Table of Contents
Introduction
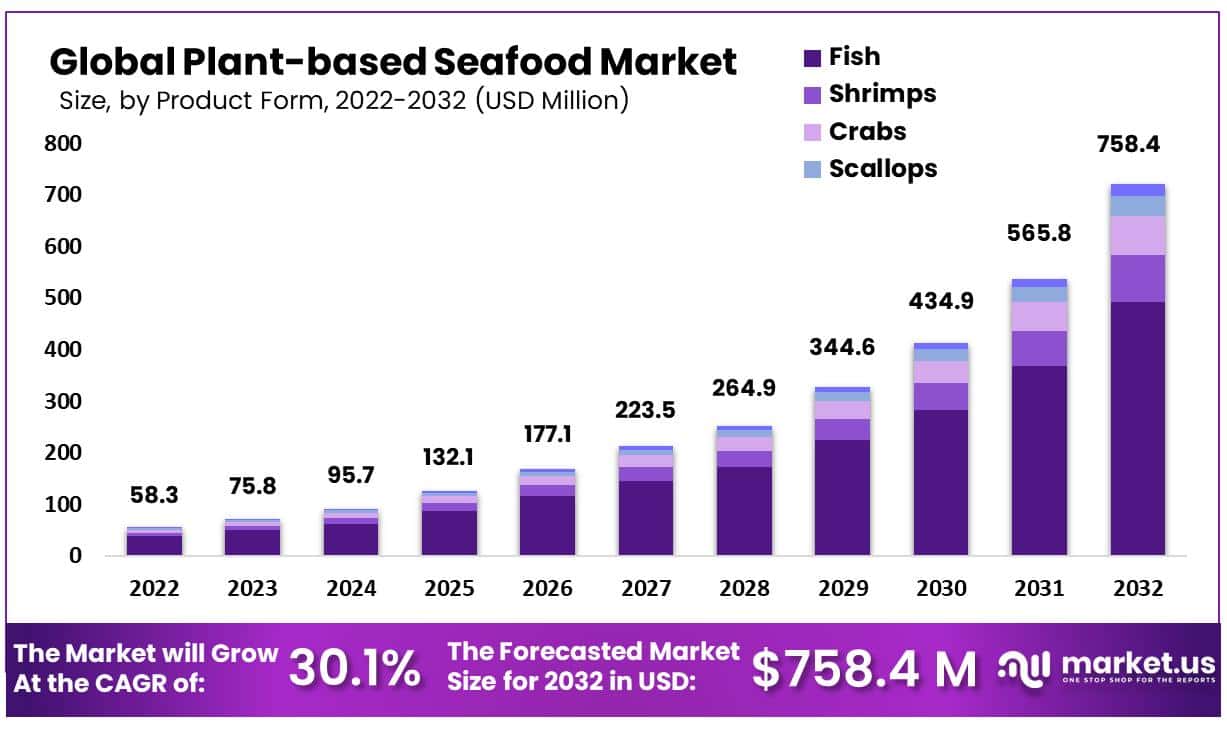
The global plant-based seafood market has experienced rapid growth, valued at USD 58.3 million in 2022, and is projected to reach USD 758.4 million by 2032, growing at an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.1%. This growth is driven by several factors, including increasing consumer awareness of health benefits, environmental concerns, and the demand for sustainable alternatives to conventional seafood. These factors are influencing both product development and market expansion globally.
A key driver of this market’s growth is the rising popularity of veganism and the shift towards plant-based diets, driven by health and environmental concerns. Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the negative impacts of traditional seafood consumption, such as overfishing and pollution, including mercury contamination in fish. As a result, plant-based seafood offers a more sustainable and healthier alternative, meeting the dietary needs of those seeking to reduce their intake of animal-based products. Moreover, innovations in food technology have enabled the production of plant-based seafood that closely mimics the taste, texture, and appearance of conventional seafood, which is appealing to a broader range of consumers, including flexitarians.
