Table of Contents
Introduction
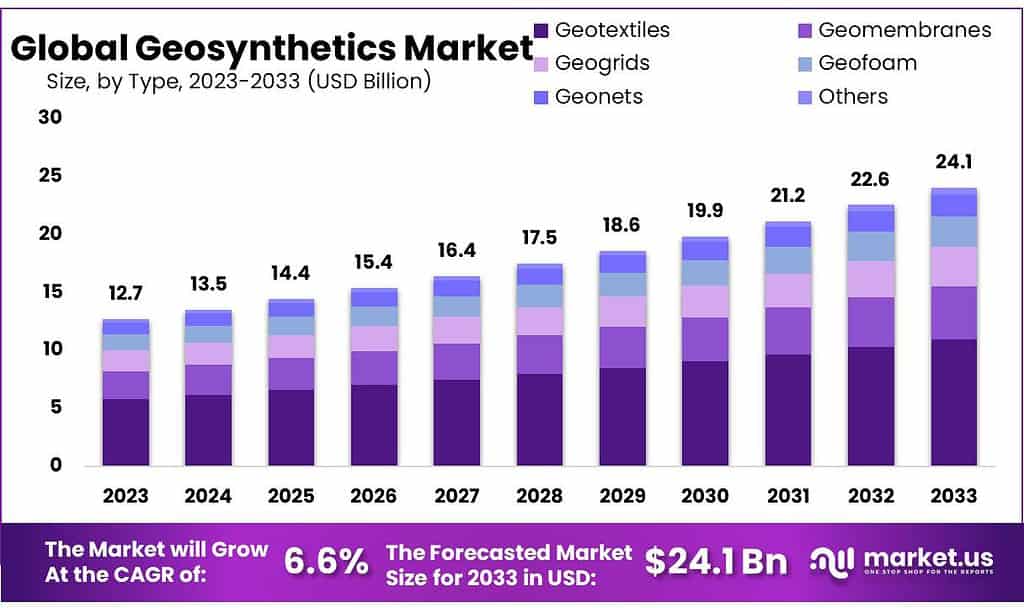
The global Geosynthetics Market is projected to grow significantly from USD 12.7 billion in 2023 to USD 24.1 billion by 2033, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% over the forecast period. Geosynthetics refers to a wide range of polymeric products used to stabilize terrain and address various civil engineering challenges. These products include geonets, geotextiles, geomembranes, and geogrids, which are manufactured from materials such as polystyrene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polyester. The demand for geosynthetics is driven by their increasing application in civil engineering and geotechnical projects, such as soil reinforcement, erosion control, and waste management.
Several growth factors contribute to the expansion of the geosynthetics market. The rapid urbanization and industrialization in emerging economies have led to increased infrastructure development, necessitating the use of geosynthetics for improved construction quality and durability. Additionally, the growing awareness of environmental sustainability has boosted the adoption of geosynthetics in projects aimed at reducing soil erosion, managing waste, and conserving water resources. For instance, geosynthetics are extensively used in landfills to prevent soil contamination and in water management systems to enhance water conservation and quality.
However, the market also faces certain challenges. The high cost of raw materials and the complex manufacturing process of geosynthetics can limit their widespread adoption, particularly in developing regions. Furthermore, the lack of standardized regulations and quality control measures in some countries can hinder market growth. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on producing cost-effective and high-performance geosynthetic products, which are expected to create new growth opportunities in the market.
Recent developments in the geosynthetics industry highlight the innovative approaches being undertaken to meet market demands. For example, advancements in manufacturing technologies have led to the production of geosynthetics with enhanced properties such as higher tensile strength, better chemical resistance, and improved durability. Additionally, companies are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices by developing geosynthetics from recycled materials, thereby reducing environmental impact and promoting circular economy principles.
Geosynthetics Statistics
- While wovens have been on a declining trend, nonwovens have been markedly on the rise with a dominating share of 41 to 53% of the annual consumption of geosynthetics.
- Nonwovens have been markedly on the rise with a dominating share of 41 to 53% of total consumption of geosynthetics(34 million m2 in 1991 to 54 million m2 in 1999).
