Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Smart Meters Market Overview
- History of Smart Meters
- Smart Meter Specifications Statistics
- Statistics of Smart Meter Deployment
- Residential/Domestic Smart Meter Statistics
- Smart Meter Coverage Trends
- Storage Capacity of Smart Meter Statistics
- Key Smart Meter Investments Statistics
- Key Smart Meter Benefits Statistics
- Concerns About Smart Meters
- Perceived Disadvantages About Smart Meters
- Regulations for Smart Meters
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Smart Meter Statistics: Smart meters are advanced digital devices used to measure and record energy, gas, or water consumption, transmitting data automatically to utility providers.
Unlike traditional analog meters, smart meters enable accurate billing, real-time monitoring, and remote data collection, improving operational efficiency and consumer awareness.
They also play a crucial role in smart grid systems by offering detailed usage patterns that help balance supply and demand.
While smart meters provide significant benefits, such as precise billing and enhanced grid management. Challenges include privacy concerns, initial costs, and technical issues.
Overall, smart meters represent a vital advancement in utility management, enhancing both efficiency and transparency.
Editor’s Choice
- The global smart meter market revenue reached USD 26.5 billion in 2023.
- The market for smart meters is predominantly driven by two key end-user segments. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and Automatic Meter Reading (AMR). Advanced Metering Infrastructure holds the majority share, accounting for 59% of the market.
- The global smart electricity meter market revenue is anticipated to reach USD 16 billion by 2027.
- Smart meters typically operate at a nominal voltage of 120V to 240V and can handle current ratings up to 320A. As seen in models like the Aclara I-210+ smart grid meter.
- By 2020, the number of smart meters installed worldwide had surged to 1,645 million units.
- As of 2021, the deployment of residential smart meters has varied significantly across different countries and regions. China leads with a full deployment, achieving 100% penetration of smart meters in households.
- Outside Europe, India‘s Ministry of Power aims to replace all traditional meters with smart meters by 2025.
Smart Meters Market Overview
Global Smart Meter Market Size Statistics
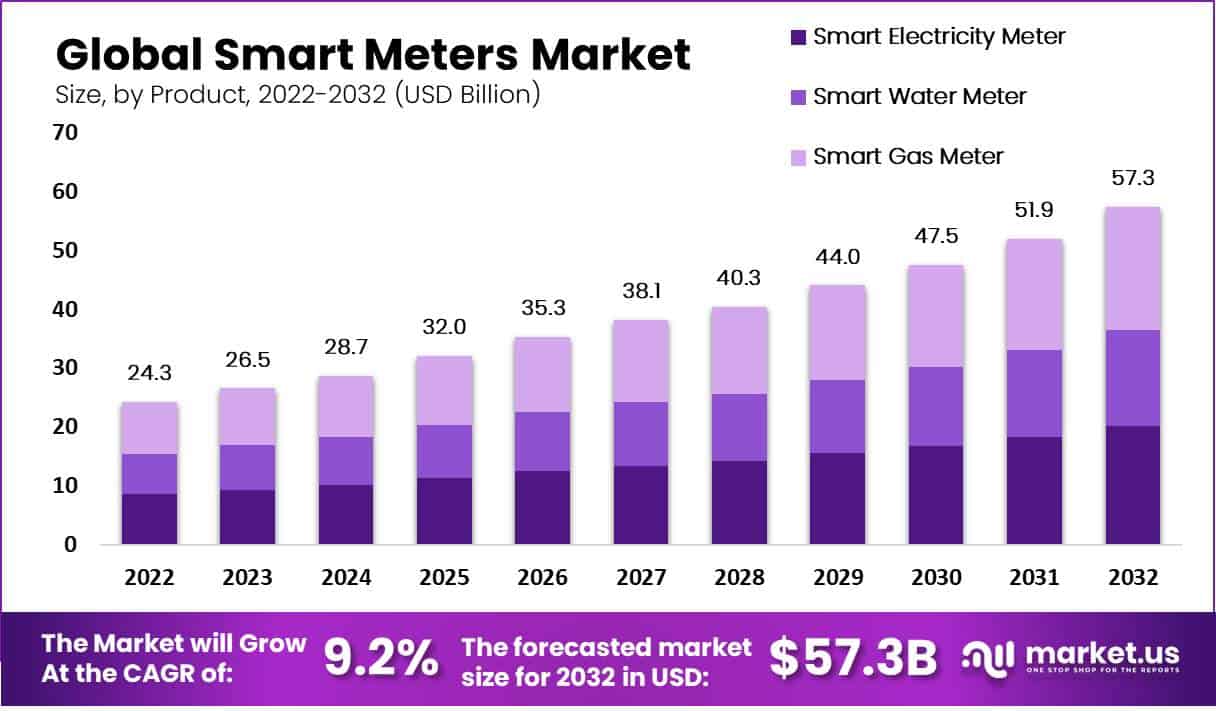
- The global smart meter market has demonstrated a consistent upward trajectory in recent years at a CAGR of 9.20%.