However, challenges remain in the plant-based seafood market. Limited product variety and consumer acceptance pose significant barriers to growth. Many consumers still prefer traditional seafood, and the availability of plant-based alternatives is not widespread in all regions. Additionally, higher production costs contribute to the relatively high price of plant-based seafood, making it less accessible to some consumers. Despite these challenges, companies are heavily investing in research and development to create innovative products that cater to varying consumer preferences.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market due to strong consumer demand for ethical, sustainable food options and the presence of key market players. In contrast, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, fueled by the large population and rising demand for plant-based protein sources. Product launches, such as plant-based shrimp and fish alternatives, are increasingly popular in these regions.
Garden Protein International, Inc. Product Innovation Garden Protein, under its Gardein brand, has expanded its portfolio of plant-based seafood alternatives. It offers fishless fillets and crabless cakes to meet consumer demand for environmentally friendly and healthy seafood alternatives. The company has also focused on expanding its distribution channels across North America and Europe.
Good Catch recently launched a new line of plant-based breaded seafood products, including fish sticks, fish fillets, and crab cakes. These products, made from a proprietary blend of six legumes, aim to replicate traditional seafood while offering a sustainable alternative. Each product contains significant protein, with crab cakes offering 15g of protein per serving. Good Catch partnered with Bumble Bee Foods in a joint venture to bring plant-based seafood to a broader market. The company has also secured $26.35 million in funding to further expand its food service reach, adding products like plant-based tuna to Veggie Grill locations and Whole Foods prepared food sections.
New Wave Foods, a key player in the plant-based shrimp segment, received significant investment from Tyson Foods. This funding has allowed the company to scale its production and distribution, aiming to provide a sustainable alternative to traditional shrimp. New Wave Foods’ focus on partnerships with major food service providers helps them gain traction in commercial settings.
Sophie’s Kitchen has expanded its distribution in the U.S., launching its vegan crab cakes and breaded shrimp at 400 Walmart stores. These gluten-free and soy-free products are designed to cater to both vegans and flexitarians, aiming to meet growing consumer interest in sustainable seafood alternatives. The company has focused on making its products more accessible to mainstream consumers. Sophie’s Kitchen also raised $5.6 million to support its expansion plans, enabling the company to scale production and innovate further in the plant-based seafood space
Statistics
- Younger (25-44), higher income (MHI of INR 50,000+), well-educated (graduates and above) people, living in urban areas and omnivores are the early adopters for plant-based meat in India.
- This cohort has a higher intent to purchase plant-based meats regularly (73% of them) and is willing to pay a price premium for
plant-based meat over conventional meat (53% of them). - 85% of early adopters say they have consumed seafood in the last 12 months and 47% are willing to accept/try plant-based. options for seafood.
- Seafood has the highest market penetration after poultry among the early adopters.
- 78% of the early adopters have consumed seafood in its conventional form in the last 3 months and 63% have consumed seafood in the last week.
- 14 times that early adopters consume conventional meat in a week, seafood is consumed about 2.7 times a week.
- Lunch and dinner are the key parts of the day for consumption, accounting for 90% of the occasions where seafood is consumed.
- Seafood has a relatively higher proportion of early adopters consuming it only at home (30% vs 21% for poultry) or cooking mostly at home (68% vs 60% for poultry).
- Fish flesh’s main constituents are water (70–80%), proteins (15–20%) and lipids (2–5%). Carbohydrates, minerals, and vitamins are also present, though in smaller concentrations, and make up about 2% of the flesh mass.
- The most abundant protein in the myocommata connective tissue is collagen, which comprises 3–10% of the proteins, and has a major role in maintaining the fillet structure and muscle cohesiveness.
- In 2018, global seafood production reached a level of 179 million metric tons (MT), 156 MT of which went towards human consumption. This amounts to an average consumption of 20.5 kg per capita, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
- Schnieder claims their meat alternative products produce 70-80% less carbon emissions compared with their meat and dairy equivalents.