- The analysis revealed an overall mean score of 2.06 and 1.74 regarding the knowledge level among fresh graduates on the types and primary functions of geosynthetics respectively.
- The secant stiffness of GTX was also reduced by damage, with retained values ranging between 61 and 70% for 2% strain and between 51 and 61% for 5% strain.
- The reductions in tensile strength were higher with the synthetic aggregate (33%) than with the natural aggregates (granite,22% and limestone, 12%).
- Stabilenka has high strengths of up to 2,500 kN/m uniaxial and 1,000 kN/m biaxial, the world’s strongest woven reinforcement fabric (next to Stabilenka Xtreme).
- Products are available with widths from 1 to 5 and weights from 100 to 350 g/m2 with different raw materials
- The direct shear tests were conducted using four different normal stresses of 40, 80, 120, and 160 kPa. All the tests involved applying the normal stress and monitoring the vertical displacement.
- The normal load was maintained constant during the shearing process. The rate of shearing was maintained at 0.5 mm/min for all the tests.
- geosynthetics made of textured and perforated high-density plastic (HDPE) tapes: available in small, medium, and large cell options ranging from 2.5 cm to 30 cm.
- By 2040 it is estimated that two billion people (25% of the world’s population) in 60 countries will have inadequate fresh water.
Emerging Trends
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials: A significant trend in the geosynthetics market is the development and adoption of sustainable materials. Companies are increasingly producing geosynthetics from recycled polymers and other eco-friendly sources. For instance, the use of recycled plastics in geotextiles and geomembranes is becoming more common, which helps reduce environmental impact and supports circular economy initiatives.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies: Technological advancements in manufacturing processes are enhancing the performance and efficiency of geosynthetics. Innovations such as 3D weaving and advanced extrusion techniques are leading to the creation of geosynthetics with improved properties, such as higher tensile strength, better durability, and enhanced resistance to environmental factors. These advancements allow for more effective applications in challenging environments.
Smart Geosynthetics: The integration of smart technologies into geosynthetics is an emerging trend. Smart geosynthetics, equipped with sensors and monitoring systems, can provide real-time data on soil conditions, stress levels, and environmental changes. This data helps in making informed decisions regarding maintenance and performance, improving the overall effectiveness of geosynthetic systems.
Increased Use in Infrastructure Projects: The application of geosynthetics in large-scale infrastructure projects is on the rise. With growing urbanization and infrastructure development, geosynthetics are being increasingly used in road construction, railway projects, and slope stabilization. Their ability to improve soil stability, reduce erosion, and manage water flow makes them crucial for modern infrastructure projects.
Enhanced Focus on Durability and Longevity: There is a growing emphasis on enhancing the durability and longevity of geosynthetics. Research and development efforts are focusing on improving resistance to chemical attacks, UV radiation, and mechanical wear. These enhancements ensure that geosynthetics maintain their performance over extended periods, even in harsh conditions.
Integration with Green Technologies: Geosynthetics are increasingly being integrated with green technologies to support sustainable construction practices. For example, geosynthetics are being used in conjunction with green roofs and permeable pavements to manage stormwater, reduce heat islands, and enhance urban green spaces.
Use Cases
Road Construction and Pavement Stabilization: Geosynthetics are extensively used in road construction to enhance soil stability and extend the lifespan of pavements. For example, geogrids and geotextiles are employed to reinforce road bases and sub-bases, reducing pavement failure and improving load distribution. In a notable case, the use of geogrids in the construction of the M-80 motorway in Spain significantly reduced the need for thick pavement layers, cutting construction costs by approximately 20%.
Landfill Liners and Covers: In waste management, geosynthetics play a critical role in preventing soil and groundwater contamination. Geomembranes, made from materials like high-density polyethylene, are used as liners and covers in landfills to contain leachate and methane gases. For instance, the Central Landfill in Rhode Island, USA, employs over 1 million square meters of geomembrane liners to effectively manage waste and protect the surrounding environment.
Erosion Control and Slope Stabilization: Geosynthetics are used in erosion control projects to stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion. Geotextiles and geogrids are commonly used in applications such as retaining walls and slope reinforcement. For example, in the 2023 rehabilitation project of the Cayo District in Belize, geotextiles were used to stabilize steep slopes and reduce erosion caused by heavy rainfall, improving soil retention and enhancing vegetation growth.