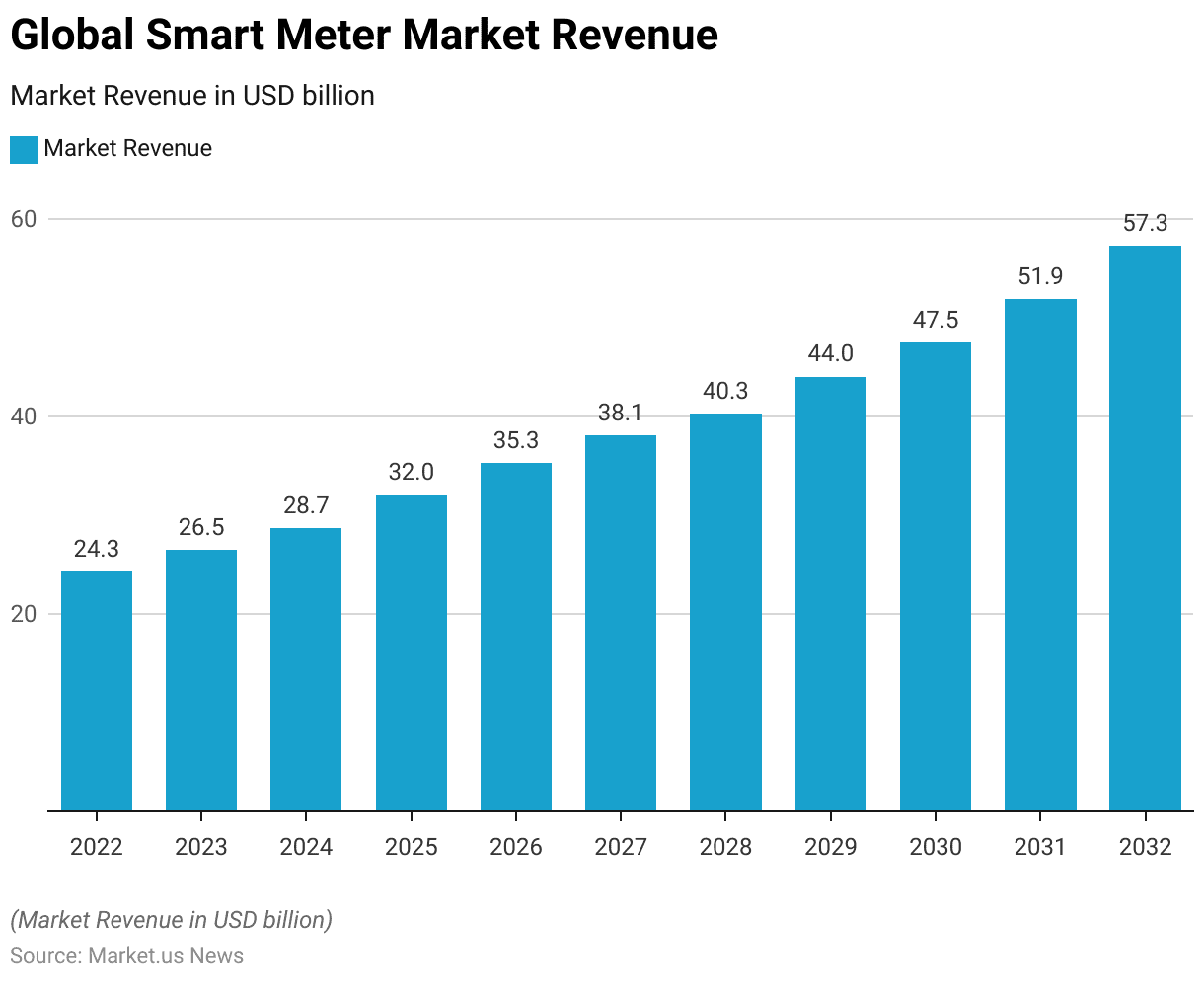
- In 2022, the market revenue was recorded at USD 24.3 billion.
- This figure rose to USD 26.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to further increase to USD 28.7 billion in 2024.
- By 2025, the market is expected to reach USD 32.0 billion, followed by USD 35.3 billion in 2026.
- The upward trend continues with an anticipated revenue of USD 38.1 billion in 2027 and USD 40.3 billion in 2028.
- By 2029, the market is forecasted to achieve USD 44.0 billion, and in 2030. It is expected to reach USD 47.5 billion.
- The market is projected to continue its growth, attaining USD 51.9 billion by 2031 and further expanding to USD 57.3 billion by 2032.
- This consistent growth highlights the increasing adoption and demand for smart meters globally.
