumption with 645.27 million metric tons, followed by vegetables at 513.94 million metric tons.
- Dairy products and eggs, fruits and nuts, confectionery and snacks, meat, and convenience food were consumed in quantities of 410.23, 266.61, 195.49, 148.3, and 89.4 million metric tons, respectively.
- The following year, 2023, saw increases across all categories, with bread and cereal products rising to 667.56 million metric tons, vegetables to 529.99 million metric tons, and dairy products and eggs to 422.74 million metric tons.
- Fruits and nuts, confectionery and snacks, meat, and convenience food also increased to 274.3, 198.66, 152.55, and 92.39 million metric tons, respectively.
Food And Nutrition Future Projections
- However, in 2027, a slight decrease is expected in bread and cereal products, which is projected to fall to 728.52 million metric tons, and vegetables, which is likely to drop to 599 million metric tons.
- Dairy products and eggs consumption is also expected to decrease to 463.74 million metric tons, while fruits and nuts decline to 296.98 million metric tons.
- Confectionery and snack consumption are expected to decrease to 195.86 million metric tons, but meat and convenience food consumption slightly adjust to 178.18 and 102.65 million metric tons, respectively.
Ideal Nutrition Intake Requirements and Guidelines
Food And Nutrition For Adults
- A nutritious adult diet includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains like maize, millet, oats, wheat, and brown rice.
- Aim for at least 400 grams of fruits and veggies daily, excluding starchy roots.
- Keep free sugars to less than 10% of total energy intake, ideally under 5%, and minimize fats to under 30% of total energy intake.
- Limit saturated fats to less than 10% of total energy intake and trans-fats to less than 1%, avoiding industrially-produced trans-fats altogether.
Food And Nutrition For Infants and Young Children
- In the initial two years of a child’s life, proper nutrition supports healthy growth and cognitive development and lowers the risk of obesity and non-communicable diseases in the future.
- Guidance for a healthy diet in infants and young children mirrors that of adults, with specific emphasis on exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months, continued breastfeeding until at least two years of age, and introduction of diverse, safe, and nutrient-rich foods alongside breast milk starting from six months onwards.
Ideal Intake of Essential Nutrients
- Daily values for nutrients serve as guidelines for maintaining a balanced diet and optimal health. These values include recommendations for various essential nutrients such as calcium, iron, vitamins, and minerals.
- For instance, it’s suggested to limit added sugars to 50 grams per day and saturated fat to 20 grams.
- Conversely, nutrients like calcium, potassium, and dietary fiber should be consumed in higher quantities, with recommended daily values of 1300 milligrams, 4700 milligrams, and 28 grams, respectively.
Global Food Energy Intake
Food Energy Intake – By Country
- In 2018, Ireland led the world in average daily dietary energy consumption per capita, with an intake of 16,520 kilojoules.
- The United States followed closely, where individuals consumed an average of 15,820 kilojoules per day.
- Belgium was not far behind, with an average daily consumption of 15,770 kilojoules per person. Turkey and
- Austria also ranked high on the list, with daily intakes of 15,530 and 15,460 kilojoules, respectively. Iceland’s average consumption stood at 15,290 kilojoules per capita.
- Romania, Canada, Germany, and Poland had slightly lower but still substantial daily energy intakes, with averages of 14,980, 14,920, 14,870, and 14,800 kilojoules per person, respectively.