Drainage Systems: Geosynthetics, including geonets and geotextiles, are utilized in drainage systems to improve water flow and prevent clogging. In urban infrastructure, these materials help manage stormwater runoff and prevent flooding. A case in point is the use of geonets in the stormwater management system of the Bangkok Skytrain project, which effectively managed large volumes of runoff and reduced the risk of urban flooding.
Green Roofs and Sustainable Landscaping: Geosynthetics are increasingly integrated into green roofing and landscaping projects to support sustainable urban development. Geotextiles and geomembranes are used to create drainage layers, retain moisture, and support plant growth. The city of Portland, Oregon, implemented green roofs with geosynthetic drainage layers on several public buildings, which helped manage stormwater and enhance urban green spaces.
Mining and Resource Extraction: In the mining industry, geosynthetics are employed in various applications such as heap leaching, tailings management, and containment systems. Geomembranes and geotextiles are used to line leach pads and tailings ponds, improving resource recovery and environmental protection. For instance, the use of geosynthetics in the heap leaching process at the Goldstrike Mine in Nevada has optimized gold recovery and reduced environmental impact.
Major Challenges
High Initial Costs: One of the primary challenges in the geosynthetics market is the high initial cost of materials and installation. Advanced geosynthetics, such as high-strength geogrids and geomembranes, can be expensive to produce and install. For instance, the cost of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) geomembranes can range from USD 1.50 to USD 3.00 per square meter, which can be a significant burden for projects with tight budgets.
Quality Control and Standards: The lack of standardized regulations and quality control measures in some regions can impact the performance and reliability of geosynthetics. Inconsistent quality can lead to issues such as reduced durability and effectiveness, which may affect the overall success of projects. For example, variations in the manufacturing standards of geotextiles can result in differences in their filtration and separation properties, potentially leading to project failures.
Environmental and Health Concerns: The production and disposal of geosynthetics raise environmental and health concerns. Some geosynthetic materials, such as those made from non-recycled plastics, can contribute to environmental pollution if not properly managed at the end of their life cycle. Additionally, the production process can involve harmful chemicals, which may pose health risks to workers. There is an increasing push towards developing more sustainable and recyclable geosynthetics to address these concerns.
Complex Installation Requirements: The installation of geosynthetics often requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Proper installation is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the materials in applications such as erosion control and soil stabilization. Mistakes during installation, such as incorrect overlap or improper sealing, can lead to significant issues and additional costs. Training and skilled labor are essential to mitigate these risks.
Performance in Extreme Conditions: Geosynthetics may face performance challenges when used in extreme environmental conditions, such as high temperatures, heavy chemical exposure, or highly dynamic loads. For example, geomembranes used in landfills must withstand aggressive chemicals and significant mechanical stress. Ensuring that geosynthetics can perform reliably under these conditions requires ongoing research and development.
Market Growth Opportunities
Increasing Infrastructure Development: The rapid expansion of infrastructure projects worldwide presents a significant growth opportunity for the geosynthetics market. As urbanization and industrialization increase, the demand for geosynthetics in road construction, retaining walls, and slope stabilization grows. For instance, major infrastructure initiatives, such as the high-speed rail projects in Asia and the extensive highway expansions in North America, require advanced geosynthetic solutions to enhance soil stability and improve construction efficiency.
Sustainable Construction Practices: The shift towards sustainable construction practices is driving demand for eco-friendly geosynthetics. The development of geosynthetics from recycled materials, such as recycled plastics in geotextiles and geomembranes, aligns with global sustainability goals. Projects like green roof installations in urban areas and sustainable landfill management systems are increasingly incorporating geosynthetics to support environmental conservation efforts.
Technological Advancements: Technological innovations in geosynthetics are creating new market opportunities. Advances such as smart geosynthetics, which include sensors and monitoring systems, offer enhanced performance and real-time data for better management and maintenance. These technologies are being adopted in various applications, including smart infrastructure and disaster management systems, providing opportunities for growth and innovation.