(Source: market.us)
Smart Meter Market Share – By End-user Statistics
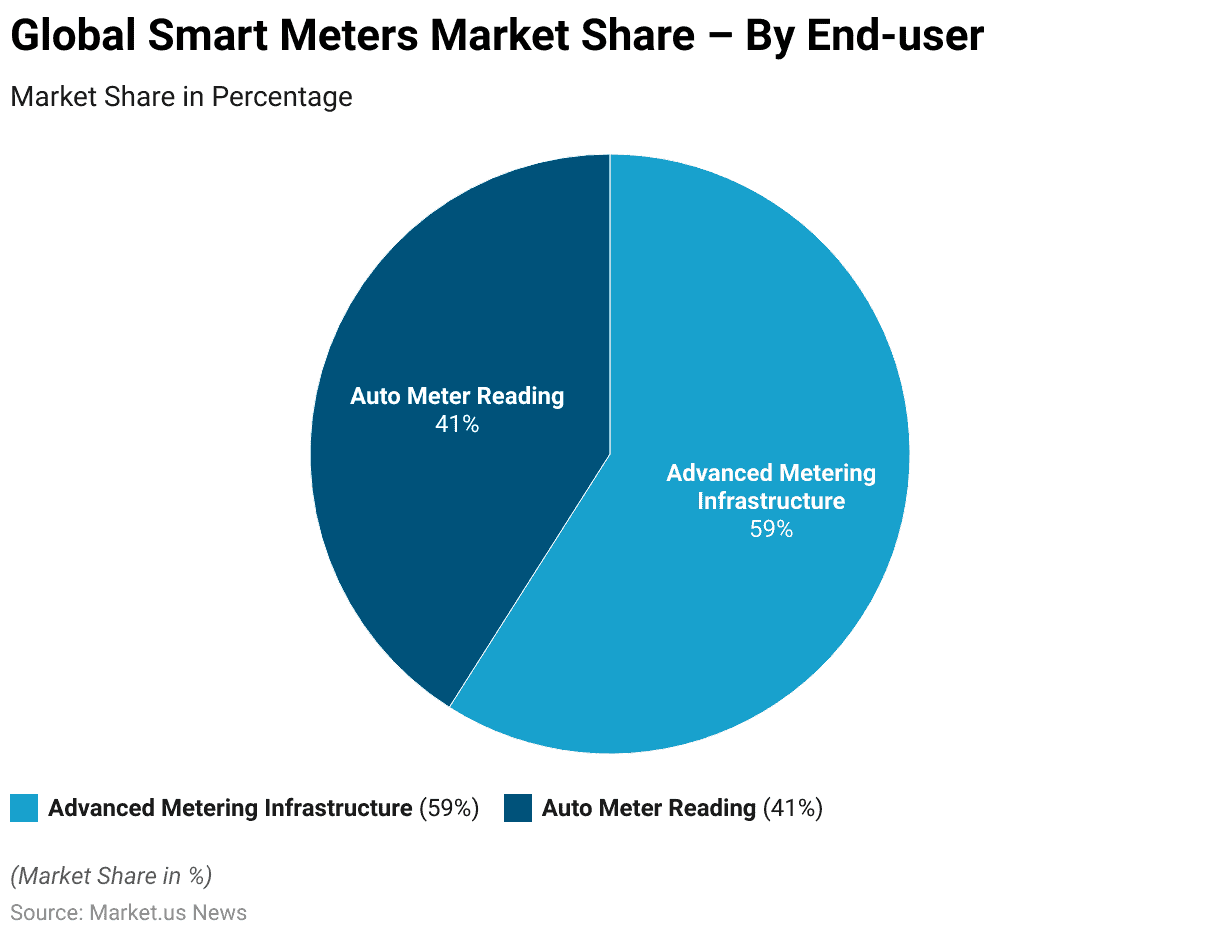
- The market for smart meters is predominantly driven by two key end-user segments. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and Automatic Meter Reading (AMR).
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure holds the majority share, accounting for 59% of the market. This significant share reflects the growing adoption of AMI systems. Which offer enhanced capabilities for real-time data collection, analysis, and management.
- On the other hand, Automatic Meter Reading represents 41% of the market share. Although AMR systems are less prevalent compared to AMI. They still play a crucial role in the market by providing efficient and accurate meter reading solutions.
- Together, these segments illustrate the diverse applications and growing importance of smart meter technologies in the energy sector.
