Table of Contents
Introduction
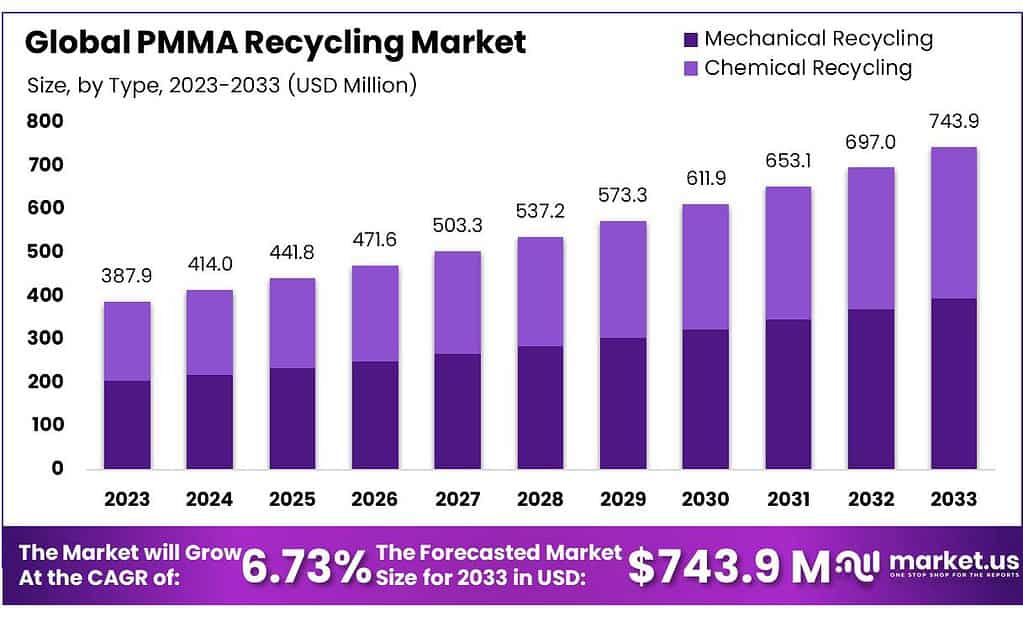
The PMMA Recycling Market, valued at approximately USD 387.86 million in 2023, is poised for significant growth, expected to reach around USD 743.94 million by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.73% during the forecast period. This market encompasses the recycling processes for Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), a versatile thermoplastic commonly used as a durable and lightweight alternative to glass in various applications such as automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
Several factors are driving the growth of the PMMA Recycling Market. Increasing environmental awareness and the push for sustainable practices are major drivers. As global concern over plastic waste grows, regulatory bodies are enforcing stricter recycling mandates, which encourage the adoption of PMMA recycling technologies. For instance, regulations in the European Union prioritize recycling and the circular economy, creating favorable conditions for market expansion.
Technological advancements also play a crucial role. Innovations in both mechanical and chemical recycling processes have improved the efficiency and quality of recycled PMMA, making it a viable material for high-value applications. For example, chemical recycling, which involves breaking down PMMA to its monomers and repolymerizing it, helps maintain the material’s properties, although it is more costly compared to mechanical methods.
However, the market faces significant challenges, particularly related to the technological and economic aspects of recycling PMMA. Mechanical recycling often leads to the degradation of the polymer’s properties, limiting its reuse in high-performance applications. Chemical recycling, while maintaining material integrity, is expensive and complex, which can deter widespread adoption. Additionally, fluctuations in the prices of virgin and recycled PMMA, influenced by global oil prices, impact the market’s profitability.
Recent developments in the market include increased investment in recycling infrastructure and advancements in recycling technologies aimed at overcoming these challenges. Key players in the industry are focusing on enhancing the efficiency of chemical recycling and expanding the applicability of recycled PMMA. These efforts are expected to drive market growth, especially as consumer demand for sustainable products continues to rise.
