Table of Contents
Introduction
The global Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) market is projected to grow from USD 65.5 billion in 2023 to USD 94.7 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.6% over the forecast period. PVC, a highly versatile thermoplastic, finds extensive use across various industries due to its durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
The construction sector is a primary driver of this growth, significantly fueled by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, especially in emerging economies like India and China. PVC’s extensive application in pipes, windows, doors, and other construction materials underpins its demand. Additionally, the healthcare industry boosts PVC demand due to its use in medical devices and packaging, leveraging its properties of biocompatibility and ease of sterilization.
Technological advancements are pivotal in expanding PVC applications. The development of energy-efficient materials and PVC formulations with enhanced properties such as fire resistance, self-healing, and antimicrobial features are opening new avenues for growth. The incorporation of bio-based materials and improved recyclability is also attracting eco-conscious consumers, further stimulating market expansion.
However, the PVC market faces notable challenges. Environmental concerns regarding PVC’s non-biodegradability and the release of harmful chemicals during production pose significant restraints. Regulatory pressures and the need for sustainable production methods are compelling manufacturers to innovate and adopt greener practices. Additionally, performance issues such as chemical resistance limitations also present hurdles that need addressing.
Recent developments in the PVC market include increased investments in recycling technologies and the exploration of bio-based alternatives. Major players are focusing on expanding their production capacities and enhancing product quality through advanced manufacturing processes. The U.S. and Germany are leading in technological advancements and infrastructure development, significantly contributing to market growth.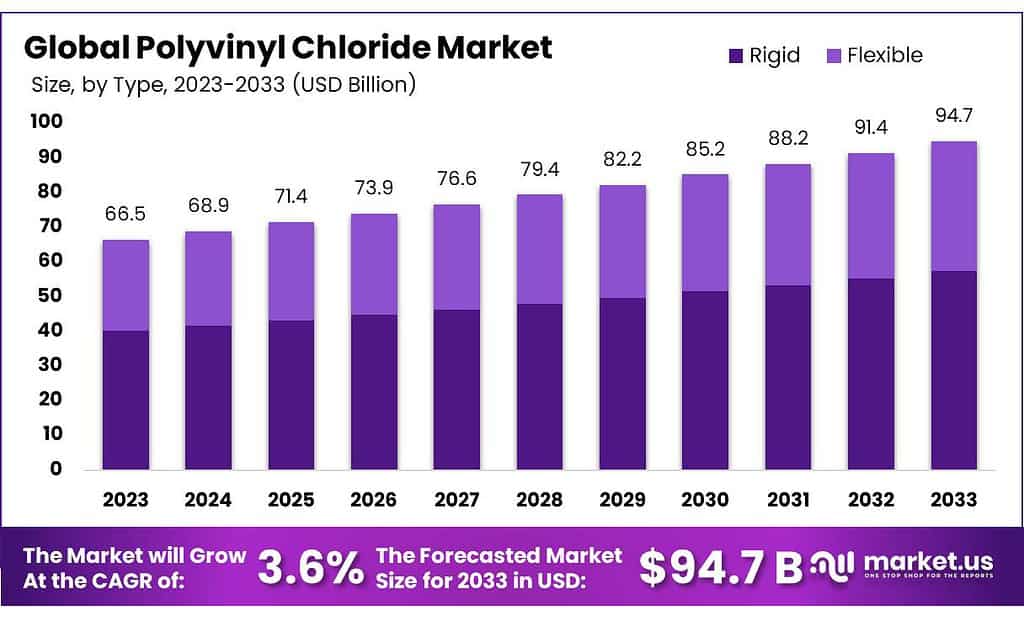
Polyvinyl Chloride Manufacturing Statistics
- CPVC Chlorine Content: Chlorinated PVC typically has chlorine content increased from 56% to 66%.
- PVC in Water Pipes: PVC pipes constitute 66% of newer water pipes in the US.
- PVC in Sewer Pipes: PVC pipes make up 75% of new sewer pipes.
- PVC in Medical Equipment: PVC accounts for about 40% of all disposable plastic medical equipment used in hospitals.