(Source: market.us)
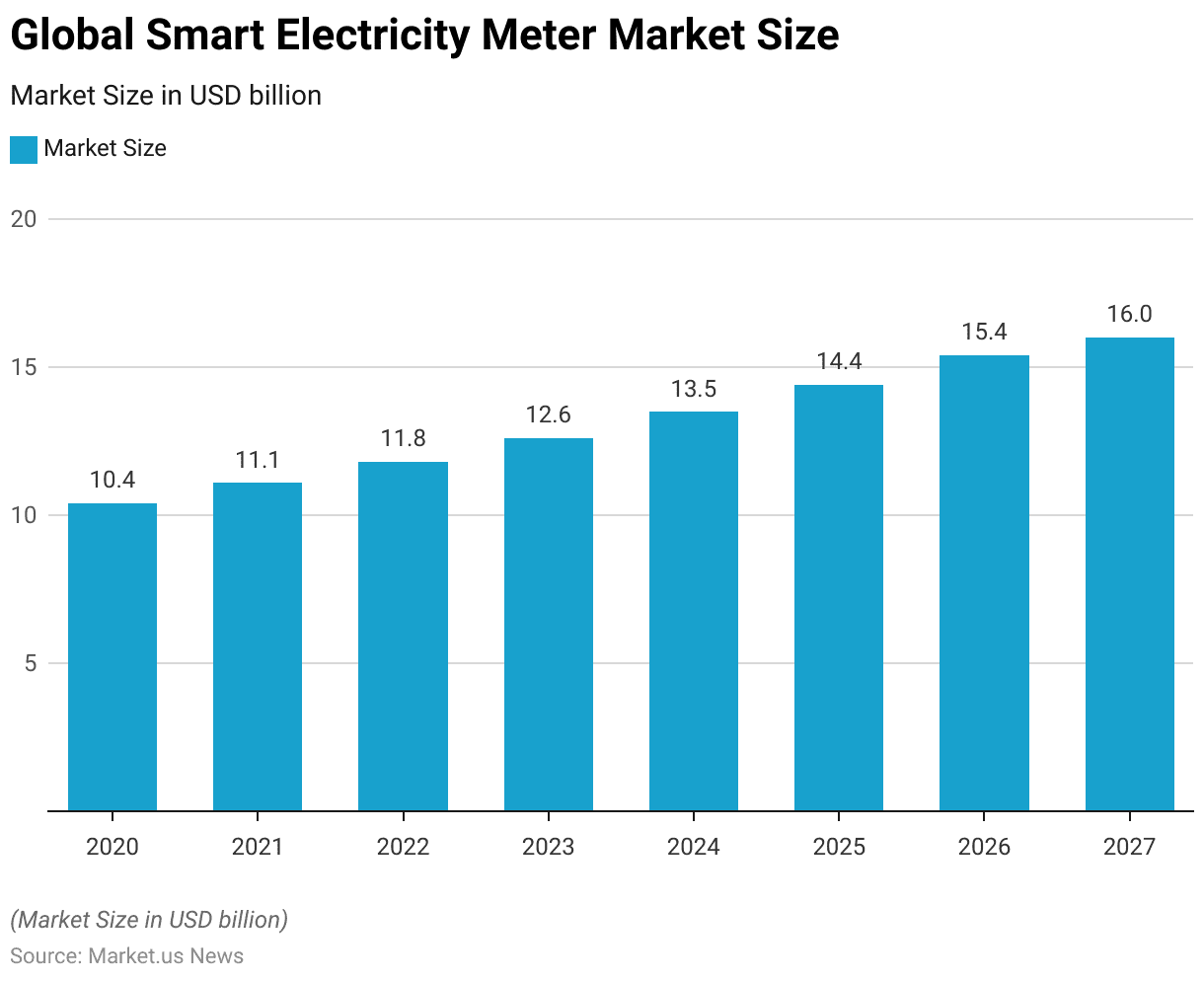
Smart Electricity Meter Market Overview Statistics
- The global smart electricity meter market has shown a steady growth pattern over the past few years. In 2020, the market size was valued at USD 10.4 billion.
- This figure increased to USD 11.1 billion in 2021 and continued to rise, reaching USD 11.8 billion in 2022.
- The upward trend persisted, with the market size expanding to USD 12.6 billion in 2023.
- Projections indicate that this growth will continue. The market is expected to reach USD 13.5 billion in 2024, USD 14.4 billion in 2025, and USD 15.4 billion in 2026.
- By 2027, the market size is anticipated to attain USD 16 billion.
- This consistent growth underscores the increasing global adoption of smart electricity meters and the rising demand for efficient energy management solutions.
(Source: Statista)
History of Smart Meters
- The history of smart meters reflects a significant evolution in metering technology, starting with the advent of traditional mechanical meters in the late 19th century.
- By the 1970s, automated meter reading (AMR) technology began to emerge, facilitating remote reading of consumption data.
- The early 2000s marked the introduction of advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), integrating two-way communication capabilities. Which allowed for real-time monitoring and data transmission.
- The deployment of smart meters accelerated around 2006, driven by initiatives to modernize energy grids and improve efficiency.
- By 2012, field testing of smart meters like the Sensus model in Saskatchewan highlighted both the potential and challenges. Including instances of overheating that led to recalls and further refinements.
- Today, smart meters are crucial for integrating renewable energy sources and enhancing grid reliability. Forming a backbone of the modern smart grid infrastructure.
(Sources: Constellation, Global News)
Smart Meter Specifications Statistics
- Smart meters, integral to modernizing energy grids, come with a range of technical specifications designed to meet various operational demands.
- These devices typically operate at a nominal voltage of 120V to 240V and can handle current ratings up to 320A, as seen in models like the Aclara I-210+ smart grid meter.
- They support frequencies of 50 or 60 Hz and are designed to function within a wide temperature range, from -40°C to +85°C, and relative humidity up to 95%, ensuring reliability in diverse environmental conditions.