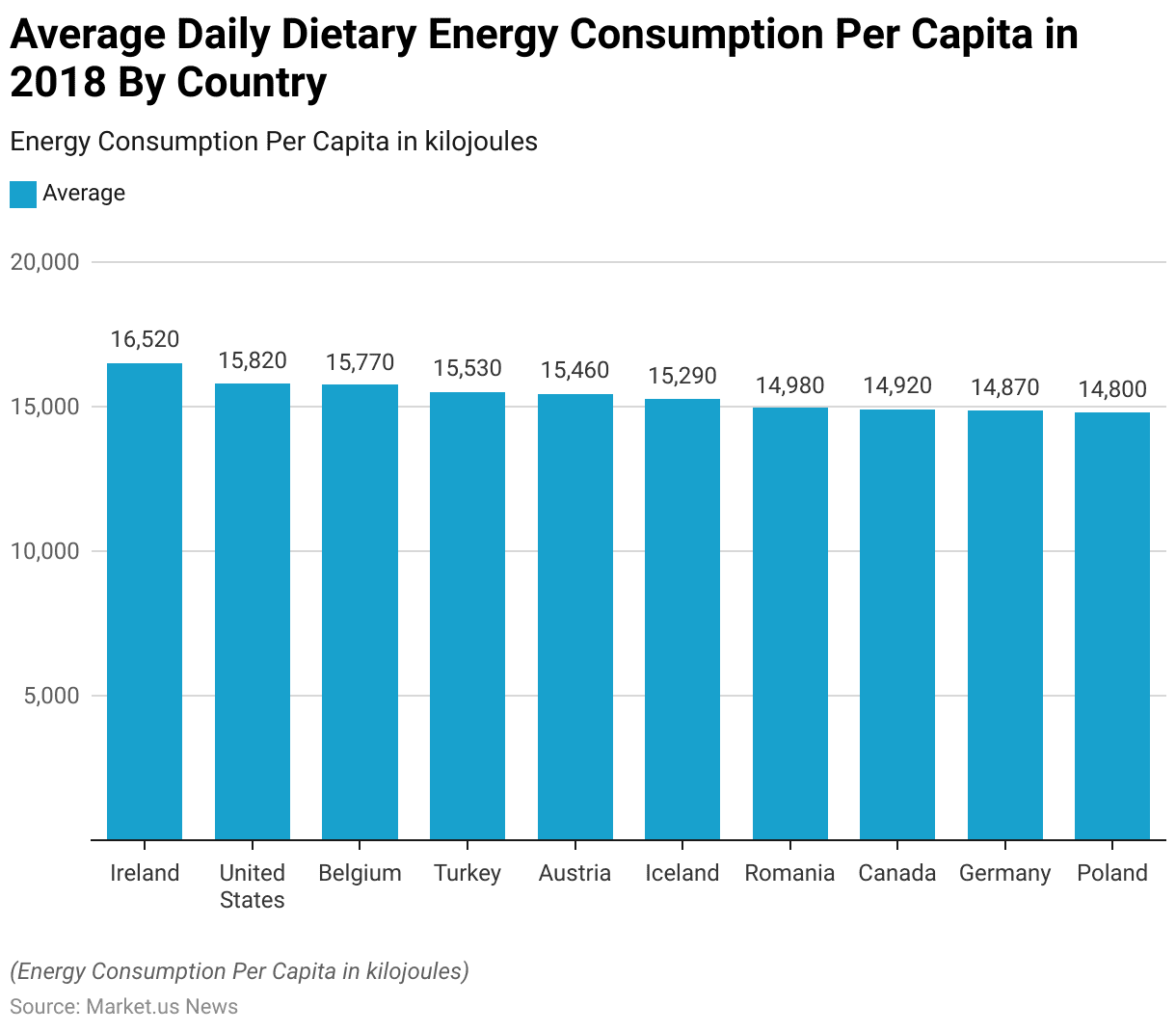
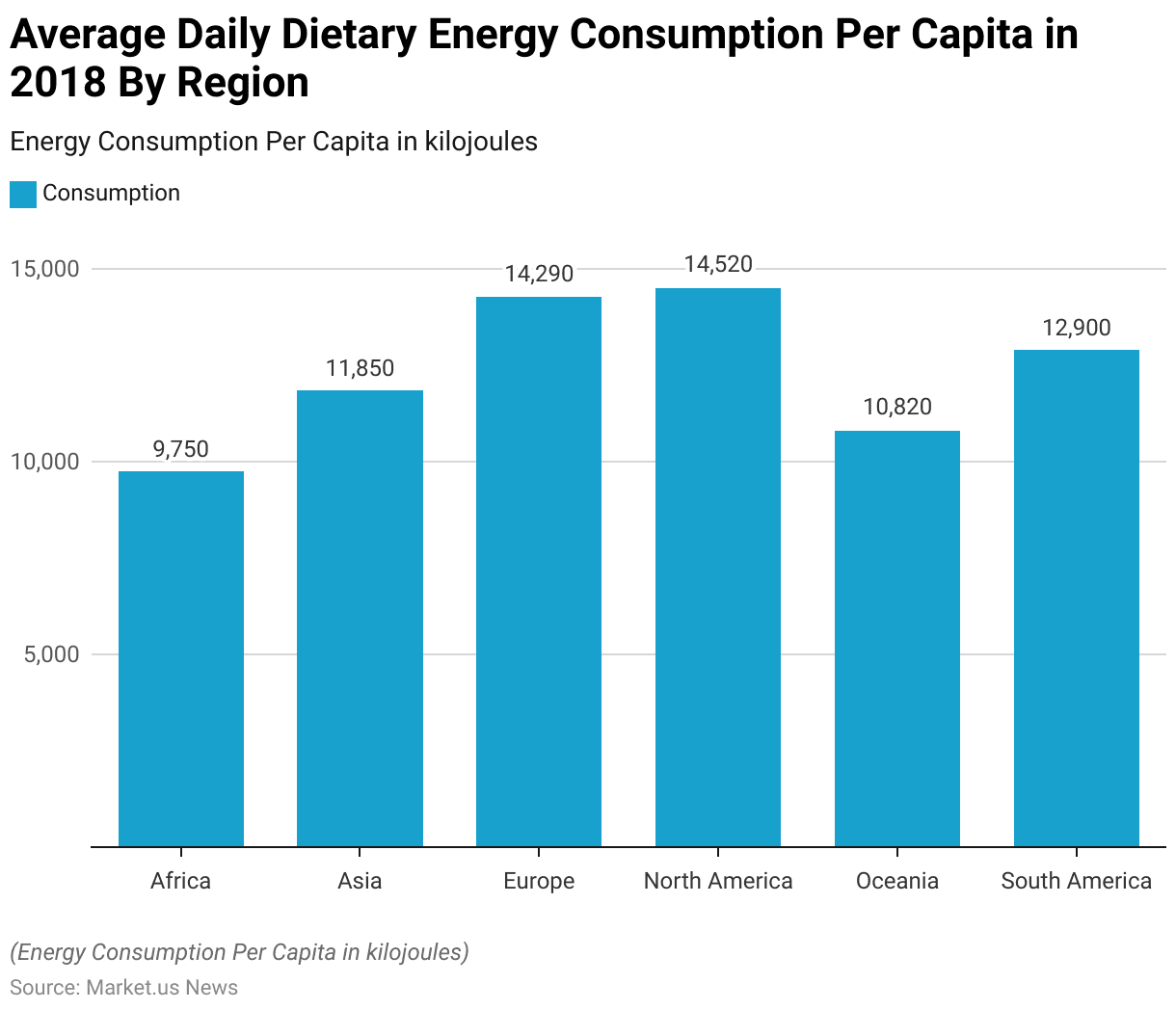
Food Energy Intake – By Region
- In 2018, global dietary energy consumption per capita exhibited significant regional variations.
- North America had the highest average daily energy intake, with individuals consuming 14,520 kilojoules per day.
- Europe followed closely with an average consumption of 14,290 kilojoules per capita.
- South America also reported substantial dietary energy intake, averaging 12,900 kilojoules per person daily.
- In Asia, the average daily energy consumption per capita was 11,850 kilojoules, reflecting moderate dietary energy levels.
- Oceania’s average intake stood at 10,820 kilojoules per person, while Africa had the lowest average daily energy consumption, with individuals consuming 9,750 kilojoules per day.
