Table of Contents
Introduction
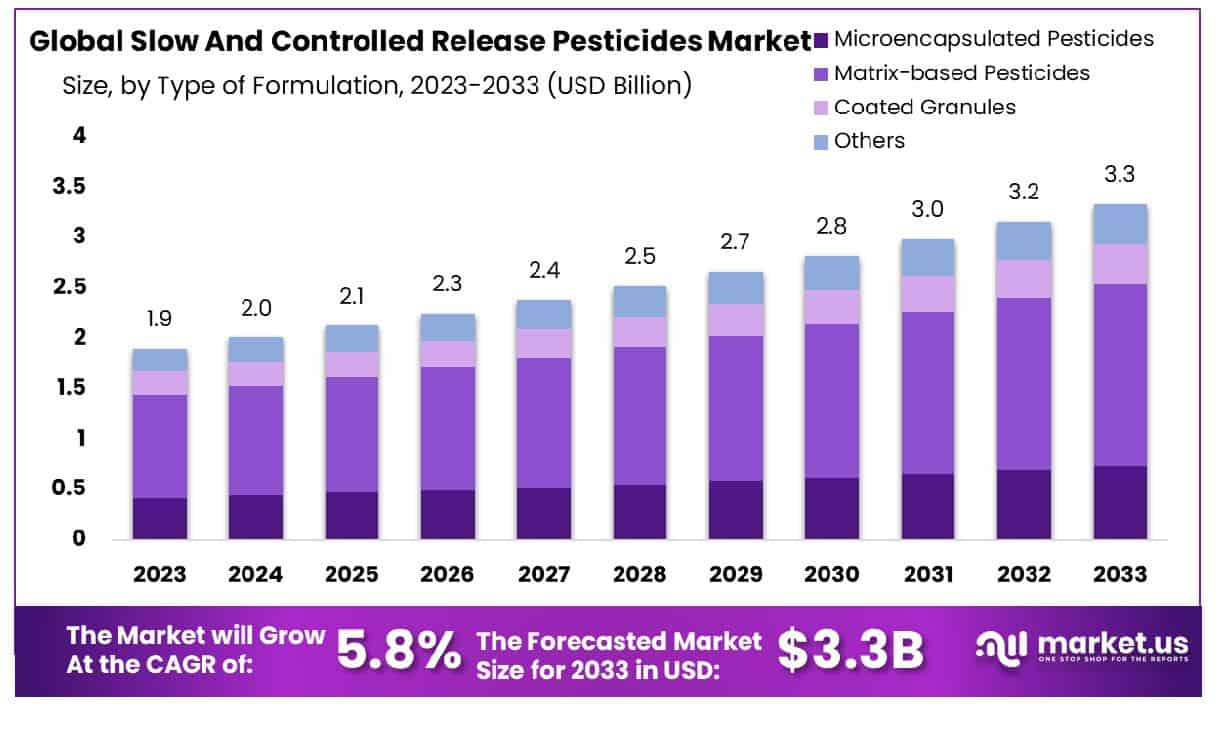
The global market for slow and controlled-release pesticides is anticipated to expand significantly, with its valuation projected to grow from USD 1.9 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 3.3 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% throughout the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices that minimize environmental impact and enhance crop yield efficiency.
However, the market faces challenges, including stringent regulatory frameworks governing pesticide use and high initial development costs for formulating slow-release technologies. Despite these obstacles, recent advancements in nanotechnology and biodegradable polymers are set to improve product efficacy and safety, thereby propelling market expansion. These developments not only address the immediate effectiveness of pesticides but also contribute to long-term sustainability goals in agriculture.
Syngenta has been actively expanding its product portfolio in the slow and controlled release pesticides segment. In recent times, they have launched new formulations that extend the effectiveness period of pesticides, reducing the need for frequent applications. Although specific sales figures are not disclosed, such innovations are likely enhancing their market share and strengthening their competitive position in the global market.
DAMA Agricultural Solutions Ltd has recently secured funding to advance their research and development in controlled release technologies. This funding boost is poised to facilitate the development of next-generation pesticide solutions that are more efficient and environmentally friendly. This strategic move is expected to not only expand their product line but also increase their influence in the market.
