Table of Contents
Introduction
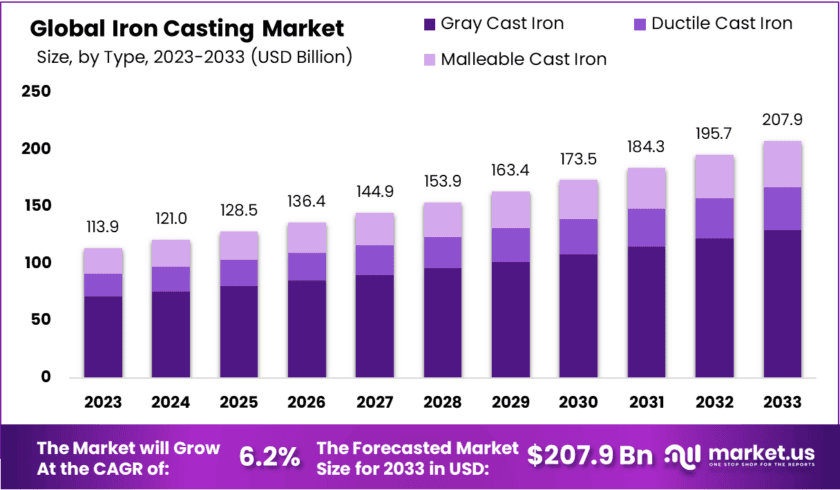
The Global Iron Casting Market size is expected to be worth around USD 207.9 Billion by 2033, From USD 113.9 Billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 6.20% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The Iron Casting Market encompasses the production and distribution of components made from various types of cast iron, such as gray iron, ductile iron, and malleable iron. These castings are utilized in a wide array of industries including automotive, construction, agriculture, power generation, and transportation. The market includes foundries, manufacturing companies, and suppliers of raw materials, offering components like engine blocks, pipes, valves, and other critical parts necessary for machinery and infrastructure.
As a fundamental segment of the broader manufacturing and heavy industries landscape, the Iron Casting Market is both mature and essential, providing foundational components to several sectors worldwide.
The Iron Casting Market. Firstly, rising industrialization and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies, are increasing demand for heavy machinery and equipment that rely heavily on iron cast components. The automotive industry remains a significant consumer of iron castings, with advancements in electric vehicles (EVs) also demanding lightweight yet durable components, favoring ductile iron usage.
Technological innovations in casting techniques, such as automation and advanced simulation software, are enhancing productivity and quality, further boosting market growth. Additionally, the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure such as wind and solar power requires substantial quantities of iron cast parts, creating a steady growth trajectory for the industry.
Iron casting products is expected to remain strong due to ongoing urbanization and industrial development projects globally. The construction sector, particularly in rapidly growing regions like Asia-Pacific and the Middle East, is a significant driver of demand for iron cast pipes, fittings, and other construction components.
Moreover, the transportation industry, encompassing automotive, railways, and aerospace, continues to require a substantial volume of iron casting components for engines, suspension systems, and other mechanical parts. The agricultural sector also contributes to demand growth, as iron castings are critical for manufacturing equipment such as tractors and harvesting machinery. The stability of these sectors, coupled with growth in emerging markets, supports a robust demand environment for the foreseeable future.
Opportunities within the Iron Casting Market are primarily linked to innovation and sustainable practices. The growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency in manufacturing processes presents an avenue for the adoption of environmentally friendly casting techniques, such as using recycled materials or energy-efficient furnace technology. Furthermore, as demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure grows, manufacturers have opportunities to develop specialized casting solutions tailored to these industries’ needs.
Geographical expansion into untapped markets, particularly in Africa and Southeast Asia, also presents growth potential for companies willing to invest in modern foundries and production facilities. By leveraging advanced technology and focusing on developing high-quality, lightweight, and durable products, market players can capture new opportunities and differentiate themselves in an increasingly competitive global market.
Key Takeaways
- The Iron Casting Market is expected to grow significantly from USD 113.9 billion in 2023 to USD 207.9 billion by 2033.This growth reflects a strong CAGR of 6.2% over the forecast period.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) leads the market, holding a 65.4% share, driven by its industrial activities and infrastructure development.
- Gray Cast Iron is the top segment, capturing 62.4% of the market due to its affordability and ease of machining.
- The automotive sector is the largest application area, representing 30.1% of the market. It uses iron castings for parts like engines and chassis.
- The importance of iron castings in the automotive industry highlights their essential role in vehicle construction and performance.
Iron Casting Statistics
- The iron casting industry employs approximately 3.6 million people worldwide, with foundries producing over 80 million tons of castings annually. This production is expected to increase by 4-6% annually, aligning with rising global demand
- The automotive industry is the largest consumer of iron castings, accounting for nearly 30.1% of the global market. This is largely due to the demand for engine blocks, brake components, and other essential automotive parts
- The industrial machinery segment makes up 26% of the market, with the remaining share divided among sectors such as construction (13%), power generation (9%), and railways (4%)
- The carbon content in iron casting ranges from 2% to 4.3%, which is higher than in steel.