PVC Market Dynamics
- India’s PVC Imports: India imported over 2.4 million tons of PVC from January to September this year.
- China’s Market Share in India: China’s market share in India’s PVC market is about 35%.
- China’s Market Share Growth: China’s market share in India increased from 2% in 2020 to 17% in 2021.
- Import Restrictions Recommendation: Recommended import restrictions for China, Taiwan, the US, and Russia total about 221,000 tons annually, with China’s quarterly quota at 20,000-21,000 tons.
PVC Recycling and Environmental Impact
- VCM Production: Approximately 13 billion kilograms of Vinyl Chloride Monomer are produced annually.
- Composition of PVC: PVC is composed of 43% petroleum derivatives and 57% sea salt.
- Environmental Benefits of Recycled PVC: Manufacturing window profiles with recycled PVC can reduce environmental danger by up to 70%.
- Emissions Reduction with Recycled PVC: Shifting to recycled PVC can result in over 60% reduction in air and water emissions.
- Plastic Waste Generation: Municipal plastic waste generation rate has increased steadily at 5% annually, while recycling is at 3%.
Emerging Trends
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices: The PVC industry is increasingly focused on reducing its environmental impact. This includes the development of green plasticizers, which improve flexibility and durability without the harmful effects associated with conventional plasticizers like phthalates. Advancements in recycling technologies, such as mechanical recycling and chemical depolymerization, are being refined to convert PVC waste into high-quality recycled materials. Additionally, companies are investing in bio-based feedstocks to create more sustainable PVC formulations
Technological Advancements: The integration of digital technologies and automation in PVC manufacturing processes is revolutionizing the industry. Predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and data analytics are enhancing production efficiency, reducing waste, and ensuring product uniformity. These technological improvements are critical for meeting increasing demand and maintaining competitive advantages in the market.
Growth in Construction and Infrastructure: The construction sector remains a dominant driver for PVC demand. PVC’s durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation make it a preferred material for pipes, fittings, roofing membranes, and insulation boards. The surge in infrastructure development, especially in rapidly urbanizing regions like Asia-Pacific, is significantly boosting the demand for PVC products. The material’s use in electrical conduits, sewage systems, and waterproofing solutions underscores its critical role in modern construction projects.
Expansion in Automotive and Electrical Applications: PVC is widely used in the automotive industry for interior and exterior components due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is driving the demand for PVC in insulation and electrical components. This trend is supported by the material’s properties such as fire resistance and ease of molding, which are essential for automotive and electronic applications.
Healthcare Industry Applications: The healthcare sector continues to be a significant market for PVC, driven by the need for single-use medical products to prevent infections. PVC is favored for its biocompatibility and sterilization ease, making it suitable for medical devices, IV bags, and other healthcare products. The ongoing efforts to develop bio-balanced PVC and enhance recycling processes further support the material’s application in this critical industry.
Regulatory and Market Challenges: The PVC market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns, particularly due to additives like lead and phthalates. Regulatory pressures, such as the European Union’s REACH regulation, are pushing manufacturers to adopt safer alternatives and sustainable practices. This transition requires significant investment in research and development to ensure compliance without compromising product performance.
Use Cases
Construction and Building Materials: Pipes and Fittings: PVC is extensively used in plumbing and drainage systems due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It accounts for over 50% of the global PVC consumption. For instance, the U.S. construction industry alone uses millions of tons of PVC pipes annually for water distribution and sewage systems.
Windows and Doors: PVC frames are preferred for their energy efficiency, low maintenance, and insulation properties. Approximately 70% of Europe’s window frames are made from PVC, highlighting its popularity in the region. Roofing Membranes: PVC roofing is used in flat or low-slope roofs, offering excellent waterproofing and weather resistance. It is estimated that the global demand for PVC roofing membranes will reach 400 million square meters by 2025.
Insulation for Cables: PVC’s excellent insulating properties make it a preferred material for electrical cables and wiring. It protects against electrical shocks and is resistant to fire. In 2023, the global market for PVC-insulated cables was valued at approximately USD 12 billion.
