Table of Contents
Introduction
The global glycerol market is expected to grow steadily over the next decade, with the market size projected to reach USD 5.9 billion by 2033, up from USD 4.9 billion in 2023, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily driven by increased demand from industries such as food and beverage, nutraceuticals, and pharmaceuticals. Glycerol’s wide-ranging applications, including as a sweetener, humectant, and preservative in food, have boosted its market presence in the food industry, particularly in products like processed meats and dairy items.
Several factors contribute to this growth trajectory. The rising demand for biodiesel, where glycerol is a byproduct, has significantly influenced the market. With the global push for renewable energy sources and the expansion of biodiesel production, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific and Europe, the availability of glycerol has increased. For example, biodiesel accounted for nearly 59.5% of the glycerol supply in 2023, underscoring its importance as a cost-effective and renewable source of glycerol. Additionally, the cosmetics and personal care sectors are substantial contributors, with glycerol being widely used for its moisturizing and emollient properties in skincare, haircare, and cosmetic formulations.
In contrast, the market faces several challenges. Price volatility of raw materials, such as vegetable oils used in glycerol production, is a notable concern. Fluctuations in biodiesel production also affect glycerol supply and prices, causing an imbalance between supply and demand at times. Furthermore, competition from substitute products, including various synthetic alternatives, limits the growth potential of glycerol in some applications. The high costs of refining crude glycerol to meet industrial standards present additional hurdles, especially for smaller market players.
Technological advancements and innovations in refining processes have led to new applications for glycerol, such as bio-based polymers and environmentally friendly de-icing agents. These developments have opened up new growth opportunities in the industrial sector. Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry’s increasing use of glycerol, particularly for its healing properties in products like cough syrups and mouthwashes, presents another significant growth avenue. This sector is expected to witness a higher CAGR compared to other industries during the forecast period.
Recent developments in the market include significant investments in research and development to improve the production processes and expand the applications of glycerol. Companies like BASF and Cargill have been active in enhancing their refining capacities, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific, which continues to dominate the market due to the rising consumption of glycerol in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products.
BASF has been actively expanding its capabilities, particularly in refining glycerol for food applications. In 2023, BASF opened a new food application center in Johannesburg, South Africa, aimed at enhancing glycerol-based product development for the food industry. The company continues to focus on innovations in glycerol applications in personal care, cosmetics, and industrial sectors.
Cargill has focused on sustainability, especially in replacing mineral oils with plant-based glycerol derivatives. In 2023, Cargill expanded its vegetable oil refinery capacity to support oleochemical and glycerol production. The company has also made strides in developing vegetable oil-based solvents and polyols, contributing to safer, eco-friendly industrial applications.
Procter & Gamble (P&G) continues to invest in the personal care and pharmaceutical sectors where glycerol is a key ingredient. Recent efforts include the company’s increased use of refined glycerol in products such as moisturizers, shampoos, and other personal care items. P&G has also focused on improving the sustainability of its supply chain, incorporating more bio-based materials.
Key Takeaways
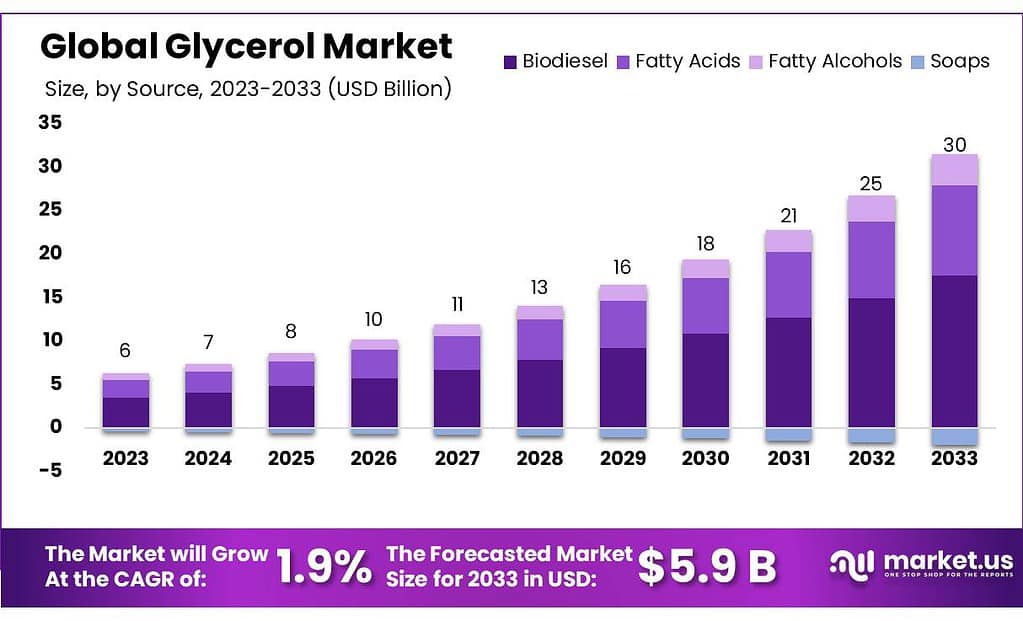
- Market Growth Projection: The global glycerol market is expected to reach approximately USD 5.9 billion by 2033, growing from USD 4.9 billion in 2023, with a CAGR of 1.9% during the forecast period.
