Table of Contents
Introduction
The global Nanomaterials Market, valued at USD 12.4 billion in 2022, is expected to reach USD 45.6 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.9% from 2022 to 2032. This significant growth can be attributed to several factors, including advancements in technology, increasing demand in various industries, and substantial investments in research and development.
Nanomaterials, characterized by their nanoscale size and unique physical and chemical properties, are increasingly used across multiple industries such as healthcare, electronics, energy, and automotive. In the medical sector, nanomaterials are pivotal for targeted drug delivery, cancer treatment, and diagnostic tools. For instance, the U.S. National Institute of Health invested approximately USD 445 million in nanomedicine research, underscoring the burgeoning opportunities in healthcare.
The electronics and energy sectors also significantly contribute to the market growth. In electronics, nanomaterials enhance the performance and efficiency of devices. The energy sector benefits from nanomaterials through their application in solar cells and energy storage systems. The growing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in the aerospace industry further propels market growth, as these materials improve fuel efficiency and performance.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region dominates the market, accounting for the largest share in 2023 due to its booming electronics and automotive industries. China and India are key contributors, with China witnessing substantial investments in nanotechnology research and applications across biomedical, electronics, and wastewater treatment sectors. North America follows closely, driven by significant research initiatives and technological advancements in the U.S..
However, the market faces several challenges. High production costs and complex manufacturing processes are significant barriers. Environmental and health concerns related to nanomaterials’ impact also pose regulatory challenges. Public perception and ethical considerations further complicate market dynamics. For example, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has highlighted potential health risks associated with certain nanomaterials, necessitating stringent regulations and safety standards.
Despite these challenges, the market holds immense potential. Continuous innovation and the development of green nanotechnology present new opportunities. Companies are focusing on improving production techniques and reducing costs to overcome scalability issues. Moreover, government policies promoting sustainable and advanced materials are likely to support market growth.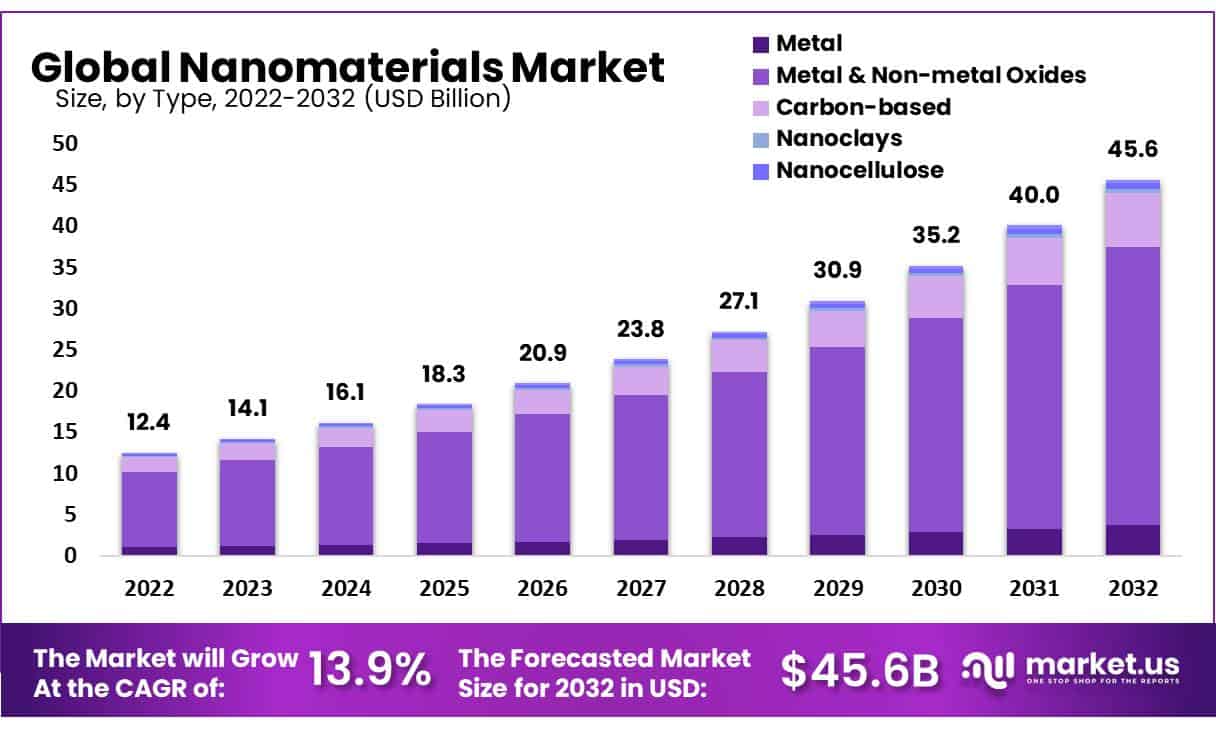
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: It is expected that the global nanomaterials market will experience a compound annual growth rate of 13.9% between 2023-2032.