The Dow Chemical Company has engaged in several strategic partnerships to leverage synergies in technology and innovation in the controlled release pesticides arena. These collaborations are aimed at enhancing their research capabilities and speeding up the commercialization of new products. Dow’s strategy focuses on strengthening its market position through innovation and collaborative efforts with other industry leaders.
BASF SE has recently introduced a new range of slow-release pesticides that promise greater efficacy and reduced environmental impact. These products have been well-received in the market, as indicated by early adoption rates among large-scale farming operations. BASF’s commitment to sustainability and innovation continues to drive their growth in this segment, helping them to meet the evolving demands of the agricultural industry.
Arysta LifeScience has expanded its geographic reach through the acquisition of smaller companies specializing in controlled release technologies. These acquisitions have not only expanded their market coverage but also enhanced their technological capabilities. By integrating these new technologies, Arysta LifeScience aims to offer more diverse solutions to meet global agricultural needs.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Global Slow And Controlled Release Pesticides Market is projected to grow from USD 1.9 Billion in 2023 to USD 3.3 Billion by 2033, at a 5.8% CAGR.
- Asia-Pacific leads with a 38% market share, valued at USD 0.7 billion.
- By Type of Formulation: Microencapsulated pesticides dominate with a 45.5% market share in formulations.
- By Mode of Action: Insecticides lead by mode of action, capturing 52.3% market.
- By Crop Type: Grains and cereals are prominent, constituting 45.6% of crops.
- By End-user: Large-scale commercial farms are major users, holding a 67.4% share.
Effectiveness and Efficiency of Conventional Agrochemicals
- The scope of CRF in controlling other pests like mosquitoes is also visualized. Introduction Applied conventional agrochemicals (90%) never reach their objective of producing the desired biological response at the precise time and in precise quantities required, due to the nonspecific and periodic application of active agents.
- The pyraclostrobin nanospheres had a uniform spherical shape with a mean particle size of 450 nm and a polydispersity index of less than 0.3. The pyraclostrobin loading capacity reached 53.6%, with excellent storage stability.
- The rising population is increasing food demand, yet actual crop production is limited by the poor efficiency of classical fertilizers. In particular, only about 40–60% of fertilizer nitrogen, 15–20% of phosphorus, and 50–60% of potassium are used by crop plants, the rest ending up polluting the environment.
- With ultraviolet photolysis, poor dispersity, and application drift, the effective utilization rate of conventional pesticides is only 10%.
- Bimodal mesoporous silica materials (BMMs) consisting of worm-like mesopores of 3 nm as well as large inter-particle pores of approximately 10–30 nm comprise an excellent drug carrier and possess high pesticide loading capacity.
Agricultural Production and Fertilizer Efficiency
- Nitrogen is the essential element that limits worldwide agricultural production. Despite numerous efforts, the N-use efficiency (NUE) in agriculture remains around 50%.
- Due to the rapid growth of the population by 2–3 billion people during the next 80 years, more crop production will be needed, which will also increase the need for fertilizers.
- Agricultural activities account for approximately 60% and 10% of the world’s anthropogenic N2O and NO sources, respectively, due to the increased utilization of N fertilizer on crop lands.
- Accounting for about 60% of N lost into the environment during growing seasons in the forms of ammonia, nitrate, and nitrous oxide, which has a significant negative impact on human health.
- Annual worldwide usage of pesticides is in millions of tons, without which 40% of crops would be lost.
Advances and Challenges in Pesticide Application
- However, due to factors such as foliar loss, evaporation, photodegradation, etc., the amount of the active ingredient of the pesticide actually acting on the target is less than 10%.
- According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, total compensation for all hourly workers increased by 4.1% over 12 months, ending in December 2023.
- Vegetable production remains a tremendous industry for Florida in terms of acreage and value. Including vegetables, melons, potatoes, and strawberries, production occurred on approximately 251,011 acres and generated more than $1.34 billion in gross sales in 2016, which ranks second among all the states.
- In the soil columns, FOMI showed better performance with lower percentages of leaching (lower than 15% in 2 days and 75% in 30 days), higher water retention capacity (WRC), and higher cation exchange capacity (CEC).
- Hydrogel agriculture technology uses insoluble gel-forming polymers to improve the water-holding properties of different soils, such as clays and sandy loams. This can increase water-holding and water use (up to 85% for sand), improve soil permeability, reduce the need for irrigation, reduce compaction, soil erosion, and leaching, and improve plant growth.