- Additional specifications include high measurement accuracy with voltage accuracy of ±0.5% and current/power/energy accuracy of ±1%, along with communication interfaces such as RF Mesh and PLC for versatile connectivity.
- Compliance with standards like ANSI C12.1, C12.20, and UL2735 further underscores their reliability and precision in residential and commercial applications.
(Sources: Central Electricity Authority, Hubbell)
Statistics of Smart Meter Deployment
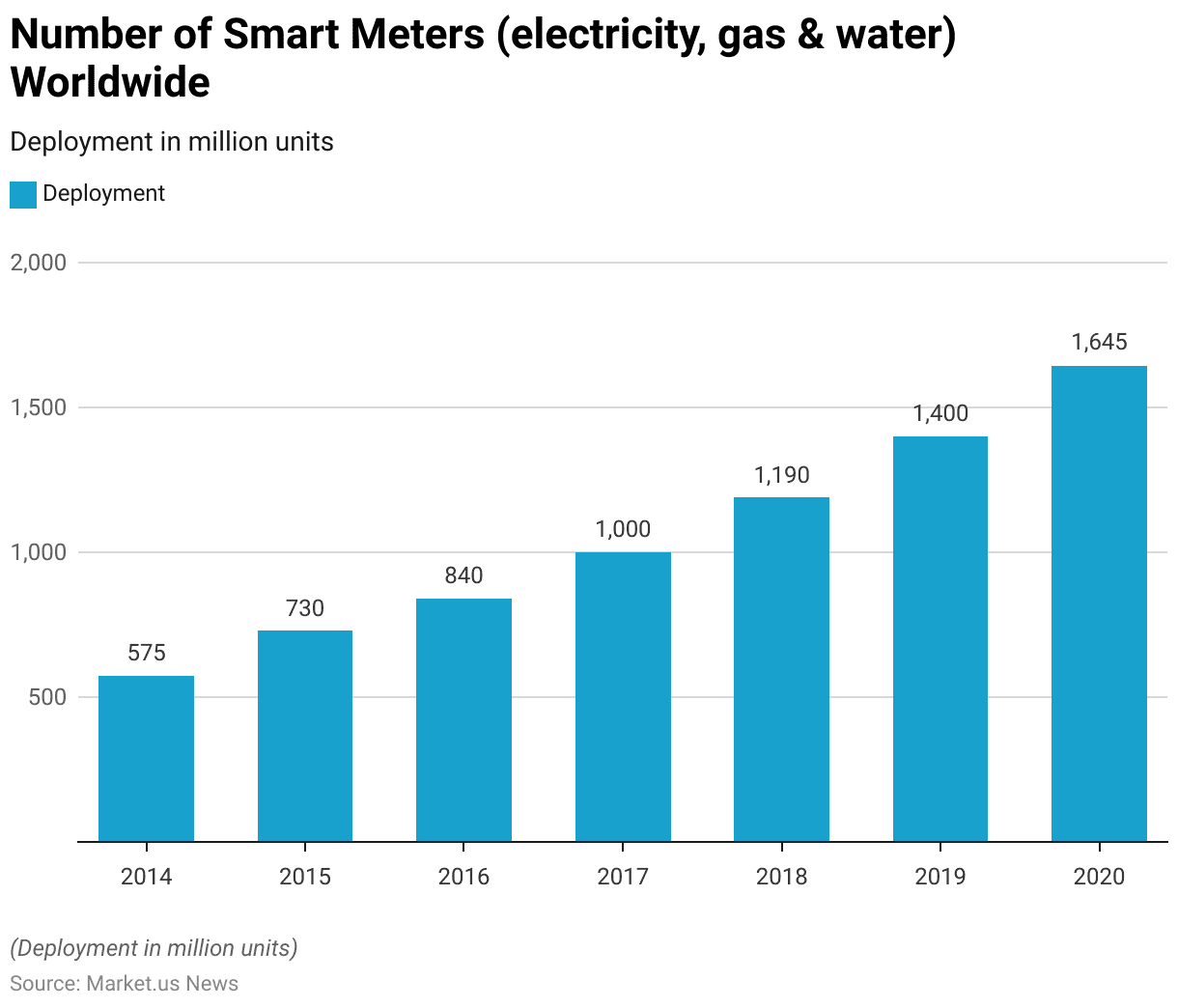
Smart Meter Deployment Worldwide Statistics
- The deployment of smart meters, encompassing electricity, gas, and water meters, has significantly increased worldwide from 2014 to 2020.
- In 2014, the number of smart meters installed globally was 575 million units.
- This number grew to 730 million units in 2015 and further to 840 million units in 2016.
- By 2017, the deployment had reached a milestone of 1,000 million units.
- The growth trajectory continued, with 1,190 million units in 2018 and 1,400 million units in 2019.
- By 2020, the number of smart meters installed worldwide had surged to 1,645 million units.
- This remarkable growth highlights the rapid adoption of smart metering technology across various utilities, driven by the need for enhanced data accuracy, efficient energy management, and improved resource allocation.