- Type Analysis: Refined Segment Dominance: Refined glycerol accounted for 78.0% of total revenue in 2023. Its versatile properties make it a sought-after ingredient in personal and home-care products.
- Source Analysis: Biodiesel Leading Source: Biodiesel held a 59.5% market share in 2023, driven by the rising demand for renewable energy sources globally.
Glycerol Statistics
- The usual production rate is 10% of glycerine per unit of biodiesel. What comes out of the transesterification process is so-called, crude glycerine with 40-90% of glycerine content.
- This by-product is then refined to increase the content of glycerine to 99.5% or 99.7%.
- Today, around 66% of the world’s glycerine supply comes from biodiesel production.
- Typically, the by-product of the waste-based biodiesel production has lower quality with glycerol content between 60-75%. However, today, there is several UCOME and TME plants whose by-product has 80% glycerol content.
- It is estimated that the current worldwide production of glycerine is 2.9 million tons per year.
- In 2015 in Europe, around 810,000 tons of glycerin was produced from veg oils and around 150,000 tons of glycerine came from the UCOME and waste fatty acid biodiesel production.
- More than 55% of the world’s demand for crude glycerine comes from two regions: Europe and South-East Asia.
- The biodiesel production for 2008 in EU27 and USA was over 7.7 and 2.3 million metric tons, respectively. That is, more than 1.0 million metric tons of glycerol was produced as a by-product.
- Currently, disposal of surplus glycerol is done by incineration. This has resulted in a market surplus of crude glycerol typically containing 20% water and esterification catalyst residues.
- According to reports, glycerol production will reach 41.9 billion L by 2020 along with developments in the biodiesel industry
- Neuberg fermentation increased glycerol synthesis, reaching conversion efficiencies ranging from 23% to 28%.
- In 2022, the distribution of downstream glycerin in East China accounted for 69% of the country’s total, and most downstream epichlorohydrin and polyether industry devices were located in East China.
- China’s glycerin supply in 2022 decreased by 331,200 MT from 2021.
- China’s glycerin supply in 2023 is forecast to increase as compared to that of 2022, with an estimated supply of 600,000 MT, an increase of 4,000 MT compared to 2022.
- Approximately 950,000 tons per year are produced in the United States and Europe; 350,000 tons of glycerol were produced per year in the U.S. alone from 2000 to 2004.
- The EU directive 2003/30/EC set a requirement that 5.75% of petroleum fuels were to be replaced with biofuel sources across all member states by 2010.
- High-purity glycerol (greater than 99.5%) is obtained by multi-step distillation; a vacuum chamber is necessary due to its high boiling point (290 °C).
- The minimum freezing point temperature is about −38 °C (−36 °F) corresponding to 70% glycerol in water.
- Glycerol has very low toxicity when ingested; its LD50 oral dose for rats is 12600 mg/kg and 8700 mg/kg for mice.
Emerging Trends
- Increased Use of Biofuels: One of the most significant emerging trends is glycerol’s role as a byproduct in biodiesel production. As global demand for biodiesel grows due to environmental regulations and the shift toward renewable energy, glycerol production has surged. Glycerol’s renewable and biodegradable nature makes it a favorable option for sustainable practices in the energy sector. The biodiesel sector contributes to over 60% of the global glycerol supply, fueling its availability.