- European Union, salmon is the second most eaten fish by weight, with the 2.36kg that each person consumed, on average, in 2019 second only to tuna. Most, 81%, of the salmon consumed in the EU that year was farmed.
- From the start of 2021 to March 2023, the price of a kilo of fresh Norwegian salmon jumped by 137%. The price increased by 33% over the first nine weeks of 2023 alone.
- Each year, over 300,000 whales and dolphins are killed as a result of bycatch
- Scientists predict that 90% of the world’s coral reefs will die by 2050
- U.S. retail sales of plant-based foods have grown 11 percent in the past year, bringing the total plant-based market value to $4.5 billion.
- The total U.S. retail food market has grown just 2 percent in dollar sales during this same period, showing that plant-based foods are a key driver of growth for retailers nationwide. Since April 2017, total plant-based food sales have increased 31 percent.
- Refrigerated plant-based meat is driving category growth with sales up an impressive 37 percent.
Emerging Trends
- Sustainability Focus: Environmental concerns such as overfishing, ocean pollution, and depletion of marine life are driving the growth of plant-based seafood alternatives. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental impact of traditional seafood, leading to increased interest in sustainable, plant-based options like fish fillets, shrimp, and tuna.
- Ingredient Innovation: Companies are exploring diverse plant-based ingredients like algae, seaweed, legumes, and fungi to replicate the taste and texture of seafood. Algae and seaweed, in particular, are gaining popularity for their nutrient density and ability to mimic the flavors of seafood, while also offering environmental benefits.
- New Product Launches: There has been a surge in the development of plant-based seafood products, including fish sticks, crab cakes, and shrimp alternatives. These products are now more widely available in supermarkets and restaurant chains, helping to meet growing consumer demand for meat-free options.
- Technology and Precision Fermentation: Advances in food technology, such as precision fermentation, are being used to enhance the flavor and texture of plant-based seafood. This technology helps companies create more realistic alternatives, making it easier for consumers to transition from traditional seafood.
- Health and Clean Label Products: Consumers are increasingly looking for plant-based seafood options that are not only sustainable but also healthier. Products with fewer artificial additives, lower fat content, and high nutritional value are gaining popularity as people prioritize health-conscious choices.
- Global Market Expansion: While the U.S. and Europe lead in market growth, regions like Asia and the Middle East are showing rising interest in plant-based seafood, driven by growing populations and shifting consumer preferences towards sustainable diets.
Use Cases
- Restaurants and Foodservice: Plant-based seafood is gaining traction in restaurants and fast-food chains. Companies like Good Catch have partnered with popular food chains to introduce alternatives like plant-based crab cakes, fish fillets, and shrimp in casual dining establishments. These products are increasingly seen on menus, allowing consumers to experience sustainable seafood alternatives while dining out. This helps promote adoption by offering a low-risk trial environment for curious consumers.
- Retail and Supermarkets: Supermarkets are stocking a growing variety of plant-based seafood products. Companies such as OmniFoods and The Plant-Based Seafood Co. have expanded their offerings, making plant-based fish fillets, shrimp, and other seafood alternatives widely available. The retail presence of these products helps meet rising consumer demand for sustainable options. For example, sales of plant-based fish products in the U.S. increased by 42% between 2019 and 2021.
- Sustainability Initiatives: The use of plant-based seafood directly supports environmental sustainability by reducing overfishing and marine ecosystem destruction. Ingredients like seaweed and microalgae, which are used in plant-based seafood formulations, are particularly sustainable due to their low environmental impact. These ingredients not only mimic the taste of real seafood but also contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Consumer Health: Plant-based seafood is becoming a popular choice for health-conscious consumers. Many products are enriched with essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, replicating the nutritional benefits of real seafood without the associated risks of mercury and pollutants found in ocean-caught fish. This makes it an appealing option for consumers looking for healthier, cleaner protein sources.
- Innovation and New Product Development: The plant-based seafood industry continues to see technological advancements. Companies are leveraging new techniques such as precision fermentation and the use of seaweed to create innovative products that replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of seafood. These innovations have led to a wider variety of seafood alternatives, including plant-based versions of tuna, salmon, shrimp, and crab.