Vanden Global Ltd.: Vanden has been at the forefront of plastic recycling, including PMMA, with recent expansions into the UAE and the GCC region. The company has been strengthening its global operations to better manage the supply and demand of recyclable plastics. Their commitment to enhancing plastic recycling processes aligns with the broader industry push towards sustainability and circular economy practices.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: PMMA Recycling Market is to reach USD 743.94 Million by 2033, from USD 387.86 Million in 2023, with a CAGR of 6.73%.
- Mechanical Recycling held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling industry, capturing more than 69.3%
- Pyrolysis held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling industry, capturing more than a 74.1% share.
- Automotive held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling market, capturing more than a 28.3% share.
- North America leads the global PMMA Recycling Market, holding a significant share of 44.5%.
Statistics
- Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) is currently produced at 3.9 million metric tons per year.
- However, it is estimated that nowadays only 10% of this production is recycled.
- Its market is expected to expand in the coming 7 years at a compound annual growth rate of 3.4%.
- The global production of plastic has reached 368 million metric tons in 2019.
- The rapid expansion of plastic production is producing a turnover of more than 350 billion euros per year, with the plastic supply chain counting on more than 55,000 companies, mostly small and medium enterprises, and giving jobs to more than 1.5 million people (Plastics Europe – Association of Plastic Manufacturers (Organization), 2020).
- The production of plastics contributes for < 10% to the global carbon footprint. The majority of crude oil (> 85%) is still dedicated to the production of energy (Sasse and Emig, 1998).
- It was estimated that < 30% of the plastic collected every year is recycled, but only 0.9% is recycled more than once (Geyer et al., 2017).
- Pyrolysis of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) may result in very high recycling rates (90-98%) of the monomer methylmethacrylate (MMA) since the cracking of MMA to lighter molecules (CO2, CO, and light hydrocarbons) is limited.
- The annual PMMA world production capacity is over 2.4 × 106 tons, but currently, only 3.0 × 104 tons are collected and recycled in Europe each year.
- Acrylic plastic also weighs around 50% less than glass of an equal thickness and has a transparency rate of 93%.
- Molten lead is added to the acrylic. This separates methyl methacrylate from the catalyst, resulting in a molten MMA of around 98% purity.
- Association of Plastics Manufacturers in Europe and the European Association of Plastics Recycling and Recovery Organisations, from the 27.1 Mt of plastic waste collected in Europe in 2016, only 31.1% was recycled, while 41.6% was burnt for energy recovery and 27.3% was disposed of in landfills.
- The PMMA waste samples contained 1 wt.% of titanium oxide (TiO2) and around 5 wt.% of the cross-linking agent ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA), as described elsewhere.
- The loss to recycle this waste is only 10 to 15%, so if one processes 100 kg, 85 to 90 kg are left to be reused as raw material.
- From collection to processing is estimated that only 30,000 tonnes of PMMA waste are currently collected for recycling annually in Europe, or only about 10% of annual production.
- Microplastic contamination of up to 12,000 particles / m³ could also be detected in Arctic Sea ice.
- American researchers have found that up to 15 percent of the 45 million contact lenses sold in the U.S.
- PFAS and other chemical compounds are classified as potentially harmful or hazardous in more than 50% of plastics, including commercially available materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Microplastics are tiny particles of synthetic polymers and plastics and their products that are less than 5 millimeters in size.
Emerging Trends
- Advanced Recycling Technologies: One of the most significant trends in PMMA recycling is the development of advanced recycling technologies, particularly chemical recycling. Traditional mechanical recycling has limitations, such as the degradation of material properties over time. However, chemical recycling, which involves breaking down PMMA into its monomer form (MMA) and then repolymerizing it, maintains the quality of the recycled material. This technology is becoming increasingly popular as it allows for higher-quality recycled PMMA, suitable for use in demanding applications like automotive and electronics.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: There is a growing focus on creating a circular economy within the plastics industry, where materials are reused and recycled to minimize waste. PMMA recycling is central to these efforts, as it helps reduce the environmental impact of plastics by keeping the material in use longer. Companies are increasingly adopting closed-loop recycling systems, where PMMA waste is collected, recycled, and used to produce new products, reducing the need for virgin materials.