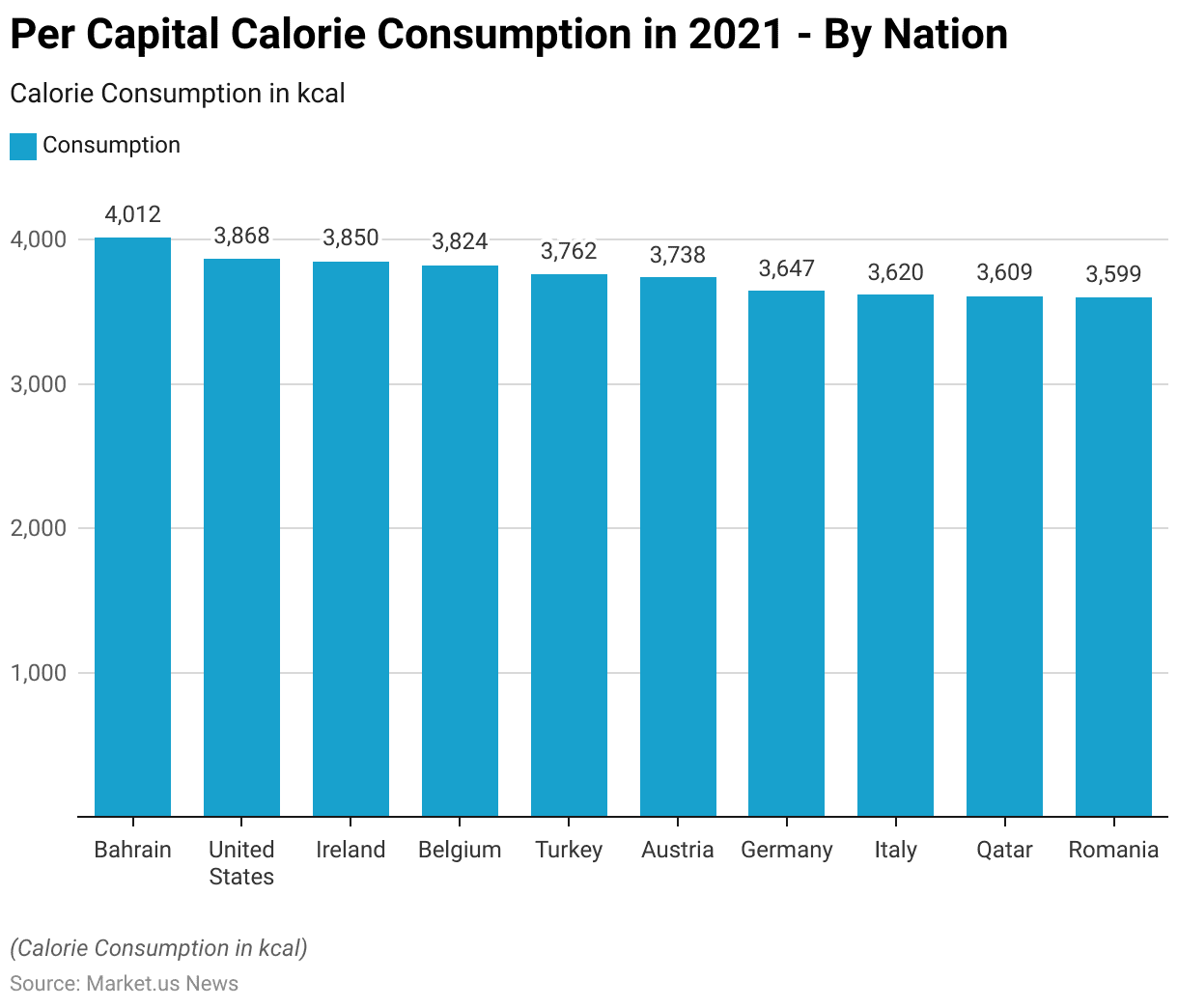
Calorie Consumption – By Nation
- In 2021, per capita calorie consumption varied widely among different countries.
- Bahrain led with the highest average daily intake, where individuals consumed 4,012 kilocalories per day.
- The United States followed with an average consumption of 3,868 kilocalories per person.
- Ireland and Belgium also reported high-calorie intakes, with averages of 3,850 and 3,824 kilocalories per day, respectively.
- Turkey and Austria recorded per capita intakes of 3,762 and 3,738 kilocalories, respectively.
- Germany’s average daily consumption stood at 3,647 kilocalories, while Italy reported 3,620 kilocalories per person.
- Qatar had a similar intake level with an average of 3,609 kilocalories per capita, and Romania rounded out the list with a daily average of 3,599 kilocalories.
Basic Facts Related to Hunger and Nutrition
- Global hunger showed little change from 2021 to 2022 but remained significantly higher than pre-COVID-19 levels, affecting approximately 9.2% of the global population in 2022 compared to 7.9% in 2019.