- Type Analysis: Of these segments, metal & non-metal oxides were found to be most profitable within the global nanomaterials market in 2022, holding onto an impressive market share of 73.88% while also projected for an attractive compound annual compounding growth rate of 14.9%.
- End User Analysis: Of these end-use applications, medical was the most lucrative one and held a 30.2% market share as of 2022.
Nanomaterials Facts And Statistics
- This technological domain delves into investigating structures and molecules ranging between 1 and 100 nanometers.
- Within this realm, nanomaterials constitute a category of substances characterized by a particle size of under 100 nm in at least one dimension.
- Nanoparticles create structures that are 100 nm or smaller.
- Modern solar cells typically encounter a surface-level sunlight reflection ranging from 2% to 10%, causing potential power loss of up to 10% due to direct optical inefficiencies.
- Nanoemulsions, colloidal dispersions falling within the size range of 50 to 1000 nm,
- Projections indicate that the global annual expenditure on chronic wound care products is expected to surpass 22 billion dollars by the year 2024.
- Generally, nanomaterials are defined as materials with dimensions ranging from 1 to 1000 nm in at least one direction, but they are typically characterized by a diameter falling within the 1 to 100 nm range
- The textile industry is one of the most water and chemical-intensive industries worldwide because
200-400 liters of water are needed to produce 1 kg of textile fabric in textile factories. - the loss of dye in the effluents of the textile industry can reach up to 75%.
- By 2023, it has been predicted that over 700 nanosatellites could be launched worldwide, up from just 88, 10 years earlier.
- Nanoclusters comprise up to 100–150 atoms (<1 nm), while nanoparticles generally refer to larger structures between 1 and 100 nm.
- The Cambridge structure database (CSD) contains experimentally observed and computationally verified small-molecule organic and metal-organic structures that have been growing steadily since 1965 and now have over 1 M structures, with over 50%
- Yan et al. have made efforts to normalize the annotations of nanoparticle databases by creating a procedure to generate 2142 nano descriptors for each nanomaterial in their open database, Pubvinas.
- The agglomeration and resulting sedimentation of nanomaterials are probed by determining the remaining particle concentration in the top 0.5-1 cm layer of dispersion.
- The aliquots of sonicated stock dispersion (paragraphs 31-34) are transferred into 50 ml
polypropylene tubes and diluted with ultrapure water to a volume of 20 ml. - The electrolyte and the pH adjustment, the volume of the samples is adjusted to 40 ml
Emerging Trends
Carbon Nanomaterials: There is significant progress in the development of carbon-based nanomaterials, such as graphene, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and carbon dots. These materials are known for their exceptional mechanical strength, chemical stability, and electrical conductivity. They find applications in electronics, tissue engineering, and the development of reinforced composite materials. For instance, graphene is being used to enhance the performance of batteries and capacitors due to its high surface area and conductivity.
Green Nanotechnology: The shift towards environmentally friendly manufacturing processes is becoming more pronounced. Green nanotechnology focuses on the fabrication of nanomaterials using plant-based or biobased raw materials. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact but also supports the development of biodegradable nanomaterials. Applications include the bioremediation of pollutants and the creation of sustainable energy solutions.
Medical and Healthcare Applications: Nanomaterials are revolutionizing the medical field through their use in drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic applications. Nanoparticles enable precise targeting of diseased cells, which improves the efficacy of treatments while minimizing side effects. This is particularly evident in cancer treatment, where nanoparticles are used for targeted drug delivery and advanced imaging techniques.
Semiconductor Nanodevices: Advances in miniaturization are driving the development of nanoscale semiconductor devices and nanorobotics. These devices are critical for high-performance computing, electronic sensing, and autonomous systems. For example, quantum dots are being used to enhance the resolution and contrast in imaging devices, which is crucial for medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring.
Environmental Applications: Nanomaterials are increasingly used for environmental protection and sustainability. They play a vital role in water treatment processes, air purification, and soil remediation. Nanocatalysts, for instance, are employed to degrade pollutants and transform hazardous substances into harmless compounds. This trend highlights the potential of nanomaterials in addressing global environmental challenges.
Energy Storage and Conversion: Innovations in nanomaterials are driving advancements in energy storage and conversion technologies. Nanomaterials are being used to improve the efficiency of batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. Their high surface area and conductivity enhance the storage capacity and charge/discharge rates of these devices, making them more efficient and reliable for energy applications.