Consumer Electronics: PVC is used in various consumer electronics for casings, connectors, and internal components, due to its durability and ease of molding.
Interior Components: PVC is used in car interiors, including dashboards, door panels, and seat coverings, because of its flexibility and aesthetic appeal. The automotive sector consumes about 7% of the total PVC production globally.
Under-the-Hood Applications: PVC is also used in making hoses and gaskets that need to withstand high temperatures and chemicals.
Medical Devices: PVC is vital in manufacturing medical devices such as IV bags, blood bags, and tubing, due to its biocompatibility and sterility. The healthcare sector accounts for approximately 4% of PVC consumption. The market for PVC medical devices is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5% through 2030. Packaging: PVC is used in blister packaging for tablets and other medical supplies because of its clarity and barrier properties.
Rigid Packaging: PVC is used for making containers and bottles, especially for products that require durability and resistance to chemicals. In 2023, the global PVC packaging market was valued at over USD 8 billion. Flexible Films: PVC films are used for packaging food items, medical supplies, and consumer goods. The market for PVC packaging films is projected to grow by 3% annually due to increasing demand for flexible packaging solutions.
Soles and Uppers: PVC is widely used in the footwear industry for making shoe soles and uppers because of its durability and water resistance. The global market for PVC footwear components is expected to reach USD 3 billion by 2027.
Consumer Goods:
Toys and Sports Equipment: PVC is used in the production of various consumer goods like toys, sports equipment, and inflatables due to its flexibility and strength. The market for PVC toys is growing, with an annual demand increase of about 2.5%.
Major Challenges
Non-Biodegradability: PVC is not biodegradable, which means it can persist in the environment for a long time. This has led to concerns about plastic pollution, particularly in marine environments where PVC waste can accumulate and harm wildlife. Efforts to improve the recyclability of PVC are ongoing, but recycling rates remain low compared to other plastics. Toxic Additives: The production and disposal of PVC involve additives like phthalates and heavy metals, which can leach into the environment and pose health risks. Phthalates, used to make PVC flexible, are linked to various health issues including endocrine disruption.
Emission of Hazardous Chemicals: During its lifecycle, PVC can emit harmful chemicals. For instance, the production of PVC releases dioxins, which are highly toxic and can cause serious health problems, including cancer and reproductive issues. These emissions occur during the manufacturing process and when PVC is burned.
Stricter Regulations: Many countries are implementing stricter environmental regulations to control the use and disposal of PVC. For example, the European Union’s REACH regulation restricts the use of certain hazardous substances in PVC products. These regulations increase the cost of production as manufacturers need to invest in alternative materials and cleaner technologies.
Alternative Materials: PVC faces competition from other materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and bioplastics, which are often perceived as more environmentally friendly. These alternatives are gaining market share, particularly in applications where environmental impact is a significant concern.
Raw Material Price Volatility: The production of PVC relies on raw materials such as ethylene and chlorine, derived from petroleum and natural gas. Fluctuations in the prices of these raw materials can affect the cost of PVC production, making it less economically viable compared to other materials during periods of high price volatility.
Market Growth Opportunities
Recycling Advancements: Improving PVC recycling processes presents significant growth opportunities. Advanced recycling technologies, such as mechanical recycling and chemical depolymerization, are being developed to convert PVC waste into high-quality recycled materials. For example, Braskem has received a grant to enhance recycling technologies aimed at extracting pure polypropylene from post-consumer resin.
Bio-Based PVC: The development of bio-based PVC from renewable sources is another promising area. This not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also addresses environmental concerns. Companies like LG Chem are collaborating to produce bio-balanced PVC, which is expected to gain traction in eco-conscious markets.
Urbanization and Smart Cities: Rapid urbanization in countries like China and India is driving demand for construction materials. PVC’s durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation make it ideal for pipes, windows, doors, and roofing membranes in residential and commercial buildings. The global PVC demand in the construction sector is expected to grow significantly as urban infrastructure expands.