(Source: Statista)
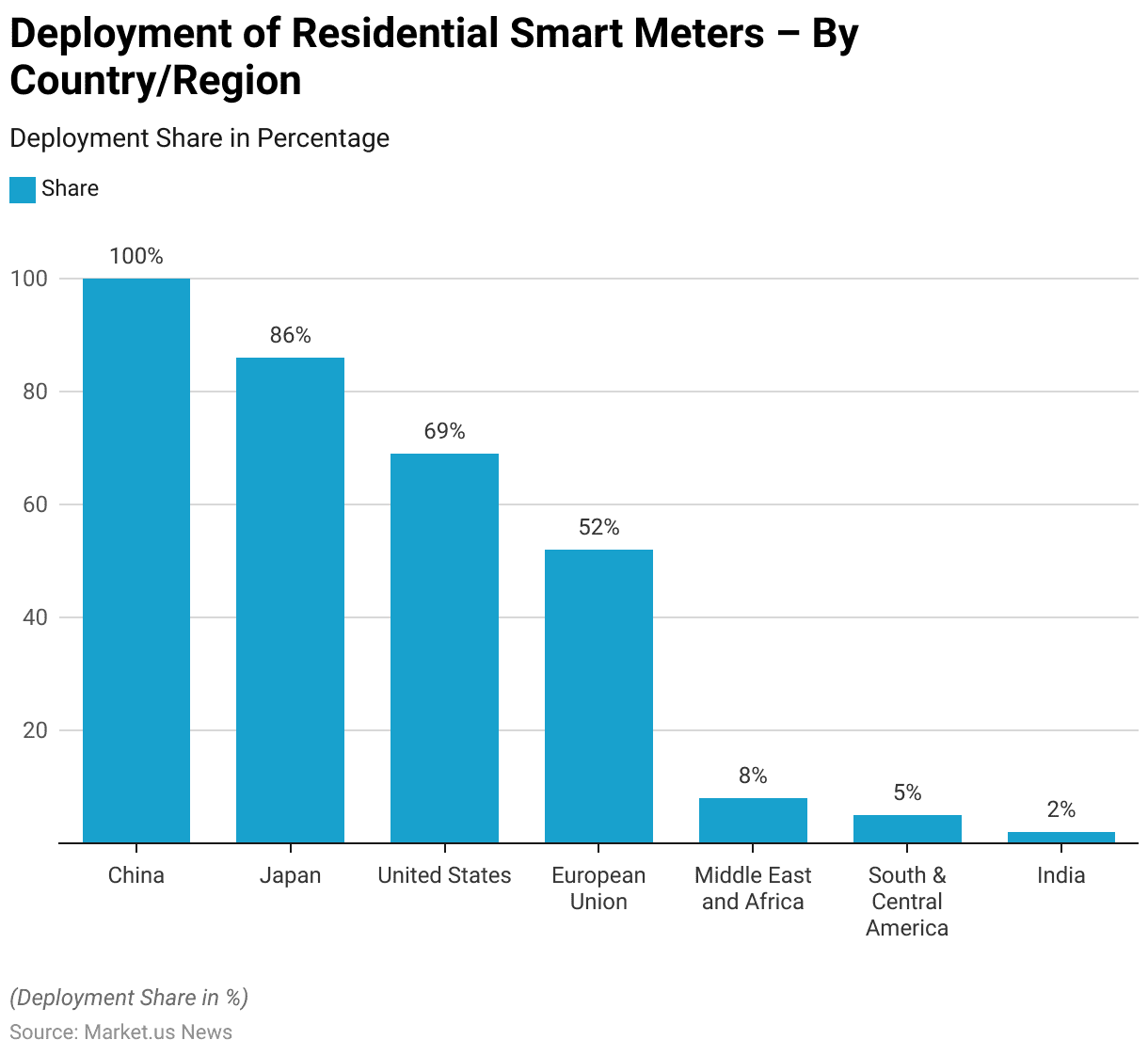
Deployment of Residential Smart Meter – By Country/ Region Statistics
- As of 2021, the deployment of residential smart meters has varied significantly across different countries and regions.
- China leads with a full deployment, achieving 100% penetration of smart meters in households.
- Japan follows with 86% of households equipped with smart meters.
- In the United States, 69% of households have adopted this technology.
- The European Union has a 52% deployment rate, reflecting substantial progress but still leaving room for further adoption.
- In contrast, the Middle East and Africa region has a significantly lower penetration rate of 8%, while South and Central America have achieved a 5% deployment rate.
- India lags, with only 2% of households having smart meters installed.
- This data underscores the disparities in smart meter adoption across regions, influenced by varying levels of infrastructure development, regulatory frameworks, and market dynamics.