Emerging Trends
- Biodegradable Formulations: There is a growing shift towards the development of biodegradable pesticides. These formulations decompose naturally in the environment, reducing ecological footprints and minimizing the potential for long-term environmental damage.
- Nanotechnology: The integration of nanotechnology in pesticide delivery systems is gaining traction. Nanoparticles are used to encapsulate the active ingredients, enhancing their stability and allowing for more precise targeting of pests. This reduces the amount of chemicals used and limits exposure to non-target organisms.
- Smart Release Systems: Advancements in sensor technology and data analytics are leading to the development of ‘smart’ pesticide systems. These products can respond to environmental conditions like moisture and temperature to release chemicals at the most effective times, thereby increasing crop yield and reducing waste.
- Customized Solutions: There is an increasing demand for customized pesticide solutions tailored to specific crop types and regional pest challenges. This trend is driving the market towards more specialized products that can offer better protection for particular crops.
- Regulatory Compliance: As regulatory standards for pesticide use become stricter globally, the market is trending towards products that can meet these evolving standards while still providing effective pest control.
Use Cases
- Extended Pest Control: Traditional pesticides often require multiple applications throughout the growing season, which can be costly and labor-intensive. Slow and controlled-release pesticides are designed to release their active ingredients over an extended period, often weeks or months, thereby reducing the need for frequent reapplication. This can lead to cost savings of up to 20-30% on application and labor.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: These pesticides minimize runoff and leaching because they release their active ingredients slowly. This controlled release reduces the chances of pesticides entering nearby water bodies or affecting non-target species. For instance, studies have shown a reduction in pesticide runoff by up to 50% compared to conventional products.
- Improved Crop Yield: By providing consistent and prolonged protection against pests and diseases, slow and controlled release pesticides enhance plant health and vigor. This consistent protection can increase crop yields by 10-15%, depending on the crop type and environmental conditions.
- Tailored Crop Management: Certain formulations can be engineered to target specific pests and activate only under certain environmental conditions, such as specific soil moisture levels or temperatures. This specificity helps ensure that pesticides are only active when needed, enhancing their effectiveness and reducing waste.
- Compatibility with Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Slow and controlled-release pesticides are ideal for use in IPM programs. Their precise delivery and reduced toxicity make them suitable for use alongside biological control agents, reducing the reliance on chemical interventions and promoting ecological balance.
Major Challenges
- High Development Costs: The research and development process for creating effective slow and controlled release formulations is both time-consuming and costly. The expense involved in developing these advanced technologies can be substantial, often requiring upfront investments ranging from millions to tens of millions of dollars before a viable product can be brought to market. This high-cost barrier can deter smaller companies from entering the market.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining regulatory approval for new pesticide products, particularly those that incorporate novel technologies like nanomaterials, can be a lengthy and unpredictable process. Regulatory agencies often require extensive data to ensure that these new products do not pose unforeseen risks to the environment or human health. The approval process can take several years, delaying market entry and adding to development costs.
- Market Adoption: Despite their benefits, there is often hesitation among farmers and agricultural producers to adopt new technologies, especially when initial costs are higher than conventional products. Changing these perceptions and demonstrating the long-term cost benefits and increased yields can require significant marketing and educational efforts.
- Complexity in Manufacturing: The production of slow and controlled-release pesticides involves complex formulation techniques that can be difficult to scale up from laboratory to industrial levels without compromising quality and effectiveness. This scaling challenge can lead to inconsistencies in product performance and increased production costs.
- Resistance Development: Like all pesticides, there is a risk that pests may develop resistance to the active ingredients used in slow and controlled-release formulations. This could undermine the long-term viability of these products, necessitating continuous research and development to stay ahead of resistance patterns.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: Developing countries are experiencing rapid agricultural expansion and modernization, which presents a significant opportunity for the adoption of slow and controlled-release pesticides. These regions often face intense pest pressures and are seeking sustainable solutions to increase crop yields without compromising environmental or human health. The market potential in these areas is substantial, with expected growth rates in pesticide usage surpassing 6-8% annually in countries like India and Brazil.
- Integration with Precision Agriculture: The trend towards precision agriculture, which uses data and analytics to optimize farming practices, is a natural fit for slow and controlled release technologies. By integrating these pesticides with IoT devices and sensors, farmers can achieve highly efficient pest control, tailored to the specific needs of their crops and local conditions. This integration can lead to a reduction in pesticide use by up to 25% while maintaining or improving crop yields.
