Table of Contents
Introduction
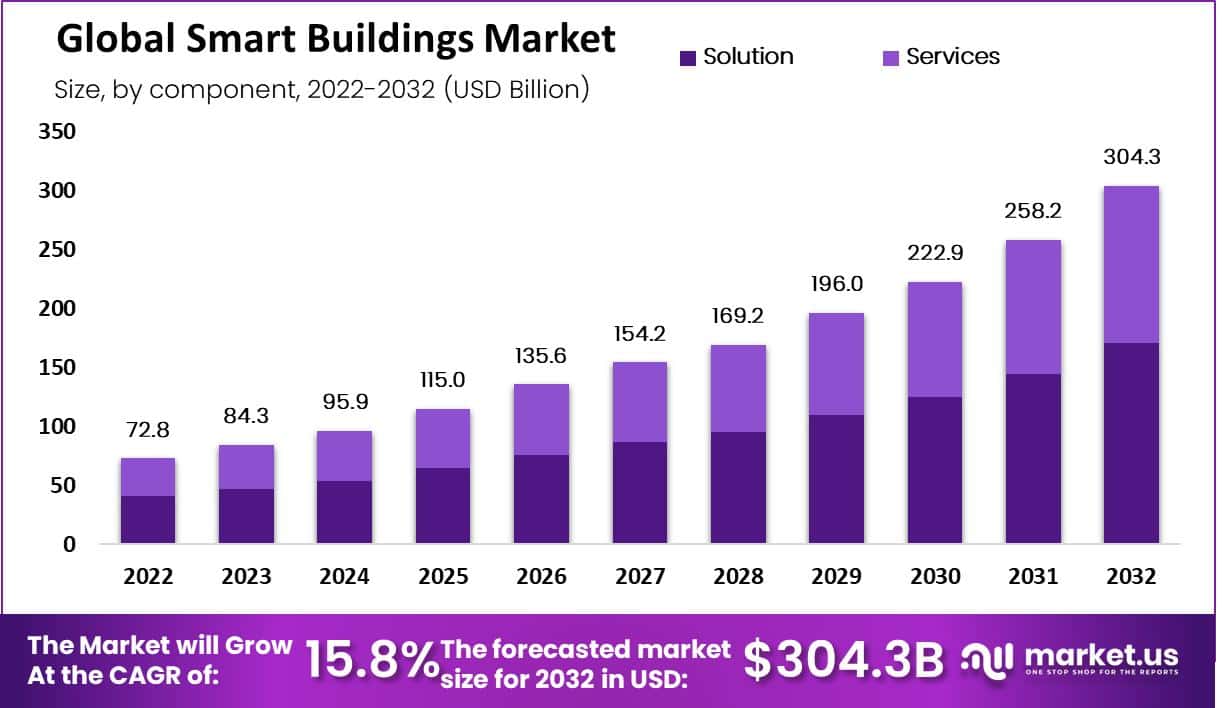
The global smart buildings market is rapidly gaining momentum, with a market size that was valued at approximately USD 72.8 billion in 2022. This market is projected to expand significantly, reaching an estimated USD 304.3 billion by 2032, driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.8% from 2022 to 2032. Smart buildings, which integrate advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing, are transforming the way buildings operate. These technologies enable buildings to become more energy-efficient, secure, and comfortable for occupants by optimizing energy use, automating systems, and providing real-time data analysis.
Several key factors are driving the growth of the smart buildings market. Firstly, the increasing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability is a major driver. Governments around the world are implementing stricter regulations and offering incentives for the construction of energy-efficient buildings, which is propelling the adoption of smart building technologies. Additionally, the rising demand for enhanced security systems, driven by concerns over safety and the need for better monitoring, is contributing to the market’s expansion. The growing adoption of IoT and AI technologies, which allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, is also fueling market growth.
Despite these growth factors, the smart buildings market faces several challenges. The high initial cost of implementing smart technologies can be a barrier for many organizations, particularly in developing regions. Additionally, concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity pose significant risks, as the increasing connectivity of building systems makes them more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols and interoperability among different systems can create complexities in the integration and management of smart building technologies.
Recent developments in the smart buildings market have focused on addressing these challenges and enhancing the capabilities of smart building systems. For instance, there has been a growing emphasis on developing more cost-effective solutions, such as modular and scalable smart building systems, which can be implemented in stages to reduce upfront costs. In terms of cybersecurity, advancements are being made in encryption and secure communication protocols to protect smart building systems from cyber threats. Additionally, the adoption of open standards and interoperability frameworks is helping to streamline the integration of different systems and devices within smart buildings.