- Projections indicate that nearly 600 million people will suffer from chronic undernourishment by 2030, with the pandemic and the conflict in Ukraine contributing to an additional 119 million undernourished individuals.
- Food insecurity varied across regions, with one-third of rural adults experiencing moderate to severe food insecurity in 2022, compared to 28.8% in peri-urban areas and 26% in urban areas.
- The global gender gap in food insecurity narrowed from 3.8% to 2.4% points between 2021 and 2022.
Global Hunger Index (GHI) Score
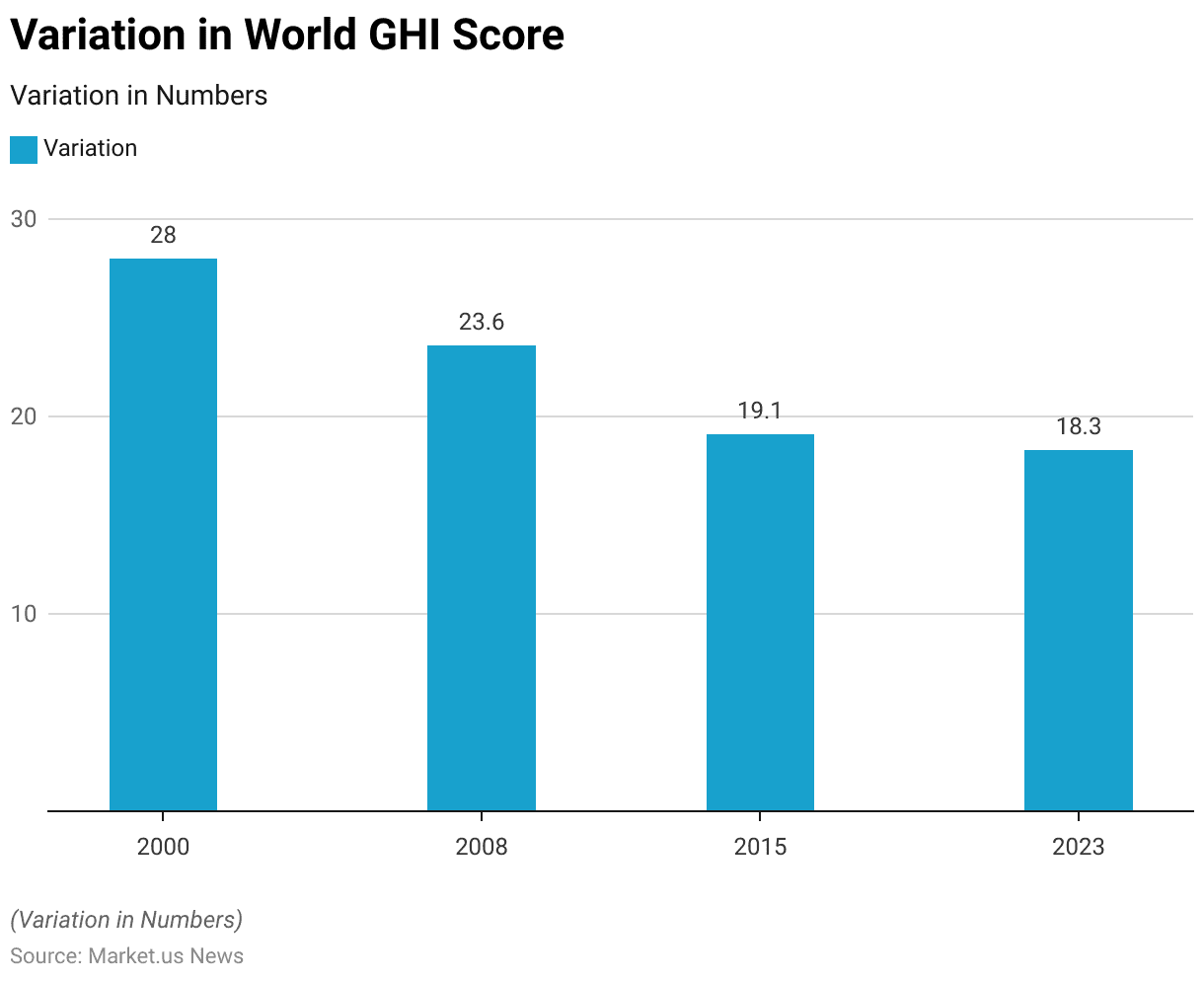
Variation in World GHI Scores
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) score has shown a significant decline over the years, reflecting improvements in global hunger levels.