- Iron is the fourth most common element in Earth’s crust, making up 35% of its mass, and is also a major part of the Earth’s core.
- The Iron Age (around 1200 BC) marked a shift where iron replaced bronze in tools and weapons.
- Ancient Egyptians used meteorite iron for jewelry as early as 4000 BC, calling it “metal from heaven.”
- The main use of iron is in steel production, a process humans have been using for 4,000 years.
- Iron is a transition metal, and too much can be toxic; 20 mg per kg of body weight is harmful, while 60 mg per kg can be lethal.
- It forms compounds with oxidation states +2 and +3, important for pigments and water purification.
- The Eiffel Tower is made of iron, using about 7,300 tons in its construction.
- 70% of the iron in the human body is in red blood cells.
Facts to Know
- Cast iron is made by melting iron ore into pig iron in a blast furnace.
- Pig iron can be used directly in casting or re-melted with other materials like iron, steel, limestone, and coke.
- Iron casting is made by combining iron with carbon, making it easy to mold.
- Iron is formed in stars during supernovas and spread across space when stars explode.
- Iron can exist in two forms: BCC at low temperatures and FCC at high temperatures, giving it flexibility in construction.
- Iron is vital for health; it helps hemoglobin in blood carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Iron deficiency is common and causes anemia, leading to tiredness and weakness.
- Steel, an iron-carbon alloy, is essential for building skyscrapers due to its strength and flexibility.
- Iron is a key part of car manufacturing, used in engines and frames for durability.
- Iron is added to foods like cereal to combat nutritional deficiencies.
- Iron mining impacts the environment, causing pollution and habitat destruction.
- Innovations in recycling and efficient processing aim to reduce these environmental impacts.
- Many cultures see iron as a symbol of strength; for example, iron horseshoes are believed to bring good luck.
- In Norse mythology, Thor’s hammer, Mjölnir, was made from iron and symbolized power.
- Iron is now being used in renewable energy, such as wind turbines and solar panels.
- Researchers are exploring iron for medical treatments, like cancer therapy and MRIs.
- Iron is the most recycled material, and its quality doesn’t degrade through recycling.
- Iron and oxygen interaction gives blood its red color.
- Mars appears red due to iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
- Iron is the most naturally magnetic element.
- Mars appears red due to iron oxide (rust) in its dust.
- Iron is the second most abundant metal on Earth.
- Meteorites contain iron as their main component.
- Steel production requires iron.
Types of Iron Casting
Iron casting involves several types, each tailored for specific properties and applications. Here’s a concise overview of the main types:
- Gray Iron Casting : The most common type, known for its machinability and vibration damping, used in engine blocks and machinery bases.
- Ductile Iron Casting (Nodular Cast Iron) : Offers high strength and flexibility due to its nodular graphite structure, ideal for automotive parts like crankshafts and gears.
- White Iron Casting : Extremely hard and wear-resistant, used in applications like grinding balls and mill liners, though its brittleness limits structural use.
- Malleable Iron Casting : Produced by heat-treating white iron, it combines strength and ductility, commonly used in pipe fittings and agricultural equipment.
- Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI) Casting : Balances strength, thermal conductivity, and vibration damping, making it suitable for high-performance engine parts and exhaust systems.
- Austenitic Iron Casting (High Alloy Cast Iron) : Alloyed for corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, used in chemical processing and marine environments.
- Alloyed Cast Iron : Enhanced with elements like silicon or chromium for improved hardness and heat resistance, tailored for specialized industrial applications.
Emerging Trends
- Green and Sustainable Practices : Iron casting companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly methods, such as using recycled materials and reducing emissions during production. Advanced filtration and waste management systems are also being integrated to minimize environmental impact and comply with stricter regulations.
- Cold Casting: Cold casting, which involves using resins and metal powders instead of molten iron, is gaining traction due to its lower energy requirements and reduced safety risks. This technique is ideal for smaller, detailed components and offers greater versatility in manufacturing.
- 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing is transforming the iron casting industry by enabling the creation of complex molds and prototypes with precision and speed. This technology allows for rapid iteration, customization, and reduced material wastage, optimizing both cost and production efficiency.
- Automation and Smart Technologies: Automation through robotics and IoT-enabled smart technologies is enhancing efficiency, quality, and safety in iron casting facilities. These advancements allow for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and better process control, driving down costs and improving product consistency.
- Lightweight and High-Performance Alloys: The development of lightweight and high-strength iron alloys is becoming crucial as industries like automotive and aerospace demand materials that improve fuel efficiency without compromising performance. These new alloys are engineered to offer enhanced durability, heat resistance, and corrosion protection.