- Expansion of Recycling Infrastructure: As demand for recycled PMMA grows, there is a corresponding expansion in recycling infrastructure. Companies are investing in new recycling facilities and upgrading existing ones to handle larger volumes of PMMA waste. For example, the recent establishment of pilot plants and full-scale recycling facilities by companies like Sumitomo Chemical highlights the industry’s commitment to expanding its recycling capacity.
- Regulatory Support and Government Initiatives: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to encourage recycling and reduce plastic waste. These regulations are driving the growth of the PMMA recycling market, as companies seek to comply with new standards and take advantage of incentives for using recycled materials. The European Union, in particular, has been at the forefront of these efforts, with policies that promote recycling and the use of recycled content in manufacturing.
- Sustainability and Consumer Demand: There is increasing consumer demand for sustainable products, which is pushing manufacturers to incorporate more recycled materials, including PMMA, into their products. Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious and prefer products that are made with recycled content. This shift in consumer behavior is encouraging companies to invest in PMMA recycling and use the recycled material in various applications, from consumer goods to construction materials.
- Global Expansion and Partnerships: Companies are expanding their recycling operations globally, often through partnerships and collaborations. For example, collaborations between technology providers and recycling companies are facilitating the development of new recycling processes and expanding the geographic reach of recycling efforts. Partnerships are also being formed to create more efficient supply chains for collecting and processing PMMA waste on a global scale.
Use Cases
- Automotive Industry: Recycled PMMA is increasingly being used in the automotive industry for manufacturing various components, such as light covers, dashboards, and interior panels. The material’s high durability, scratch resistance, and optical clarity make it an ideal choice for automotive applications. According to recent developments, automakers are adopting recycled PMMA to meet stringent environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable vehicles. The use of recycled PMMA in this industry helps reduce the carbon footprint and lowers manufacturing costs by minimizing the need for virgin materials.
- Construction and Architecture: In the construction and architectural sectors, recycled PMMA is utilized in creating durable and aesthetically pleasing products, including windows, skylights, and interior partitions. The material’s ability to withstand environmental elements while maintaining its clarity and strength makes it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. The construction industry’s shift towards green building practices has increased the demand for recycled materials, with PMMA being a popular choice due to its longevity and low maintenance requirements.
- Consumer Goods: Recycled PMMA is widely used in the production of consumer goods, such as electronics, household items, and fashion accessories. For instance, it is commonly found in smartphone screens, watch covers, and eyewear. The growing consumer preference for eco-friendly products is driving manufacturers to incorporate recycled PMMA into their designs. This not only reduces environmental impact but also resonates with eco-conscious consumers, enhancing brand value and appeal.
- Medical Devices: The medical industry is another critical area where recycled PMMA is finding applications. It is used in the manufacturing of medical devices such as dental implants, optical lenses, and prosthetics. The material’s biocompatibility, clarity, and ease of sterilization make it suitable for medical applications. As the healthcare sector faces increasing pressure to reduce waste and adopt sustainable practices, the use of recycled PMMA is expected to grow, helping medical manufacturers meet both environmental and regulatory requirements.
- Signage and Display: One of the traditional uses of PMMA has been in signage and display applications. Recycled PMMA is now being utilized to create durable and weather-resistant signs, advertising displays, and exhibition booths. This is particularly beneficial in outdoor environments, where the material’s resistance to UV light and harsh weather conditions ensures long-lasting performance. The use of recycled PMMA in signage also aligns with the growing trend of sustainable advertising, where businesses seek to minimize their environmental footprint while maintaining high visual standards.