- In 2000, the world GHI score was 28, indicating a high level of hunger.
- By 2023, the world GHI score had reached 18.3, demonstrating a steady reduction in global hunger over the past two decades.
Malnutrition and Undernutrition Statistics
- In 2022, around 390 million adults globally were underweight, while a staggering 2.5 billion were overweight, with 890 million classified as obese.
- Among children and teenagers aged 5-19 years, 390 million were overweight, including 160 million diagnosed with obesity, and an additional 190 million faced thinness.
- Additionally, an estimated 149 million children under five years old suffered from stunting, while 37 million dealt with being overweight or obese.
Global Obesity Statistics
- In 2022, the global overweight population among adults aged 18 and older reached 2.5 billion, with 890 million suffering from obesity, marking a significant increase from 1990.
- This equates to 43% of adults being overweight, up from 25% in 1990.
- Overweight prevalence varied by region, ranging from 31% in certain areas to 67% in others.
- Additionally, about 16% of adults worldwide were classified as obese in 2022, more than double the rate in 1990.
- The issue extends beyond adults, with approximately 37 million children under five years and over 390 million children and adolescents aged 5–19 years worldwide being overweight.
- This represents a sharp rise from 1990, with overweight prevalence among this age group increasing from 8% to 20%.
- Furthermore, while only 2% of children and adolescents were obese in 1990, the figure rose to 8% by 2022, affecting 160 million young people globally.
Food Security Statistics