ABB Ltd. In June 2023, ABB strengthened its smart building portfolio by acquiring Eve Systems GmbH, a leader in smart home products. This acquisition makes ABB a prominent player in the smart home market, particularly in technologies supporting the Matter and Thread standards. These standards enhance interoperability among smart home devices, which is crucial as the demand for energy-efficient retrofitting increases. The financial terms were not disclosed, but the move aligns ABB with the growing consumer focus on energy management and sustainability.
Cisco Systems Inc.: Cisco has been focusing on enhancing its smart building technologies through its Digital Building Solutions platform. This platform integrates building management systems with IT networks to optimize energy use and improve occupant comfort. Cisco’s approach involves leveraging its expertise in networking and security to create more efficient and secure building environments. Recent developments include partnerships and collaborations that integrate Cisco’s IoT technologies with other building systems to enhance connectivity and data management.
Hitachi Ltd.: Hitachi has been focusing on integrating its smart building technologies with its broader smart city initiatives. While specific recent acquisitions were not highlighted, Hitachi’s strategy includes using advanced data analytics and IoT to optimize building operations as part of its Lumada platform. This platform is designed to drive digital transformation across various sectors, including smart buildings, by leveraging AI, machine learning, and big data.
Smart Buildings Statistics
- Without action, energy demand in the building sector could increase by 30% by 2060 – the same as all the energy used by households in the US, the EU & China in 2015. iea.org
- Buildings use about 40% of global energy, 25% of global water, 40% of global resources, and they emit approximately 1/3 of GHG emissions. unep.org
- Energy used in the buildings sector—which includes residential and commercial structures—accounted for 20% of global delivered energy consumption in 2018.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects that global energy consumption in buildings will grow by 1.3% per year on average from 2018 to 2050. EIA.GOV
- Residential and commercial buildings consume approximately 60% of the world’s electricity. euenergycentre.org
- 220 million existing buildings – or 75% of the building stock –
- According to a World Green Building Council study, enhancing ventilation and indoor air quality can improve worker productivity by 8-11%, and enhancing lighting conditions can improve productivity by 23%.
- It has been estimated that approximately 36% of carbon emissions come from buildings, with 40% of the world’s energy consumption also coming from buildings.
- ABB’s Smart Buildings division is present in over 100 countries, with around 35 manufacturing sites delivering more than 1.5 million products a day.
- The smart building market in Latin America is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32.2% from 2021 to 2028.
- An estimated 25% of energy consumed in the commercial real estate sector is also wasted and around 75% of buildings in the EU are considered energy inefficient, according to research from smart building analyst Memoori.
- Given that Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) and lighting can account for up to 50% of energy use in typical commercial buildings there is a clear case for leveraging IoT and M2M smart building technologies to reduce energy consumption – as much as 50% in some estimations.
- Manufacturers of sensors used in smart buildings will also see demand skyrocket, to exceed 1 billion units annually in 2026 from 360 million in 2022; representing a growth of 204%.
Emerging Trends
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Smart buildings are increasingly utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to automate building management systems (BMS). These technologies enable predictive maintenance, optimize energy consumption, and enhance security. For instance, AI-driven systems can analyze data from various sensors to predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: With buildings accounting for nearly 40% of global carbon emissions, there is a significant push toward energy-efficient and sustainable building practices. Smart buildings are incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, and energy storage solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Additionally, advanced energy management systems are being deployed to monitor and optimize energy usage in real-time, contributing to significant cost savings and sustainability.
- IoT-Enabled Smart Buildings: The Internet of Things (IoT) is at the core of smart buildings, enabling connectivity between various building systems such as HVAC, lighting, security, and more. IoT devices collect data that can be analyzed to improve building operations, enhance occupant comfort, and ensure safety. The trend towards more IoT integration is expected to continue, with smart sensors and devices becoming more prevalent in both new constructions and retrofits.
- Enhanced Security and Safety Features: Security is a growing concern in smart buildings, leading to the development of more sophisticated security systems. These include facial recognition, biometric access controls, and AI-powered surveillance systems that can detect unusual activities in real time. Moreover, the focus on cybersecurity is intensifying as building systems become more interconnected and data-rich.
- Health and Wellbeing of Occupants: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the trend of smart buildings focusing on the health and well-being of occupants. This includes improved indoor air quality (IAQ), contactless technologies, and smart HVAC systems that adjust ventilation based on occupancy levels. Buildings are now designed with occupant health in mind, utilizing technologies that monitor and improve air quality, reduce the spread of germs, and ensure a comfortable environment.