Top Use Cases for Iron Casting
- Automotive Industry: Iron casting is essential for manufacturing engine blocks, cylinder heads, and brake components due to its excellent strength, thermal conductivity, and cost-efficiency. The automotive sector remains a dominant consumer as demand for durable and heat-resistant components grows.
- Infrastructure and Construction: Iron castings are extensively used in constructing water and sewage pipes, manhole covers, and bridge components. The material’s high compression strength and longevity make it ideal for infrastructure projects, particularly as global governments increase spending on construction and modernization efforts.
- Industrial Machinery: This sector leverages iron castings for producing heavy-duty machinery parts like gears, pumps, and compressors. With iron’s machinability and wear resistance, it supports efficient and long-lasting industrial equipment, crucial for sectors such as mining and manufacturing.
- Power Generation: Ductile iron castings are integral in the wind energy sector and thermal power plants, where components must withstand extreme conditions. The ability of iron castings to maintain reliability even at low temperatures makes them a preferred choice for energy infrastructure applications.
- Railways and Transportation: Rail systems utilize iron castings for critical components such as couplers, brakes, and railway wheels. Growing investments in rail infrastructure modernization particularly in North America and Europe are driving demand for durable iron cast parts essential for safety and efficiency.
Major Challenges
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter emission standards and environmental policies are compelling iron foundries to adopt cleaner technologies and sustainable practices. This requires significant investment in green technologies and recycling processes, increasing operational costs.
- Fluctuating Raw Material Costs: The price volatility of key inputs like iron ore and energy, exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions, poses a major risk. This unpredictability can erode margins and create cost management difficulties for foundries, especially smaller ones.
- Labor Shortages and Skill Gaps: The industry struggles with a shortage of skilled labor and an aging workforce, which impacts productivity and the ability to adopt advanced manufacturing technologies. Training new workers and integrating automation are necessary but require time and resources.
- Competition from Alternative Materials: Lightweight and high-strength materials, such as aluminum and composites, are increasingly preferred in sectors like automotive and aerospace. This shift reduces demand for traditional iron castings, pressing the industry to innovate and improve product offerings.
- Rising Energy Costs: High energy consumption in foundries, coupled with increasing energy prices, particularly in regions like Europe, poses a significant financial burden. Efficient energy management and investment in renewable energy sources are crucial but come with high upfront costs.
Top Opportunities
- Automotive Lightweighting: The shift towards lighter vehicles, particularly electric and hybrid models, is boosting demand for advanced iron castings that offer high strength with reduced weight. This trend is essential for improving vehicle efficiency and complying with stricter emission standards
- Infrastructure Development: Investment in global infrastructure, particularly in North America and Asia-Pacific, is accelerating the demand for iron castings in construction machinery, pipes, and valves. These cast components are essential for projects related to urbanization and industrial expansion
- Green Manufacturing Initiatives: The industry is increasingly focusing on sustainable production techniques. Emphasizing the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient processes presents significant growth potential, as stakeholders look to minimize carbon footprints and meet regulatory compliance
- Machinery & Equipment Modernization: Industries such as agriculture, mining, and industrial manufacturing are modernizing their equipment, requiring robust and durable iron cast components. This trend is particularly prominent in emerging markets looking to enhance productivity and equipment longevity
- Adoption of Industry 4.0 Technologies: The integration of advanced manufacturing technologies like automation, AI, and real-time monitoring systems is transforming the iron casting process. Companies investing in these technologies benefit from increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved precision, opening opportunities for premium, high-performance cast product
Recent Developments
- In February 2024 – Tata Steel: Tata Steel is restructuring and merging its subsidiaries to boost iron casting capacity and streamline operations. The strategy aims for a more integrated supply chain, reflecting the trend toward vertical integration for optimized production and distribution.
- In 2023, Nippon Steel Corporation (NSC): NSC announced it will acquire U.S. Steel for $55.00 per share, valuing the deal at $14.9 billion. The acquisition, approved by both companies’ boards, offers a 40% premium over U.S. Steel’s stock price as of December 15, 2023.
- In December 2023, Monomoy Capital Partners: Monomoy Capital Partners acquired Waupaca Foundry, North America’s top iron casting supplier. The acquisition, closing in early 2024, aims to expand operations across diverse sectors, focusing on enhancing efficiency and market presence.
Conclusion
The global iron casting market is projected to see sustained growth due to robust demand from industries such as automotive, industrial machinery, and construction. Despite challenges posed by fluctuating raw material prices and environmental concerns, the market benefits significantly from technological advancements in casting techniques, which enhance efficiency and product quality. Additionally, the increasing adoption of recycled materials is expected to support sustainability efforts within the industry, potentially opening new avenues for growth. As regions like Asia Pacific continue to industrialize, their contribution to global demand for iron castings is anticipated to rise, reinforcing the market’s expansion in the foreseeable future.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