Major Challenges
- High Production Costs: Plant-based seafood products often come with a higher price tag compared to their animal-based counterparts. The use of specialized ingredients like algae, seaweed, and pea protein, along with advanced production technologies, increases the overall cost of production. For instance, seaweed and microalgae, though highly sustainable, are still more expensive than traditional plant proteins like soy and peas.
- Limited Consumer Acceptance: While awareness around plant-based alternatives is growing, plant-based seafood still lags in consumer acceptance. Many consumers remain unfamiliar with these products and are hesitant to try them, especially since seafood is a category associated with specific flavors and textures that are hard to replicate. Despite some success in replicating fish-like flavors using ingredients like nori and kombu, many consumers feel that plant-based alternatives do not yet fully match the taste or texture of real seafood.
- Scaling Production and Availability: Plant-based seafood companies are still in the early stages of scaling production. Achieving price parity with traditional seafood remains a significant hurdle due to smaller production scales and supply chain challenges. As companies expand, they will need to overcome production limitations and improve distribution to make plant-based seafood widely accessible.
- Nutritional Parity: Another challenge is achieving the same nutritional value as traditional seafood, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, iodine, and vitamin B12. While some products are fortified with these nutrients, creating a nutritionally equivalent product that is widely accepted by consumers remains a work in progress.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Rising Environmental Awareness: With growing concerns about overfishing, ocean pollution, and marine life depletion, consumers are seeking sustainable alternatives. Plant-based seafood products, which offer a low environmental impact compared to traditional seafood, are well-positioned to capitalize on this demand. Sustainable ingredients like seaweed and algae are increasingly popular due to their minimal environmental footprint.
- Health-Conscious Consumers: As more people shift toward healthier diets, plant-based seafood offers a cholesterol-free, low-fat alternative to traditional seafood, while providing essential nutrients like omega-3s. These health benefits make plant-based seafood an attractive option for consumers looking for clean, nutritious protein sources. Products fortified with vitamins and minerals to match the nutritional profile of conventional seafood are becoming more common.
- Technological Innovations: Advances in food technology, such as precision fermentation and the use of algae and seaweed, are enhancing the taste and texture of plant-based seafood. These innovations are improving product quality and making alternatives more appealing to consumers. With ongoing improvements, plant-based seafood is expected to replicate the taste and texture of traditional seafood more accurately.
- Expansion into Global Markets: While the U.S. and Europe are leading the way, there is significant potential for growth in regions like Asia and the Middle East, where seafood consumption is high. Companies are beginning to introduce plant-based seafood into these markets, driven by local demand for sustainable food solutions
Key Player Analysis
In 2023, Good Catch continued to expand its innovative plant-based seafood offerings, focusing on sustainable and ocean-friendly products. In May 2023, the company launched a new line of breaded plant-based seafood products, including fish sticks, fish fillets, and crab cakes. These products are made from a proprietary six-legume blend, mimicking the texture and flavor of traditional seafood while offering a sustainable alternative to overfishing and marine pollution. Additionally, Good Catch secured key partnerships with major retailers such as Sprouts Farmers Market, expanding the availability of its products across the U.S.
In 2023, New Wave Foods continued to make strides in the plant-based seafood sector, focusing on plant-based shrimp as its flagship product. Made from sustainable seaweed and plant proteins, New Wave Foods is targeting the $9 billion global shrimp market, as shrimp is the most consumed seafood in the U.S., with 1.5 billion pounds eaten annually. The company raised $18 million in Series A funding in 2021, with backing from Tyson Ventures and other investors. This funding allowed them to expand production and introduce their plant-based shrimp to restaurants and food service operations across the U.S., with plans to roll out additional products such as plant-based lobster, scallops, and crab.