- Bioplastics and Green Chemicals: Glycerol is increasingly being utilized in the production of bio-based polymers and other green chemicals. These applications align with the growing consumer and industrial demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. Innovations in biotechnology have made it possible to convert glycerol into valuable bioproducts like biodegradable plastics, used in packaging, agriculture, and more.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care Applications: The personal care and cosmetics industry is a major driver of glycerol demand due to its moisturizing, lubricating, and emollient properties. Glycerol is used extensively in skincare, haircare, and personal hygiene products. The shift toward natural and organic ingredients in beauty products has further boosted the adoption of glycerol in formulations.
- Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Growth: Glycerol’s non-toxic and non-allergenic properties make it valuable in pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. It is used as a solvent, humectant, and preservative in products such as cough syrups, mouthwashes, and toothpaste. This trend is expected to accelerate as healthcare awareness and nutraceutical consumption increase, particularly in emerging markets.
- Environmental Focus and Waste Utilization: Innovations in refining technology are allowing more efficient purification of crude glycerol, which is often considered a waste product. Companies are exploring new methods to utilize crude glycerol in producing high-value products, such as biofuels and fertilizers, minimizing waste and contributing to circular economy efforts.
Use Cases
- Pharmaceuticals: Glycerol is extensively used in the pharmaceutical industry as a solvent, sweetener, and preservative. It is a common ingredient in cough syrups, elixirs, and expectorants due to its ability to retain moisture and improve texture. Additionally, it is used in medical applications such as suppositories and wound care ointments, where its humectant properties help keep the skin hydrated. The pharmaceutical market for glycerol continues to grow, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific, where the healthcare industry is expanding rapidly. In 2022, the pharmaceutical sector accounted for approximately 10-12% of global glycerol demand.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Glycerol is used as a sweetener, humectant, and preservative in various food products, including baked goods, processed meats, and beverages. It helps to maintain moisture levels, extend shelf life, and improve texture. In the beverage industry, glycerol is used as a thickener and stabilizer. Glycerol’s use in this industry is particularly growing due to its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a safe food additive. The global food and beverage sector consumes around 15-20% of the total glycerol produced.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Glycerol’s moisturizing and emollient properties make it a key ingredient in skincare products, lotions, shampoos, and soaps. It helps to smooth the skin, maintain hydration, and improve the texture of formulations. The cosmetic industry’s demand for glycerol is driven by the growing consumer preference for natural and organic products, with glycerol fitting in as a plant-based and environmentally friendly alternative. The personal care sector represents over 30% of global glycerol consumption, and this demand is projected to rise as the global beauty industry grows.
- Biofuels (Biodiesel Production): Glycerol is a major byproduct of biodiesel production, with around 10% of the weight of biodiesel converted to crude glycerol. With the expansion of biodiesel as a renewable energy source, the supply of glycerol has increased significantly. This surplus has led to the exploration of new ways to utilize crude glycerol in industries such as biofuels, animal feed, and industrial chemicals. The biodiesel sector is responsible for nearly 60% of global glycerol production, showcasing its importance in renewable energy.
- Chemical Industry: Glycerol is used in the chemical industry for producing various derivatives such as propylene glycol, epichlorohydrin, and other solvents. These chemicals are essential in the production of plastics, resins, and antifreeze. Glycerol’s chemical properties allow it to serve as a feedstock for these high-demand materials. The chemical sector consumes about 10-15% of global glycerol annually.
- Tobacco Industry: Glycerol is also used in the tobacco industry, where it helps maintain moisture in tobacco products, particularly in chewing tobacco and moist snuff. It is used to enhance the texture and ensure a longer shelf life. The application of glycerol in this industry, though relatively smaller in comparison, remains significant for product quality control.
Major Challenges
- Overproduction and Surplus from Biodiesel: A major challenge is the overproduction of glycerol as a byproduct of biodiesel manufacturing. With the expansion of biodiesel production, particularly in Europe and Asia, there is an excess supply of crude glycerol. This surplus leads to lower prices, which negatively impacts profitability for producers. As biodiesel output grows, the glycerol market faces supply-demand imbalances, making it difficult for companies to stabilize prices.