Use Cases
Healthcare: Diagnostics and Treatment: Nanomaterials significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficacy. For example, nanoparticles are used in developing biomarkers that improve early disease detection. Poly-Dtech, a French startup, uses nano-molecule biomarkers in medical imaging, enhancing detection efficiency in assays and diagnostics. The global market for nanomaterials in healthcare is growing rapidly, with applications in cancer treatment, drug delivery systems, and medical imaging technologies.
Wound Care and Implants: Nanomaterials improve the performance of wound dressings and surgical implants. These materials enhance the healing process and reduce infection rates, benefiting millions of patients worldwide.
High-Performance Components: Nanoscale semiconductor devices and nanorobotics are revolutionizing the electronics industry. Startups like QDI Systems fabricate quantum dots for high-resolution imaging and optoelectronic devices, crucial for advancing consumer electronics and medical diagnostics. The miniaturization enabled by nanomaterials supports the development of ultra-dense memory technologies and compact microprocessors.
Nanobots: Used for remote monitoring and servicing in hazardous environments, these tiny robots enhance safety and efficiency in industrial applications.
Water and Waste Management: Nanotechnology is crucial for sustainable water filtration and pollution remediation. Aavalor GreenTech, a UK-based startup, uses graphene-based nanotechnology for efficient water purification, removing heavy metals and contaminants without requiring energy. This technology is vital for industrial waste purification and desalination, reducing environmental impact.
Carbon Capture: Nanomaterials are used in carbon capture solutions to reduce emissions from industries and households, helping combat climate change.
Improved Energy Devices: Nanomaterials are essential for advancing batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. They enhance energy storage capacity and efficiency. For instance, nanomaterials are used in the development of next-generation battery technologies, contributing to the growing renewable energy sector.
Enhanced Materials: Nanomaterials improve the strength, durability, and other properties of construction materials. Concrene, a UK startup, integrates graphene into concrete, enhancing its mechanical properties and sustainability. This innovation supports the construction industry’s shift towards more robust and environmentally friendly materials.
Industrial Additives: Companies like Nemo Nanomaterials develop nanocarbon-based additives to enhance the properties of industrial materials, making them stronger, lighter, and more conductive. These additives are crucial for manufacturing high-performance products, from bike frames to bulletproof vests.
Major Challenges
Health and Environmental Risks: One of the primary concerns with nanomaterials is their potential impact on human health and the environment. Studies have shown that certain nanomaterials can be toxic if inhaled, ingested, or if they come into contact with skin. For example, titanium dioxide nanoparticles, commonly used in various products, have been linked to potential health risks, such as respiratory issues and cancer when inhaled in significant amounts. The long-term environmental impact of nanomaterials, especially their persistence and accumulation in ecosystems, remains unclear and requires further research.
Regulatory Challenges: The rapid development of nanotechnology has outpaced regulatory frameworks, leading to gaps in safety standards and guidelines. Regulatory bodies like the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and national agencies are working to establish guidelines, but the diversity and complexity of nanomaterials make standardization difficult. This lack of clear regulations can hinder market growth and create uncertainty for manufacturers and consumers alike.
High Production Costs: The production of nanomaterials often involves sophisticated and expensive techniques, such as chemical vapor deposition and molecular beam epitaxy. These high production costs can limit the widespread adoption of nanomaterials, particularly in cost-sensitive industries. For instance, the production of high-quality carbon nanotubes and graphene remains expensive, which restricts their use to high-value applications.
Scalability Issues: Scaling up the production of nanomaterials from laboratory settings to industrial levels poses significant challenges. Maintaining the quality and uniformity of nanomaterials at large scales is difficult and can lead to inconsistencies in performance. This issue is particularly pertinent in applications requiring precise material properties, such as in electronics and pharmaceuticals.
Public Perception and Ethical Concerns: There is a growing public concern regarding the ethical implications and potential risks of nanotechnology. Misinformation and lack of awareness about the benefits and safety measures associated with nanomaterials can lead to public resistance and hinder technological adoption. Ethical issues, including privacy concerns related to nano-surveillance and the potential for misuse in military applications, also need to be addressed.
Market Growth Opportunities
Healthcare and Medicine: Nanomaterials are revolutionizing healthcare through enhanced drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic applications. Nanoparticles can deliver drugs precisely to targeted cells, improving treatment efficacy and reducing side effects. For instance, cancer treatments using nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems are more effective and less toxic than traditional methods. The global nanomedicine market is expected to grow significantly, driven by advancements in nanotechnology and increasing investments in healthcare.
Electronics and Semiconductors: The miniaturization trend in electronics benefits greatly from nanomaterials. Nanoscale semiconductor devices, such as quantum dots and nanowires, enhance the performance and energy efficiency of electronic devices. These materials are essential for developing next-generation transistors, memory devices, and displays. With the ongoing demand for smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic devices, the nanomaterials market in the electronics sector is poised for substantial growth.