- In 2018, 14.3 million households in the U.S. faced food insecurity, indicating they lacked the financial means to access adequate food.
- This affected 37.2 million individuals, with 6.8% experiencing low food security and 4.3% facing very low food security.
- Additionally, 29.7 million people lived in food deserts, defined as low-income areas more than one mile away from a supermarket.
- In 2021, 118.5 million U.S. households, or 89.9%, were food secure, according to the USDA. However, 13.5 million households, or 10.2%, encountered food insecurity at some point during the year.
- Among them, 8.4 million households experienced low food security, and 5.1 million had inadequate food security.
Food Prices and Its Impact on Nutrition
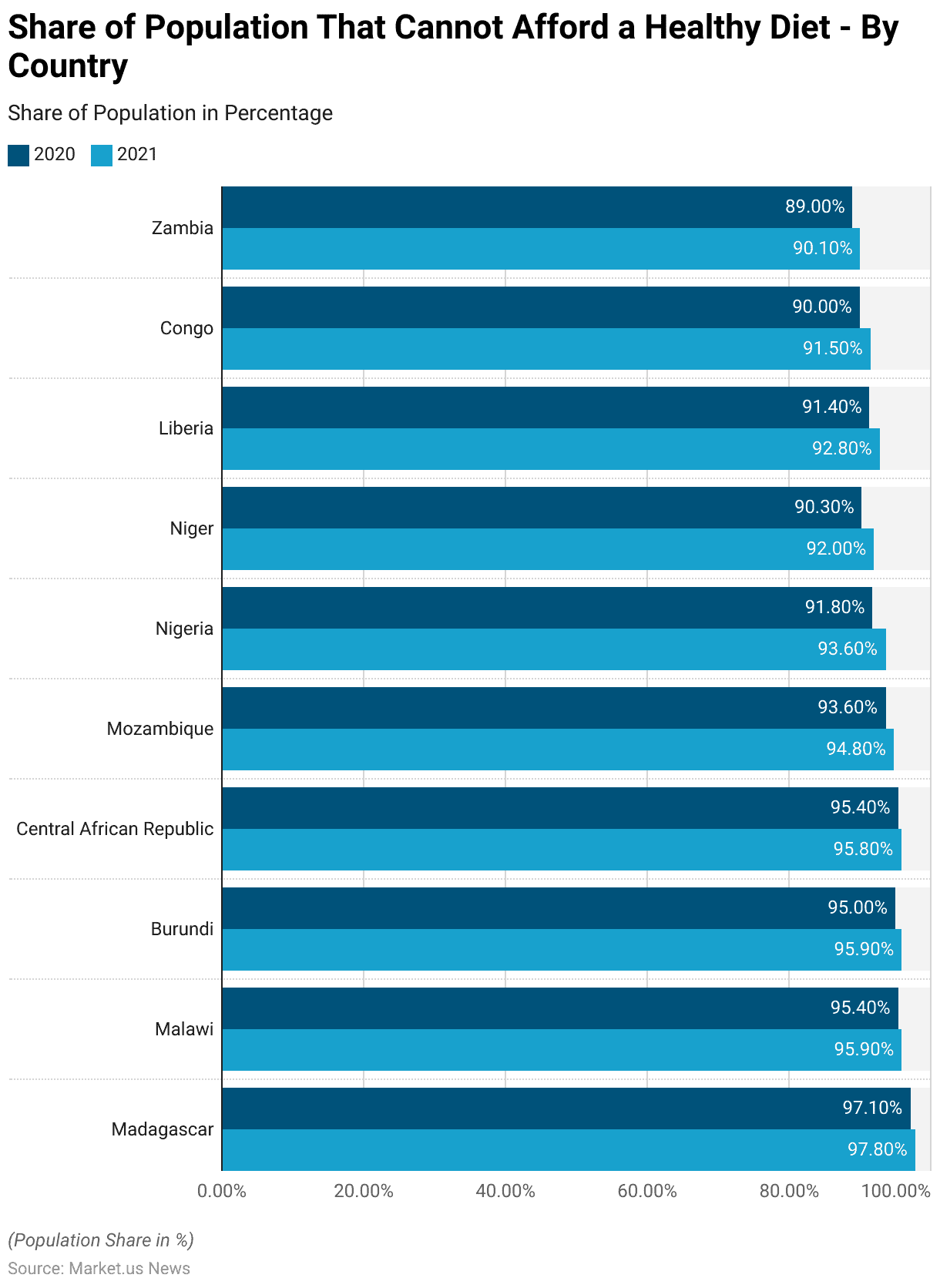
Population Around the Globe That Cannot Afford a Healthy Diet
- In 2021, the share of the population that could not afford a healthy diet remained alarmingly high in several countries.
- Madagascar led with 97.8% of its population unable to afford a healthy diet, up from 97.1% in 2020.
- Similarly, Malawi and Burundi both saw increases, with rates rising to 95.9% from 95.4% and 95.0%, respectively.
- The Central African Republic also experienced a slight increase, with the rate rising from 95.4% to 95.8%.
- Mozambique followed, with 94.8% of its population unable to afford a healthy diet, up from 93.6%.
- In Nigeria, the rate increased from 91.8% to 93.6%, while Niger saw a rise from 90.3% to 92.0%.
- Liberia’s rate increased from 91.4% to 92.8%, and the Congo saw an increase from 90.0% to 91.5%.
- Zambia also experienced an increase, with the rate rising from 89.0% to 90.1%.