- Refining Costs and Technical Barriers: Converting crude glycerol into high-purity glycerol suitable for industrial and pharmaceutical use is a complex and costly process. Crude glycerol often contains impurities like methanol and fatty acids, which require advanced purification techniques. Smaller producers, especially in developing regions, struggle to invest in the necessary refining infrastructure, limiting their market participation.
- Competition from Alternative Products: Glycerol competes with other synthetic and natural alternatives in industries like personal care, food, and chemicals. Substances such as propylene glycol and other humectants sometimes offer lower costs or more favorable properties, making it harder for glycerol to maintain its market share. The growing interest in synthetic alternatives that can perform similar functions is a notable challenge for the glycerol market.
- Fluctuating Raw Material Prices: The price of glycerol is closely tied to the cost of raw materials such as vegetable oils and animal fats, which are subject to fluctuations due to market dynamics, weather conditions, and geopolitical factors. Price volatility in these raw materials can increase production costs, further squeezing profit margins for glycerol manufacturers.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Expansion in Biofuels and Biodiesel: With the global push toward renewable energy sources, glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, is benefiting from the increasing demand for biodiesel. As countries adopt more stringent environmental policies to reduce carbon emissions, biodiesel production is expected to grow, particularly in Europe and Asia-Pacific. This creates a surplus of glycerol that can be repurposed for industrial use. The biodiesel sector already accounts for over 60% of global glycerol production, and further growth in this sector will likely increase the availability and application of glycerol.
- Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Expansion: The pharmaceutical sector offers significant growth potential for glycerol, which is widely used as a solvent and preservative in various medical formulations. The increasing demand for medicines, especially in emerging markets such as India and China, is expected to drive the use of glycerol in pharmaceutical products. Additionally, as consumers prioritize health and wellness, the nutraceutical industry, which uses glycerol in supplements and health products, is poised for expansion.
- Biodegradable Plastics and Green Chemicals: Glycerol’s role in producing bio-based and biodegradable plastics is an emerging growth area, aligning with the global shift toward sustainability. Industries are increasingly using glycerol to manufacture biodegradable polymers and green chemicals, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This trend is particularly strong in Europe, where environmental regulations promote the adoption of eco-friendly materials.
- Personal Care and Cosmetics: The rise in demand for natural and organic personal care products has fueled glycerol’s use in cosmetics and skincare products. Its moisturizing properties make it a key ingredient in a wide range of beauty products, and the demand for these products continues to grow globally, especially in Asia-Pacific.
Key Player Analysis
In 2023, BASF SE made significant advancements in the glycerol sector, primarily focusing on sustainability and refining capabilities. One key highlight in March 2023 was BASF’s continued expansion of glycerol applications, particularly for bio-based chemicals and biodegradable plastics. This aligns with global trends toward eco-friendly products, especially in Europe. Additionally, in July 2023, BASF opened a food application center in South Africa, aimed at refining glycerol for use in food and beverage industries, enhancing glycerol’s role in food formulations. BASF’s efforts also included improving the efficiency of glycerol production processes at its Ludwigshafen site. By October 2023, BASF had strengthened collaborations with biofuel companies to manage surplus crude glycerol from biodiesel production, making it a sustainable raw material for various industries
In 2023, Cargill made notable strides in the glycerol sector by advancing sustainability initiatives and expanding its vegetable oil-based products. In March 2023, Cargill increased its focus on producing eco-friendly glycerol from plant-based raw materials as part of its broader commitment to sustainability. This aligns with the company’s strategy to replace traditional petroleum-based chemicals with renewable alternatives. By July 2023, Cargill enhanced its refining capacity for glycerol, specifically targeting its use in bioindustrial applications, such as bioplastics and green chemicals. This move not only supports the growing demand for biodegradable products but also helps manage surplus crude glycerol from biodiesel production, further promoting circular economy practices.
In 2023, Procter & Gamble (P&G) expanded its glycerol usage within its personal care and health products segments. In April 2023, P&G increased its focus on using plant-based glycerol in skincare and hygiene products, aligning with the growing consumer demand for natural and sustainable ingredients. This shift toward bio-based raw materials is part of the company’s strategy to enhance product formulations for its brands like Olay and Crest. By June 2023, P&G reported that glycerol, used for its moisturizing properties, was a key ingredient in its growing portfolio of personal care products, contributing to P&G’s 4% organic sales growth in the beauty sector.