Energy-Efficient Buildings: PVC’s insulating properties contribute to energy efficiency in buildings. This is particularly important in regions focusing on sustainable construction practices. As energy-efficient buildings become more prevalent, the demand for PVC materials used in insulation and window frames is expected to rise.
Medical Devices and Packaging: The healthcare sector offers robust growth potential for PVC. Its use in medical devices like IV bags, blood bags, and tubing is driven by the need for sterile, biocompatible materials. The global market for PVC medical devices is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5% through 2030, driven by the increasing demand for healthcare services.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): The rise of electric vehicles is boosting the demand for PVC in automotive applications. PVC is used for insulation in electrical components, as well as for interior parts like dashboards and door panels. The lightweight and durable nature of PVC makes it suitable for enhancing the efficiency and aesthetics of EVs.
Smart Manufacturing: The integration of digital technologies in PVC manufacturing, such as predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and data analytics, is enhancing production efficiency and product quality. This trend towards smart manufacturing processes is expected to drive growth in the PVC market by reducing costs and improving sustainability.
Recent Developments
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. is a leading player in the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sector, with significant operations and continuous expansions to meet global demand. In 2023, Shin-Etsu focused on enhancing its PVC production capabilities through its subsidiary, Shintech Inc., located in the U.S. Specifically, Shintech began constructing a new integrated PVC plant in Plaquemine, Louisiana, with an investment of $1.49 billion. This new facility is set to increase Shintech’s annual PVC production capacity by 290,000 tons and caustic soda by 270,000 tons, aiming for completion by the end of 2024. This expansion aligns with Shintech’s strategy to leverage the competitive advantage of local ethylene production, a key raw material for PVC, thereby strengthening its position as the world’s largest PVC producer.
Formosa Plastics Corporation has been actively expanding its polyvinyl chloride (PVC) production capabilities in 2023 and 2024. In December 2023, the company announced the official opening of its new Mother’s Room at its Point Comfort, Texas site, marking it as the first manufacturing site to achieve the Silver Level Mother-Friendly Worksite designation in Texas. This reflects their commitment to supporting employees and fostering a positive workplace environment.
Occidental Chemical Corporation (OxyChem), a subsidiary of Occidental Petroleum Corporation, has been actively involved in the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sector. In 2023, OxyChem reported consistent PVC production, leveraging its advanced manufacturing facilities in the United States. Throughout 2023, OxyChem focused on enhancing its environmental sustainability practices and expanding its PVC production capacity to meet increasing market demand. In the first half of 2024, the company continued its investment in modernizing equipment and adopting cleaner production methods, maintaining its position as a key player in the global PVC market. The company’s strategic initiatives reflect its commitment to efficiency and environmental responsibility.
INEOS Group Limited has been actively expanding its operations in the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sector. The company reported significant financial growth with EBITDA reaching €516 million in Q1 2024, up from €444 million in Q1 2023. This growth was driven by stable demand in North American and European markets, despite softer conditions in Asia. INEOS also focused on enhancing its production capabilities and sustainability efforts. In February 2024, the company issued new Senior Secured Term Loans and Senior Secured Notes worth approximately €2.4 billion to fund acquisitions and expansions, including the acquisition of ethylene oxide and derivatives assets in the U.S. and France. These strategic moves are aimed at bolstering INEOS’s position in the global PVC market and ensuring a steady supply of raw materials for PVC production.
Conclusion
The polyvinyl chloride (PVC) market continues to demonstrate robust growth and resilience, driven by increasing applications across various sectors such as construction, healthcare, automotive, and packaging. In 2023 and 2024, significant investments and advancements in recycling technologies have propelled the market forward, addressing environmental concerns and enhancing sustainability. For example, companies are focusing on bio-based feedstocks and improving recycling processes to reduce the ecological footprint of PVC products.
The construction industry remains the largest consumer of PVC, utilizing it for pipes, fittings, and insulation due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the automotive sector’s shift towards electric vehicles has spurred demand for PVC in insulation and cable applications. Despite challenges such as regulatory pressures and competition from alternative materials, the market is poised for continued growth, driven by technological innovations and expanding applications across diverse industries.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