Major Challenges
- Technical Complexity: One of the primary challenges in PMMA recycling is the technical difficulty associated with maintaining the material’s quality during the recycling process. Mechanical recycling often leads to the degradation of PMMA’s molecular structure, resulting in reduced optical clarity, strength, and durability. This limits the recycled material’s applicability, particularly in high-performance uses like optical lenses and automotive components. Chemical recycling, which offers a solution by breaking down PMMA into its monomers, is complex and requires advanced technology. However, it is significantly more expensive and energy-intensive compared to mechanical methods.
- Economic Viability: The economic aspect of PMMA recycling is another major challenge. The high costs associated with setting up and maintaining recycling facilities, especially those that employ chemical recycling, can be prohibitive. Additionally, the market price of virgin PMMA often fluctuates, sometimes making recycled PMMA less competitive. When the price of virgin PMMA drops, the demand for recycled PMMA can decrease, leading to reduced profitability for recycling operations.
- Market Demand and Infrastructure: While there is a growing demand for recycled materials, the infrastructure for collecting and processing PMMA waste is still underdeveloped in many regions. This limits the availability of high-quality recycled PMMA. Moreover, inconsistent regulations across different regions can create uncertainty, hindering the development of a stable global market for recycled PMMA.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Technological Innovations: Advancements in chemical recycling technologies offer significant growth opportunities for the PMMA recycling market. Chemical recycling processes, which break down PMMA into its monomers (MMA), allow for the production of high-quality recycled PMMA that can be used in demanding applications such as automotive components and optical products. The development and scaling of these technologies can help overcome the limitations of mechanical recycling, which often degrades the material’s properties. Companies investing in cutting-edge recycling technologies can capitalize on the growing demand for high-purity recycled PMMA.
- Sustainability Initiatives: As global awareness of environmental sustainability increases, so does the demand for recycled materials. Governments and industries are increasingly adopting circular economy practices, where materials like PMMA are reused and recycled to minimize waste and reduce the reliance on virgin resources. Companies that align their operations with these sustainability goals can access new markets and customer segments that prioritize environmentally friendly products. This trend is particularly strong in regions like Europe, where strict regulations and consumer preferences are driving the demand for recycled plastics.
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: The growing industrialization and urbanization in emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, present substantial growth opportunities for the PMMA recycling market. These regions are experiencing an increasing demand for construction materials, automotive components, and consumer goods, all of which can benefit from the use of recycled PMMA. By expanding recycling infrastructure and capabilities in these regions, companies can tap into a rapidly growing market while contributing to global sustainability efforts.
Key Players Analysis
Vanden Global Ltd. is a leading player in the PMMA recycling sector, focusing on collecting, processing, and supplying recycled PMMA to various industries. The company operates globally, providing recycling services that convert PMMA waste into reusable materials. Vanden’s expertise lies in managing the entire recycling process, from waste collection to delivering high-quality recycled PMMA for applications in automotive, construction, and consumer goods. Their commitment to sustainability and innovation has positioned them as a key contributor to the circular economy.
Renov8, a subsidiary of Just Right, is at the forefront of chemical recycling in the PMMA sector. The company is known for its collaboration with Coperion to develop an advanced recycling system that thermally converts PMMA into liquid rMMA at their facility in Abu Dhabi’s Kezad Polymers Park. This innovative approach allows Renov8 to efficiently recycle PMMA, maintaining the material’s quality for high-value applications, thus supporting the industry’s shift towards sustainable practices and circular economy principles.
Heathland B.V. is a prominent recycler in the PMMA sector, based in the Netherlands. They specialize in processing post-industrial and post-consumer PMMA waste into high-quality recycled materials. Heathland is particularly noted for leading the MMAtwo project, an innovative initiative aimed at developing advanced depolymerization techniques for PMMA waste, transforming it back into valuable raw materials. Their work supports the shift towards a circular economy by providing sustainable recycling solutions that extend the lifecycle of PMMA materials.
Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. has made significant strides in the PMMA recycling industry by establishing a pilot plant for recycling PMMA in Niihama, Japan. This facility is dedicated to developing a comprehensive recycling system that collects and repurposes used acrylic resin. Sumitomo’s initiative is focused on creating high-quality recycled PMMA for use in various industries, including automotive and construction, highlighting their commitment to sustainability and innovation in recycling technologies.
Plastic Expert is recognized for its specialized capabilities in PMMA recycling in the UK, where it addresses the complex challenges associated with recycling acrylics like PMMA sheets or panels. As a leader in handling Group 7 plastics, which are less commonly recycled by other firms, Plastic Expert provides a vital service that facilitates the recycling of acrylic waste. This includes transforming scrap acrylic into new products, such as flat sheets and various shapes, suitable for diverse industrial applications. Their approach not only supports sustainability but also helps businesses manage their acrylic waste more effectively by providing tailored collection and recycling services.
Trinseo Ltd. has been actively involved in advancing PMMA recycling through its focus on depolymerization technology. This method allows for the sustainable recycling of PMMA into methyl methacrylate (rMMA), which can then be reused to produce new PMMA products. By investing in chemical recycling processes, Trinseo supports the circular economy model, aiming to reduce waste and enhance the reusability of PMMA materials. Their efforts are crucial for promoting environmental sustainability and supporting industries that rely on high-quality recycled PMMA
Lucite International Alpha B.V., part of Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, is actively advancing circular solutions for PMMA recycling. They are collaborating with Agilyx Corporation to develop commercial-scale chemical recycling of PMMA into virgin-quality methyl methacrylate (MMA), enhancing sustainability in the plastics industry. This initiative underscores Lucite’s commitment to creating a fully circular economy for PMMA, aiming to establish robust recycling processes that accommodate various PMMA feedstocks and effectively handle contaminants.
Starlinger leads in recycling technology for various materials, including PMMA. Their focus is on providing high-tech machinery that processes PMMA waste into reusable materials. Starlinger’s equipment is designed to support the efficient conversion of PMMA scrap into high-quality granules, thereby facilitating the production of new PMMA products. This contribution is pivotal in promoting sustainability and resource efficiency within the PMMA recycling industry, ensuring that PMMA’s lifecycle is extended and its environmental impact is minimized.
Pekutherm Kunststoffe GmbH specializes in recycling PMMA and other plastics through a proprietary purification process that restores the recycled material to near-virgin quality. Their focus is on creating a sustainable cycle by transforming waste PMMA into reusable resources, thereby contributing to environmental conservation and reducing industrial reliance on new raw materials. Their operations highlight a commitment to advancing PMMA recycling technologies and expanding the market for recycled PMMA products.
Mitsubishi Chemical has been actively involved in developing circular solutions for PMMA, focusing on the molecular recycling of PMMA back into MMA (methyl methacrylate). They have partnered with Agilyx Corporation to refine and commercialize this technology, aiming to establish a fully sustainable lifecycle for PMMA products. Mitsubishi’s efforts include constructing facilities dedicated to this recycling process, with a strong emphasis on maintaining the high purity and performance of recycled MMA, aligning with global sustainability goals, and reducing environmental impact.
Conclusion
The PMMA recycling market is poised for substantial growth as technological advancements, regulatory support, and increasing environmental awareness drive the demand for sustainable materials. Innovations in chemical recycling processes, such as those developed by companies like Mitsubishi Chemical and Agilyx, are making it possible to recycle PMMA into high-purity MMA, enabling a truly circular economy for this versatile material. Despite challenges, such as the high costs associated with advanced recycling technologies, the market is expected to expand as industries increasingly prioritize sustainability. The ongoing efforts to enhance recycling infrastructure and processes will play a crucial role in meeting global demand for recycled PMMA, supporting broader environmental goals, and reducing reliance on virgin resources.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