In 2023 and 2024, Sophie’s Kitchen has continued to expand its presence in the plant-based seafood market. The company has focused on innovative products like vegan crab cakes and breaded shrimp, which are available in major retailers such as Walmart and Whole Foods. These products are gluten-free, soy-free, and non-GMO, catering to health-conscious consumers.
Ocean Hugger Foods, known for its innovative plant-based seafood alternatives, made a strong comeback in 2023 after pausing operations during the pandemic. In March 2021, the company entered a joint venture with Nove Foods, a subsidiary of Thailand-based NRF, to relaunch its products globally. Ocean Hugger’s flagship product, Ahimi, a tomato-based alternative to raw tuna, and Unami, an eggplant-based eel alternative, have gained significant attention in the food service sector. In 2023, Ocean Hugger expanded its portfolio and focused on scaling production to meet increasing demand in North America, Europe, and Asia, aiming to disrupt the seafood industry further.
In 2023, Ocean’s Halo continued to grow its presence in the plant-based seafood sector with a focus on kelp-based products, leveraging sustainable ingredients like seaweed. The company, based in the San Francisco Bay Area, produces a variety of organic, plant-based products, including broths, noodles, and seaweed snacks. Ocean’s Halo has gained traction in retail stores across the U.S. and Europe, promoting products like its kelp-based ramen and broths, which are marketed as eco-friendly and nutritious alternatives.
In 2023 and 2024, SoFine Foods BV continues to be a key player in the plant-based food industry, producing a wide range of plant-based products, including fish alternatives. Based in the Netherlands, the company leverages its extensive experience to produce sustainable and healthy products that meet the growing demand for plant-based proteins across Europe. Their fish alternatives, along with other plant-based meat substitutes, are made using a combination of protein sources such as soy, combined with herbs and spices, ensuring both taste and nutrition. SoFine’s products are available through private labels for retail, food service, and industry sectors, and their modern production facility adheres to the highest quality standards. SoFine Foods also focuses heavily on sustainability, using non-GMO soybeans and reducing its environmental footprint.
In 2023 and 2024, Quorn Foods, a leader in plant-based alternatives, has continued to focus on innovation and expansion in its mycoprotein-based products, including plant-based seafood. Quorn’s use of mycoprotein, derived from fungi, has allowed the company to create seafood-like products that are sustainable and nutritious. As part of its strategy, Quorn expanded its food service partnerships with major chains such as KFC and Greggs, helping to make plant-based seafood options more accessible across Europe.
In 2023 and 2024, PURIS Foods has continued to expand its role in the plant-based protein sector, focusing heavily on pea protein as a sustainable solution for various food products, including plant-based seafood alternatives. PURIS, known for its non-GMO and organic plant-based ingredients, has positioned itself as a key supplier for major plant-based brands. Its recent developments include innovations in protein extraction and processing, like the launch of PURIS 2.0, a cleaner and more neutral-tasting pea protein designed for high-protein beverages and other plant-based applications. Additionally, their efforts to improve texture and flavor make their pea protein a preferred ingredient in products like plant-based shrimp and fish alternatives.
In 2023, The Plant-Based Seafood Co. continued to innovate in the alternative seafood space with its award-winning brand, Mind Blown. The company launched shelf-stable plant-based scallops in March 2023, marking the first product of its kind, which does not require refrigeration. This innovation allows the company to cater to consumers seeking convenient, sustainable seafood alternatives. Additionally, in October 2023, The Plant-Based Seafood Co. announced a partnership with Sam Rust Seafood to distribute its plant-based seafood to a wider market, combining its sustainable approach with traditional seafood distribution methods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the plant-based seafood market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable and healthy food alternatives. Innovations in ingredients, like algae and pea protein, have enabled companies to replicate the taste and texture of traditional seafood, making these alternatives appealing to both vegans and flexitarians. As environmental concerns about overfishing and marine pollution grow, plant-based seafood offers a viable solution for consumers looking to reduce their impact on the planet. Major brands, such as Good Catch and The Plant-Based Seafood Co., are leading the market with new products and partnerships that enhance product availability and quality.