Expansion in Emerging Markets: Emerging markets in regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa present significant growth potential for geosynthetics. Rapid urbanization and infrastructure development in these regions are driving demand for geosynthetic solutions. For example, infrastructure projects in India and China are increasingly utilizing geosynthetics for road construction, erosion control, and waste management.
Regulatory and Policy Support: Government regulations and policies that promote sustainable construction and environmental protection are boosting the geosynthetics market. Incentives and regulations aimed at reducing soil erosion, managing stormwater, and improving landfill management create favorable conditions for geosynthetic products. The implementation of green building codes and environmental regulations in various countries supports the adoption of geosynthetics in construction projects.
Recent Developments
Propex Operating Company LLC has been making significant advancements in the geosynthetics sector in 2023 and 2024. In June 2024, Propex expanded its manufacturing capabilities at its Ringgold, Georgia facility, which houses the industry’s largest geosynthetic capacity. This expansion aims to meet the increasing demand for geosynthetic products used in infrastructure projects like levees, roads, and bridges. In April 2023, Propex focused on enhancing its product offerings in erosion control and stabilization solutions, emphasizing sustainable practices by leveraging innovative geotextiles that reduce construction costs and environmental impact. Propex’s acquisition by Solmax in December 2021 further strengthened its position in the market, allowing the company to expand into new segments like turf reinforcement and pavement rehabilitation, offering comprehensive solutions for transportation and civil infrastructure projects.
AGRU America, a leading company in the geosynthetics sector, has been actively expanding its operations and enhancing its product offerings throughout 2023 and 2024. In March 2024, AGRU America announced a $7.8 million investment to expand its manufacturing capabilities in Williamsburg County, South Carolina, which will create six new jobs and support the increased demand for its high-quality geosynthetics products. This expansion aligns with the company’s mission to develop innovative engineering plastics solutions for various applications, including environmental protection and infrastructure development. In November 2023, AGRU America received the EDAWN Existing Industry Award in Manufacturing Excellence, recognizing its commitment to quality and innovation in geosynthetic lining systems. The company’s strategic investments in new manufacturing facilities and technologies have strengthened its position in the market, with plans to introduce more production lines in 2024.
Tensar International Corporation, a leader in the geosynthetics sector, has been actively contributing to infrastructure and construction projects through its innovative solutions. In January 2023, Tensar hosted a webinar to discuss the use of geogrids in civil construction projects, highlighting their role in improving stability and durability. In March 2023, Tensar released its next-generation InterAx geogrid product, designed to enhance ground stabilization while reducing costs. Throughout 2023, Tensar focused on expanding its educational outreach by participating in various conferences, such as the GEOANZ 2024 Conference in July, where they shared advancements in geosynthetics for sustainable pavements. In December 2021, Tensar was acquired by Commercial Metals Company, which aims to leverage Tensar’s geosynthetic technologies to expand its offerings in construction solutions. The acquisition strengthens both companies’ commitment to providing sustainable and resilient infrastructure solutions
Officine Maccaferri S.p.A. has been making significant strides in the geosynthetics sector throughout 2023 and 2024. In March 2024, the company completed the acquisition of a majority stake in Nesa S.r.l., a leading provider of environmental monitoring systems. This acquisition enhances Maccaferri’s capabilities in IoT technologies, crucial for infrastructure projects. In April 2024, Maccaferri announced the opening of a new manufacturing facility in California, aimed at expanding production capacity for rockfall protection products. This facility is strategically located to improve service delivery and reduce shipping costs. Maccaferri has also focused on sustainability, emphasizing the use of geosynthetics for soil stabilization and erosion control, which are environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional construction materials. This aligns with their mission to provide innovative solutions that reduce environmental impact .
Conclusion
The geosynthetics market is set for continued robust growth, driven by increasing infrastructure development, the shift towards sustainable construction practices, and ongoing technological advancements the market reflects a growing recognition of geosynthetics’ role in enhancing construction efficiency and environmental management. Key factors such as rising urbanization, regulatory support for sustainable practices, and the integration of innovative technologies like smart geosynthetics are propelling market expansion.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