In 2023, Oleon NV made notable advancements in its glycerol sector, focusing on expanding production capacity and sustainable practices. In June 2023, Oleon inaugurated its first production facility in Conroe, Texas, marking a significant milestone in the company’s global expansion. This facility, which required over $50 million in investment, initially focused on warehousing and blending, with plans to integrate an esterification unit in 2024. The plant supports Oleon’s glycerol-based solutions for industries such as lubricants and crop protection, aligning with the company’s sustainability goals.
In 2023, KLK OLEO continued to strengthen its position as a major player in the global glycerol sector. In March 2023, the company expanded its glycerine production, focusing on its PALMERA and EDENOR glycerine products, which are used across various industries, including pharmaceuticals and personal care. This growth was part of a broader initiative to meet the increasing global demand for sustainable oleochemicals. KLK OLEO also emphasized sustainability by enhancing their commitment to responsible sourcing and environmental management, as seen with their Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) certification efforts throughout the year.
In 2023, Dow focused on expanding its sustainable glycerol production by launching new bio-based and circular feedstock products, particularly in the propylene glycol (PG) sector. In March 2023, Dow introduced two varieties of sustainable PG solutions, both incorporating bio-circular and recycled feedstocks. These solutions, which include Propylene Glycol CIR and Propylene Glycol REN, are designed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and enhance sustainability. The launch aligns with Dow’s broader goal of promoting circular economies, particularly in sectors such as personal care, food ingredients, and industrial applications.
In 2023, Wilmar International Ltd. made significant advancements in the glycerol sector, particularly through its production of oleochemicals, which include glycerol derived from palm oil. Throughout the year, Wilmar’s glycerol production was closely linked to its broader oleochemical and biodiesel operations. In August 2023, Wilmar reported continued expansion in its biodiesel production, which generates glycerol as a byproduct. This expansion is part of Wilmar’s strategy to leverage its vertically integrated supply chain, from palm oil plantations to refining and downstream chemicals, including glycerol. The company has focused on sustainable practices, with its operations adhering to the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) standards, ensuring environmentally responsible production.
In December 2023, ADM (Archer Daniels Midland) expanded its presence in the glycerol sector by increasing its oilseed crush and glycerin refining capacities in Brazil. ADM added 400,000 metric tons of oilseed crush capacity at facilities in Campo Grande, Porto Franco, and Uberlandia, which boosts its ability to supply renewable feedstocks. Additionally, ADM acquired a controlling stake in Buckminster Química, a Brazilian producer of refined glycerin. This acquisition strengthens ADM’s portfolio by allowing it to meet the growing demand for sustainably sourced, bio-based glycerin across various industries, including food, feed, fuel, and consumer products.
In 2023, Kao Corporation made strategic advancements in its glycerol sector, focusing on sustainable production and innovation in personal care and chemical applications. In August 2023, Kao revised its Mid-term Plan (K27), placing a strong emphasis on sustainability as the core of its business. The company integrated glycerol into various personal care products, leveraging its moisturizing and emollient properties to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly cosmetics and skincare solutions. Kao also implemented structural reforms aimed at improving operational efficiency and profitability across its global supply chain.
In 2023, Emery Oleochemicals continued its focus on sustainability and innovation within the glycerol sector. The company expanded its product offerings with the launch of sustainable polymer additives and enhanced glycerol production capacity, particularly through its involvement in renewable and bio-based chemicals. In July 2023, Emery Oleochemicals’ Cincinnati plant achieved RSPO Mass Balance (MB) Certification, ensuring that its glycerol and other products sourced from palm oil met strict sustainability standards. Additionally, the company showcased new developments in esters technology, which leverages glycerol as a key component, aimed at improving performance in applications such as electric vehicle fluids and 3D printing. These efforts underline Emery’s commitment to sustainability and expanding the applications of glycerol in green chemistry and polymer innovations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the global glycerol market is poised for steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and renewable energy. With the increasing shift toward sustainability, glycerol’s role as a byproduct of biodiesel production and its use in bio-based chemicals and biodegradable plastics further enhances its appeal. However, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and the need for advanced refining techniques remain. Nonetheless, ongoing innovations, coupled with rising demand for eco-friendly and sustainable products, position glycerol as a critical component in the future of green chemistry and industrial applications.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