- Retrofitting Existing Buildings: Retrofitting older buildings with smart technologies is becoming a significant trend. As governments and organizations push for sustainability, retrofitting allows older buildings to meet modern energy efficiency standards without the need for new construction. This includes upgrading HVAC systems, installing smart lighting, and integrating building management systems that connect older infrastructure to the latest technologies.
- Adoption of Smart Building Standards: The rise of global standards, such as the WELL Building Standard and LEED certification, is driving the adoption of smart building practices. These standards encourage the integration of technologies that enhance energy efficiency, sustainability, and occupant well-being. Compliance with such standards is becoming a key factor in the design and operation of smart buildings.
Use Cases
- Commercial Office Buildings: Energy Management In commercial office buildings, smart systems are used to optimize energy usage by controlling HVAC systems, lighting, and other energy-consuming devices. For example, Edge Amsterdam, a smart office building in the Netherlands, uses 28,000 sensors to monitor light, temperature, humidity, and occupancy. This system has reduced the building’s energy consumption by 70% compared to traditional office buildings. Occupant Comfort In addition to energy savings, smart buildings enhance occupant comfort by adjusting lighting and temperature based on individual preferences. The same sensors used in the Edge Amsterdam can personalize workspaces, contributing to increased productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Smart Homes: Home Automation: Smart homes are equipped with systems that automate lighting, heating, and security based on the resident’s behavior and preferences. For instance, Nest Thermostats learn the user’s schedule and adjust the temperature accordingly, leading to an average energy saving of 10-15% on heating and cooling bills. Smart security systems, like Ring Video Doorbells, provide homeowners with real-time alerts and video footage of their property. These systems can be integrated with other smart devices, such as smart locks and alarms, to provide comprehensive home security solutions.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: In smart hospitals, such as the Ospedale dell’Angelo in Venice, IoT devices monitor patients’ vital signs and environmental conditions. This data helps healthcare providers make informed decisions in real time, improving patient outcomes. The hospital also uses smart systems to optimize energy use, contributing to significant cost savings. Smart buildings in healthcare settings also play a critical role in infection control. For example, smart HVAC systems can adjust airflow and filtration based on real-time data to reduce the spread of airborne diseases.
- Educational Institutions: Educational institutions are using smart technologies to create more interactive and efficient learning environments. For instance, Arizona State University uses smart building technologies to monitor energy usage and optimize classroom conditions. This has led to a reduction in energy consumption by 15%, while also enhancing the learning environment through better lighting and temperature control. Universities like MIT have implemented smart security systems that integrate video surveillance, access control, and emergency notification systems. These systems enhance campus safety by providing real-time data and analytics to security personnel.
- Retail Stores In retail, smart building technologies are used to enhance the shopping experience. Amazon Go stores, for example, use a combination of sensors, computer vision, and deep learning to enable cashier-less checkouts. This not only improves customer convenience but also provides data on shopping patterns that can be used to optimize store layouts and inventory management.
- Energy Efficiency: Retail stores like Walmart have implemented smart energy management systems that monitor and control lighting, refrigeration, and HVAC systems across multiple locations. These systems have helped Walmart reduce its energy consumption by 20% per square foot across its U.S. stores.
Major Challenges
- High Initial Costs: One of the primary challenges of implementing smart building technologies is the high upfront cost. These costs include the installation of IoT devices, sensors, automation systems, and the necessary software to manage these components. Retrofitting existing buildings with smart technologies can be particularly expensive, making it a less attractive option for some building owners and developers. For instance, while the long-term savings from energy efficiency and reduced maintenance can offset these costs, the initial investment remains a barrier for many.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: As smart buildings rely heavily on interconnected devices and the collection of vast amounts of data, concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity are significant. Smart building systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can compromise sensitive data and disrupt building operations. The complexity of securing a network of interconnected devices also adds to the challenge, particularly in protecting against unauthorized access and ensuring the integrity of data.
- Interoperability Issues: Another major challenge is the lack of standardization and interoperability among different smart building systems and devices. Many smart devices and systems are designed by different manufacturers and often use proprietary protocols, making it difficult to integrate them seamlessly into a single, cohesive system. This lack of interoperability can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs, as building operators may need to invest in multiple platforms to manage different systems effectively.
- Complexity in Implementation and Maintenance The complexity of implementing and maintaining smart building systems is another challenge. These systems require specialized knowledge to install, configure, and maintain, which can increase operational costs and the need for skilled personnel. Additionally, as technologies evolve rapidly, keeping systems up to date can be challenging and costly.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Government Initiatives and Regulations: Governments around the world are increasingly focused on reducing carbon emissions, which presents a significant opportunity for the growth of smart buildings. Regulations mandating energy efficiency and incentives for green building practices are driving the adoption of smart technologies. For example, the European Union’s Green Deal and the U.S. government’s focus on sustainable infrastructure are pushing for the modernization of existing buildings and the construction of new smart buildings that comply with stricter energy efficiency standards.