- Innovations in Biodegradable Technologies: There is a growing demand for sustainable agricultural inputs, including pesticides that minimize environmental impact. Innovations in biodegradable and eco-friendly pesticide formulations not only meet regulatory requirements but also appeal to the environmentally conscious consumer. Developing products that degrade harmlessly increases market appeal and can capture a premium price point.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Strategic partnerships between pesticide manufacturers and agricultural technology companies can facilitate the development and distribution of slow and controlled-release products. These collaborations can leverage the strengths of each party, such as advanced R&D capabilities and extensive distribution networks, to accelerate market penetration and adoption.
- Regulatory Support and Incentives: As governments worldwide push for more sustainable farming practices, regulatory support and incentives for the use of environmentally friendly pesticides are increasing. Companies that develop and market slow and controlled-release pesticides can benefit from subsidies, tax breaks, and preferential purchasing policies, especially in markets that are aggressively addressing environmental concerns.
Key Players Analysis
Syngenta is actively engaged in the slow and controlled release pesticides sector, offering products like Demand CS insecticide, which uses iCAP technology to ensure up to 90 days of control against a variety of pests. This technology allows for sustained release and effective pest management, making it a reliable choice for professional pest control.
Arysta LifeScience Corporation is actively involved in the slow and controlled release pesticides sector, focusing on delivering advanced solutions that optimize pesticide use and minimize environmental impact. Their efforts are geared towards enhancing agricultural productivity by providing prolonged protection against pests, which is crucial in today’s context of limited arable land and increasing food demands.
DuPont, transitioning to Corteva Agriscience, integrates DuPont Crop Protection, DuPont Pioneer, and Dow AgroSciences, enhancing its market presence in slow and controlled-release pesticides. This alignment under the Corteva brand amplifies their focus on sustainable agriculture, aiming to boost farm productivity while nurturing consumer health through advanced crop protection technologies.
Kingenta Group is a prominent player in the slow and controlled-release fertilizers sector. Established in 1998, this Chinese high-tech enterprise focuses on the research, development, and marketing of various specialty fertilizers including slow/controlled-release products. These fertilizers are designed to match nutrient release with plant needs throughout the growing season, thereby minimizing nutrient loss and enhancing efficiency. Kingenta’s offerings are particularly noted for their role in sustaining nutrient levels in the soil, which supports optimal crop growth conditions.
Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. actively develops slow and controlled-release pesticides, enhancing crop protection through innovative formulations that prolong effectiveness and reduce environmental impact. This strategic focus is evident in their dedicated research and development efforts aimed at introducing advanced agricultural solutions that ensure sustainable farming practices.
Bayer AG is at the forefront of developing slow and controlled-release pesticides as part of their crop protection innovations. Their approach combines advanced chemical and biological products with digital and precision technologies to tailor solutions that meet specific agricultural needs. This strategy enhances farmer productivity and contributes significantly to global food security by effectively managing pests with a reduced environmental impact.
BASF SE is actively engaged in the slow and controlled release pesticides sector, focusing on innovative solutions like Fendona® CS, which employs advanced micro-mesh encapsulation technology. This technology effectively preserves the active ingredients, allowing them to act on pests over extended periods, enhancing both efficacy and sustainability in pest management. Such developments demonstrate BASF’s commitment to advancing agricultural productivity through scientifically enhanced products.
The Dow Chemical Company has developed innovative solutions in the sector of slow and controlled-release pesticides, focusing on enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of pesticide delivery. Their advancements help extend the duration of pesticide activity, reducing environmental impact, and improving crop yields by ensuring consistent and targeted pesticide release.
Conclusion
The market for slow and controlled-release pesticides is positioned for steady growth, driven by the escalating demand for sustainable agricultural practices and the need to reduce environmental impact. These innovative pesticide formulations not only enhance the efficiency of crop protection but also align with regulatory trends favoring environmentally friendly farming solutions.
As manufacturers continue to invest in research and development, the market is expected to witness further innovations and expansion. For stakeholders, this represents a promising investment opportunity, especially in regions where precision agriculture is becoming increasingly prevalent. Moving forward, the adoption of these advanced pesticide solutions is likely to become a standard practice, reflecting the industry’s commitment to sustainability and efficacy.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