(Source: International Energy Agency)
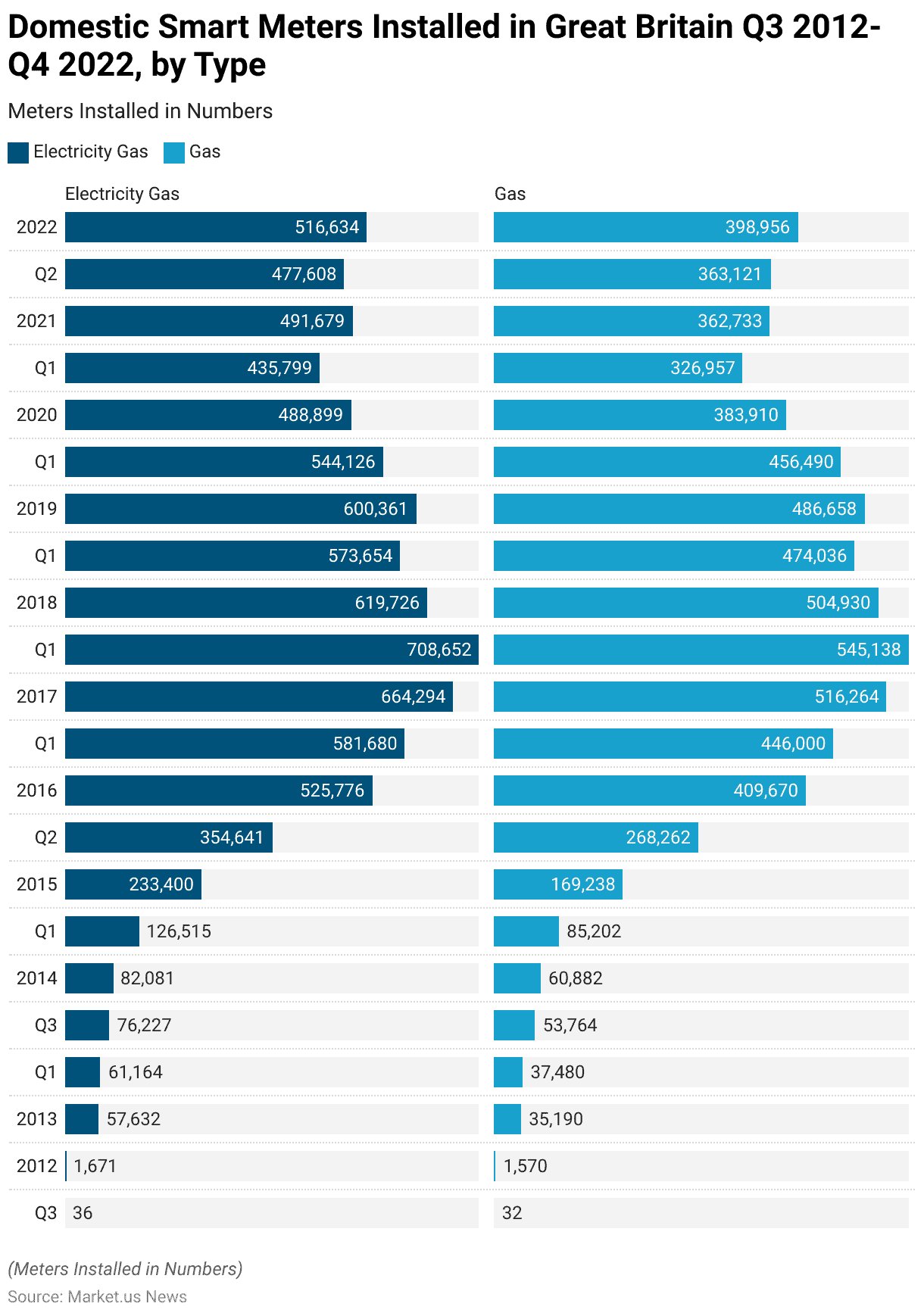
Residential/Domestic Smart Meter Statistics
Domestic Smart Meter Installed – By Type Statistics
2012-2016
- From the third quarter of 2012 to the fourth quarter of 2022, the installation of domestic smart meters by large energy suppliers in Great Britain saw substantial growth. In the third quarter of 2012, only 36 electricity and 32 gas smart meters were installed.
- By the end of 2012, these numbers had increased significantly to 1,671 and 1,570, respectively. The upward trend continued, with 57,632 electricity and 35,190 gas smart meters installed by the third quarter of 2013.
- This growth persisted into 2014, with installations reaching 61,164 for electricity and 37,480 for gas in the first quarter and further rising to 82,081 and 60,882, respectively, by the fourth quarter.
- The first quarter of 2015 saw a marked increase, with 126,515 electricity and 85,202 gas meters installed. This upward momentum was sustained through 2015, culminating in 233,400 electricity and 169,238 gas meters by the fourth quarter.
- The pace of installations continued to accelerate, with 354,641 electricity and 268,262 gas meters in the second quarter of 2016 and peaking at 525,776 electricity and 409,670 gas meters by the end of 2016.
2017-2022
- In 2017, installations reached 581,680 for electricity and 446,000 for gas in the first quarter, growing to 664,294 and 516,264 by the third quarter. The first quarter of 2018 saw 708,652 electricity and 545,138 gas meters installed.