- Rising Demand for Energy Efficiency: As energy costs continue to rise, the demand for energy-efficient buildings is growing. Smart building technologies, such as automated energy management systems and IoT-enabled devices, allow for significant reductions in energy consumption. For instance, buildings equipped with smart energy management systems can reduce energy usage by up to 25%, making them highly attractive to businesses and property owners looking to cut costs.
- Growth of Smart Cities: The global push towards developing smart cities provides a robust growth opportunity for the smart buildings market. Smart buildings are a key component of smart cities, as they integrate with broader urban infrastructure to optimize resources, improve sustainability, and enhance the quality of life for residents. The development of smart cities in regions such as Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America is expected to drive the demand for smart buildings over the next decade.
- Advancements in AI and IoT: The ongoing advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are creating new opportunities for the smart buildings market. AI-driven analytics and IoT connectivity enable more precise control over building systems, predictive maintenance, and enhanced occupant comfort, leading to smarter and more efficient buildings.
Key Player Analysis
ABB Ltd. has been actively expanding its presence in the smart buildings sector, focusing on innovative technologies that enhance energy efficiency, security, and comfort in buildings. In June 2023, ABB acquired Eve Systems GmbH, a leading smart home product company, to strengthen its portfolio in home automation and smart building solutions. This acquisition positions ABB as a leader in technologies supporting the Matter and Thread standards, which are critical for interoperability among smart devices. Additionally, ABB has been integrating its ABB Ability™ platform, which combines IoT, AI, and cloud computing, to optimize building management systems. This platform has been instrumental in reducing energy consumption and enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities in smart buildings
In 2023, Cisco Systems Inc. continued to expand its influence in the smart buildings sector by leveraging its expertise in networking, security, and IoT technologies. Throughout the year, Cisco focused on enhancing its Cisco Smart Building Solutions platform, which integrates IT and building management systems to create more efficient and secure building environments. For example, in March 2023, Cisco introduced updates to its Catalyst Digital Building Series switches, designed to support PoE (Power over Ethernet) for IoT devices, enabling easier integration of smart lighting, HVAC systems, and security cameras. By June 2023, Cisco had partnered with several real estate developers to deploy these technologies in new smart building projects across North America and Europe. These initiatives are part of Cisco’s broader strategy to drive digital transformation in the built environment, offering solutions that not only improve energy efficiency but also enhance occupant experiences.
In 2023, Emerson Electric Co. made significant strides in the smart buildings sector by focusing on expanding its automation and control technologies. In January 2023, Emerson completed the acquisition of Verdant, a leader in energy management solutions, particularly for the hotel and hospitality industries. This acquisition allowed Emerson to enhance its smart building offerings by integrating Verdant’s cloud-based platform with its products, which are designed to optimize energy use and improve environmental sustainability in buildings. In May 2023, Emerson further strengthened its position by updating its Sensi product line, which includes smart thermostats that are increasingly being adopted in both residential and commercial buildings for better energy management. These efforts underscore Emerson’s commitment to advancing smart building technologies that promote energy efficiency and operational intelligence.
In 2023, Hitachi Ltd. continued to make significant contributions to the smart buildings sector by integrating advanced digital technologies through its Lumada platform. In March 2023, Hitachi announced the expansion of its Lumada-based solutions, which leverage AI, IoT, and big data analytics to optimize building operations and enhance energy efficiency. These solutions have been deployed in several smart city projects, particularly in Asia, where Hitachi plays a crucial role in developing interconnected urban environments. In July 2023, Hitachi further advanced its smart building initiatives by collaborating with local governments in Japan to retrofit existing public buildings with smart technologies aimed at reducing energy consumption and improving overall building management. These efforts reflect Hitachi’s broader strategy to lead in the digital transformation of infrastructure, making buildings more sustainable, efficient, and responsive to the needs of their occupants.
In 2023, Honeywell International Inc. continued to advance its position in the smart buildings sector by enhancing its suite of intelligent building solutions. In February 2023, Honeywell introduced updates to its Forge enterprise performance management software, which now includes enhanced capabilities for energy optimization and predictive maintenance. These updates allow building operators to reduce energy consumption by up to 25% and improve operational efficiency through real-time data analysis and AI-driven insights. In April 2023, Honeywell launched its Sustainable Buildings Solutions initiative, focusing on integrating renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies into building management systems. This initiative is part of Honeywell’s broader commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2035, with a significant emphasis on making buildings smarter and more sustainable. These developments demonstrate Honeywell’s ongoing commitment to leveraging digital technologies to create more efficient and environmentally friendly building environments.