Environmental Impact
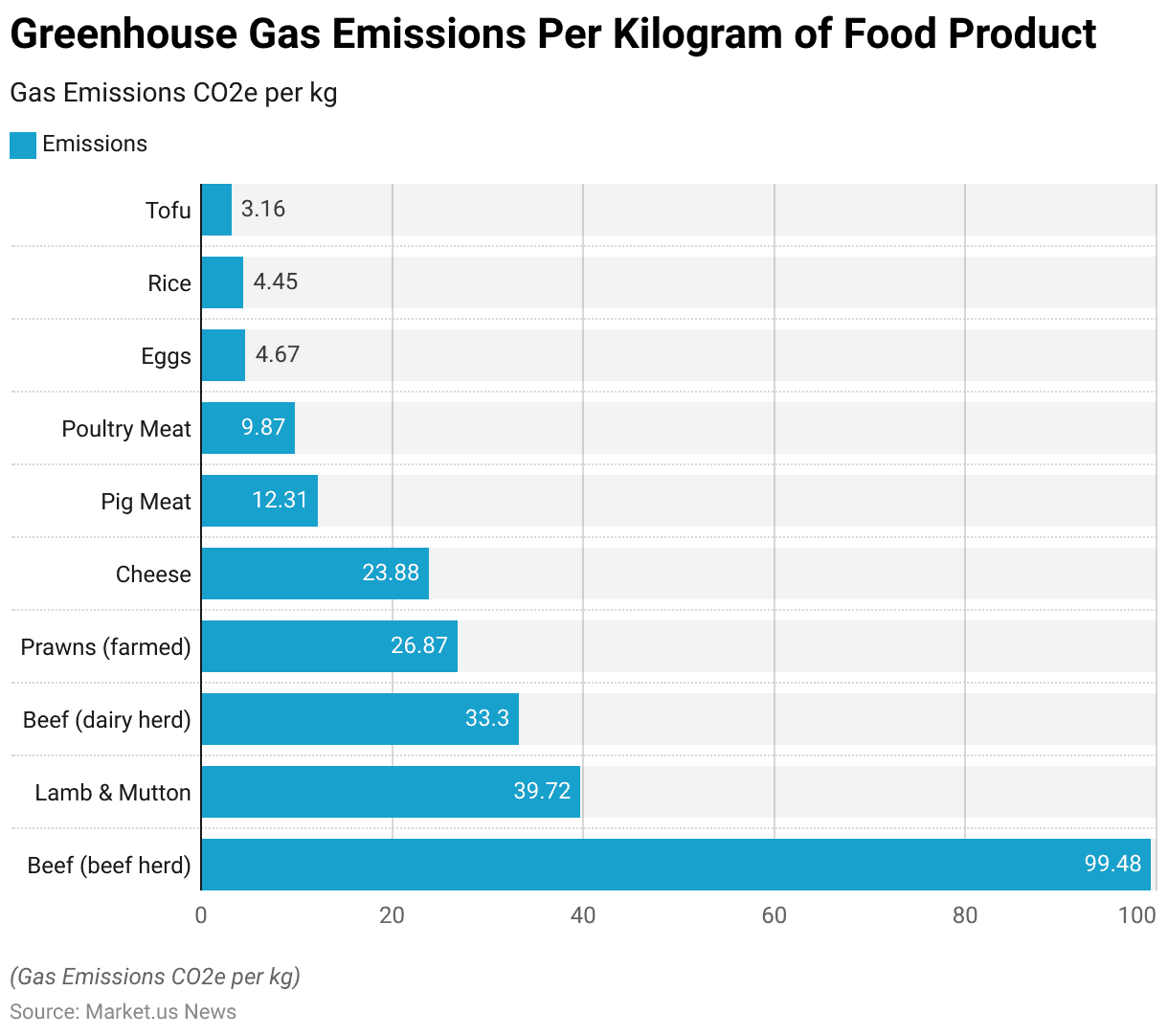
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Per Kilogram of Food Product
- Greenhouse gas emissions vary significantly across different food products.
- Beef from beef herds is the highest emitter, producing 99.48 kg of CO2 equivalent per kilogram.
- Lamb and mutton follow with 39.72 kg CO2e per kg, while beef from dairy herds emits 33.3 kg CO2e per kg.
- Farmed prawns produce 26.87 kg CO2e per kg, and cheese emits 23.88 kg CO2e per kg.
- Pig meat results in 12.31 kg CO2e per kg, and poultry meat emits 9.87 kg CO2e per kg.
- Among lower-emission foods, eggs generate 4.67 kg CO2e per kg, rice produces 4.45 kg CO2e per kg, and tofu results in 3.16 kg CO2e per kg.
Latest Food and Nutrition Trends
- 52% of survey participants consider the ingredient list when purchasing food and beverages.
- Half of Generation Z and 65% of Millennials believe their food choices have an impact on the environment.
- Nearly four in ten Americans, or 39%, take environmental sustainability into account when buying food and beverages.
- Generation Z is unique in asserting that foods, beverages, and nutrients contribute to their emotional and mental well-being.
- About 30% of Americans have adjusted their diet and nutrition habits to manage stress.
- 73% of Americans snack daily, primarily due to hunger or thirst (34%) or as a treat (25%).
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