Energy Storage and Conversion: Nanomaterials are critical for advancing energy storage solutions, such as batteries and supercapacitors, and energy conversion devices, like solar cells and fuel cells. Their high surface area and conductivity improve the efficiency and capacity of these devices. For example, incorporating graphene into battery electrodes significantly enhances their performance. The push for renewable energy and the need for efficient energy storage solutions create a robust market opportunity for nanomaterials.
Environmental Applications: Nanomaterials play a crucial role in environmental protection and sustainability. They are used in water purification, air filtration, and pollution remediation. For instance, nanomaterials can remove heavy metals and organic pollutants from water, making it safe for consumption. The growing focus on environmental sustainability and the need for advanced pollution control technologies drive the demand for nanomaterials in environmental applications.
Automotive and Aerospace: The automotive and aerospace industries benefit from nanomaterials through lightweight and high-strength materials that enhance fuel efficiency and performance. Nanocomposites and carbon nanotubes are used to manufacture lighter and stronger components, reducing the overall weight of vehicles and aircraft. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also reduces emissions. The increasing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and enhancing vehicle performance presents significant growth opportunities for nanomaterials in these sectors.
Recent Developments
American Elements is a significant player in the nanomaterials sector, offering a wide range of high-purity metals, chemicals, and nanoparticles. In 2023, the company expanded its product line and production capabilities, focusing on various industries such as aerospace, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. Monthly data from 2023 indicates consistent growth and innovation. For example, in January, American Elements introduced new graphene-based materials for advanced battery applications, enhancing energy storage efficiency. In March, the company expanded its titanium dioxide nanoparticle production, addressing the increasing demand in the cosmetics and coatings industries. By June, American Elements had scaled up the production of quantum dots for high-resolution imaging devices, reflecting the growing market for advanced semiconductor materials. Throughout the year, the company maintained a robust research and development pipeline, driving advancements in nanotechnology applications.
ACS Material LLC, a leading provider in the nanomaterials sector, has shown significant advancements and market activities throughout 2023 and 2024. In January 2023, the company expanded its graphene product line, introducing new high-purity graphene nanoplatelets aimed at enhancing the performance of electronic devices and energy storage systems. By March, ACS Material had scaled up the production of silver nanowires, which are critical for flexible and transparent conductive films used in touch screens and solar cells. In June, the company launched a series of mesoporous silica materials, such as SBA-15, which have applications in drug delivery and environmental remediation. Throughout the year, ACS Material has maintained a strong focus on innovation and customer-specific solutions, collaborating closely with research institutions and industry partners to develop tailored nanomaterial products.
Arkema has made significant strides throughout 2023 and 2024. In January 2023, Arkema focused on enhancing its portfolio of advanced materials by expanding production capacities for high-performance polymers and specialty adhesives. By March, the company had ramped up the development and commercialization of new nanomaterials, particularly in the field of fluorochemicals and specialty acrylates, which are crucial for various industrial applications. In June 2023, Arkema announced the acquisition of PI Advanced Materials, enhancing its capabilities in high-performance polymers and marking a strategic step in its growth plan. The company continued to invest in sustainable innovations, aiming for a substantial increase in its EBITDA margins by the second half of 2024, supported by major industrial projects in Asia and the U.S. Arkema’s focus on sustainable solutions and advanced materials is expected to drive its sales growth and maintain strong financial performance in the upcoming years.
Cabot Corporation has been actively involved in the nanomaterials sector, showcasing significant advancements and developments throughout 2023 and 2024. In January 2023, Cabot introduced new high-performance carbon nanostructures to enhance the conductivity and mechanical properties of various materials. By March, the company had scaled up its production capabilities for these nanomaterials, addressing the growing demand in electronics and energy storage applications. In June 2023, Cabot launched its EVOLVE® Sustainable Solutions platform, focusing on developing sustainable and high-performance reinforcing carbons. This initiative aligns with Cabot’s commitment to achieving net zero emissions by 2050. Moving into 2024, Cabot continued to expand its nanomaterials portfolio with innovations aimed at improving the efficiency and sustainability of industrial processes. The company’s strategic focus on sustainability and performance materials has driven robust financial results and positioned it as a leader in the nanomaterials market.
Conclusion
The nanomaterials market is poised for significant growth driven by their unique properties and wide-ranging applications across various industries. This growth is fueled by increasing demand in sectors such as healthcare, electronics, energy, and construction. Moreover, the rise in environmental regulations and sustainable practices has led to a surge in the use of nanomaterials in renewable energy and pollution control technologies. The ongoing research and development activities, along with strategic partnerships and investments by key players like Cabot Corporation and Arkema, are set to further enhance the market landscape, making nanomaterials a cornerstone of future technological innovations.