In 2023, Johnson Controls continued to lead in the smart buildings sector by expanding its digital solutions and sustainable building technologies. In March 2023, the company introduced enhancements to its OpenBlue platform, which integrates AI, IoT, and cloud technologies to optimize building operations, improve energy efficiency, and ensure occupant comfort. The new updates focused on predictive maintenance and advanced energy management, helping clients reduce their carbon footprint by up to 30%. In June 2023, Johnson Controls announced a partnership with several global cities to implement smart building solutions aimed at achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. This initiative reflects Johnson Controls’ commitment to driving innovation in smart buildings, particularly through technologies that promote sustainability and efficiency in urban environments.
In 2023, Legrand SA made significant advancements in the smart buildings sector by focusing on expanding its range of connected solutions that enhance building efficiency and user experience. In February 2023, Legrand launched new additions to its Eliot program, which aims to accelerate the development of connected products in smart buildings. These new products include advanced lighting controls and energy management systems designed to reduce energy consumption and improve sustainability. By May 2023, Legrand had also introduced its latest Legrand Integrated Solutions (LIS) platform, which integrates various building systems—such as lighting, HVAC, and security—into a unified smart building management system. This platform is aimed at making buildings more responsive to occupant needs while reducing operational costs. Legrand’s ongoing innovation in the smart buildings sector reflects its commitment to driving energy efficiency and enhancing connectivity in both residential and commercial buildings.
In 2023, Schneider Electric SE continued to solidify its position in the smart buildings sector by enhancing its range of digital energy management and automation solutions. In January 2023, Schneider Electric launched new features for its EcoStruxure™ platform, which integrates IoT, AI, and cloud computing to optimize building energy use, improve sustainability, and increase operational efficiency. These updates were particularly focused on expanding the platform’s capabilities in predictive maintenance and energy monitoring, helping building operators reduce energy consumption by up to 20%. In April 2023, Schneider Electric announced a strategic partnership with several global real estate firms to implement its smart building solutions in new urban developments, furthering its commitment to promoting sustainable and resilient infrastructure. These efforts are part of Schneider Electric’s broader goal to drive digital transformation in the built environment, making buildings smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable.
In 2023, Siemens AG continued to drive innovation in the smart buildings sector by expanding its range of digital solutions aimed at enhancing energy efficiency and building automation. In March 2023, Siemens introduced new enhancements to its Desigo building management system, which now includes advanced analytics and AI capabilities to optimize energy usage and improve building operations. This update allows facility managers to reduce energy consumption by up to 30% while also improving occupant comfort. In June 2023, Siemens partnered with several global tech firms to integrate IoT and edge computing technologies into its smart building solutions, further enabling real-time data processing and decision-making. These initiatives are part of Siemens’ broader strategy to lead the digital transformation of building infrastructure, making buildings more sustainable, intelligent, and responsive to the needs of occupants.
In 2023, Telit, a global leader in the Internet of Things (IoT), made significant strides in the smart buildings sector by enhancing its IoT connectivity solutions, which are critical for integrating and managing smart building systems. In February 2023, Telit introduced its OneEdge™ platform with new features designed to simplify the deployment of IoT devices in smart buildings. This platform supports a wide range of building management applications, including energy monitoring, HVAC control, and security systems, by providing reliable, scalable, and secure IoT connectivity. By May 2023, Telit had also expanded its collaboration with several building automation companies to integrate its IoT modules into smart building infrastructure, enabling real-time data collection and analysis to optimize building operations. These developments underscore Telit’s commitment to advancing the smart buildings market by providing the essential connectivity and management tools needed to support the growing demand for intelligent, energy-efficient buildings.
In 2023, IBM Corporation advanced its efforts in the smart buildings sector by leveraging its expertise in artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing. In March 2023, IBM introduced new features to its IBM Maximo application suite, specifically designed for smart building management. These enhancements focused on using AI-driven analytics to predict maintenance needs and optimize energy consumption, helping building operators reduce costs and improve efficiency. By June 2023, IBM had also expanded its partnerships with leading real estate and facility management firms to implement its smart building technologies across various commercial and industrial properties. These developments are part of IBM’s broader strategy to integrate AI and IoT into building management systems, enabling smarter, more sustainable, and responsive environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the smart buildings market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for energy efficiency, enhanced occupant comfort, and advanced operational control. This expansion is fueled by technological advancements such as the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence, and building automation systems. Key market players are investing significantly in R&D to develop innovative solutions that address sustainability concerns and improve building management.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