- However, there was a decline by the fourth quarter of 2018, with installations dropping to 619,726 for electricity and 504,930 for gas. This downward trend continued into 2019, with 573,654 electricity and 474,036 gas meters in the first quarter, although a slight increase was observed in the third quarter.
- The first quarter of 2020 recorded 544,126 electricity and 456,490 gas meters, with a noticeable decline by the third quarter to 488,899 and 383,910, respectively. The downward trend persisted into 2021, with installations reaching 435,799 for electricity and 326,957 for gas in the first quarter.
- By the fourth quarter, the numbers slightly recovered to 491,679 and 362,733. In 2022, installations remained relatively stable, with 477,608 electricity and 363,121 gas meters in the second quarter and concluding the year with 516,634 and 398,956, respectively, in the fourth quarter.
- This data highlights the dynamic nature of smart meter deployment in Great Britain, marked by initial rapid growth, subsequent fluctuations, and eventual stabilization.
(Source: Statista)
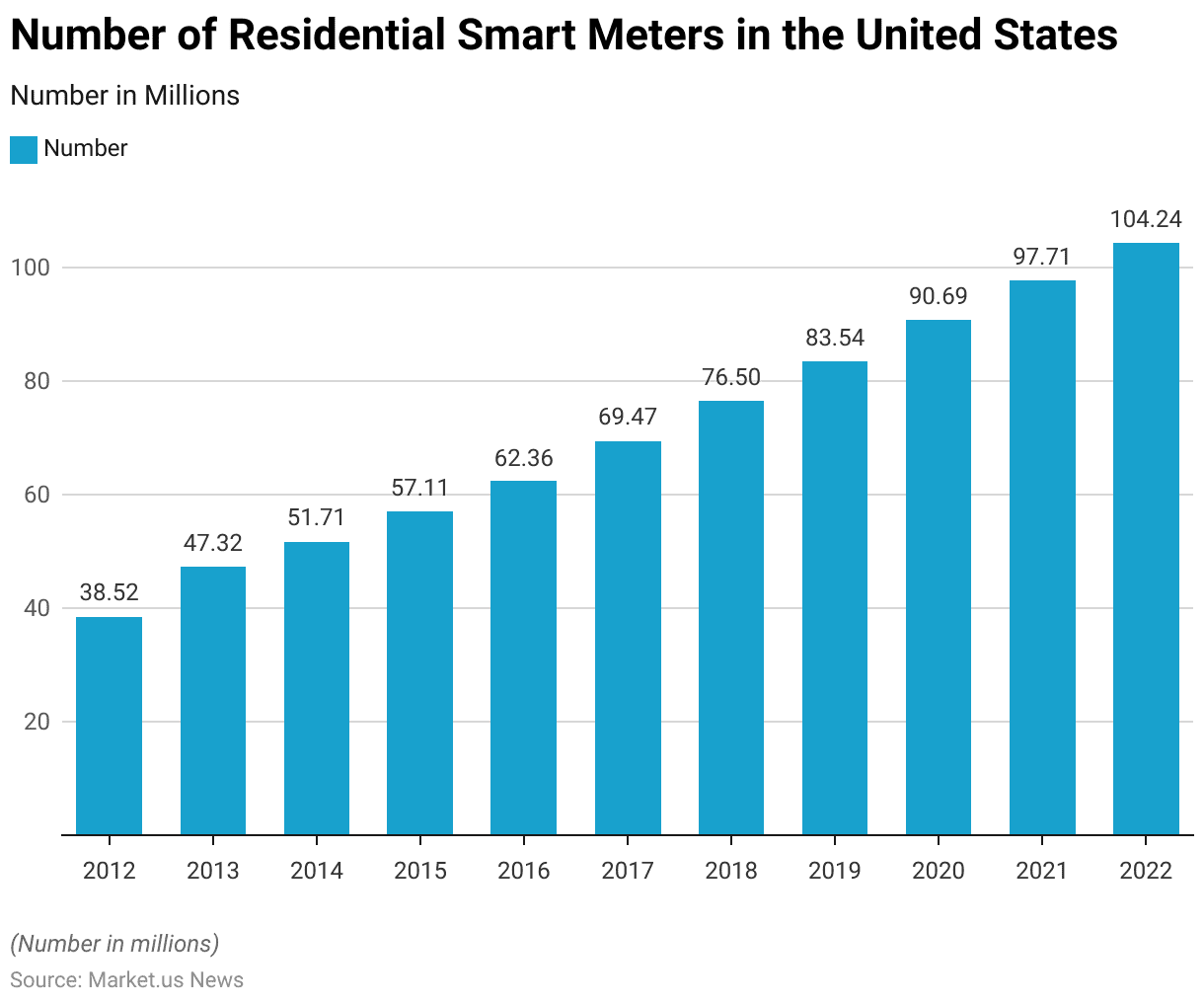
Residential Smart Meter Statistics
- The deployment of residential advanced meters in the United States has experienced significant growth from 2012 to 2022.
- In 2012, 38.52 million smart meters were installed across the country.
- This number increased to 47.32 million in 2013 and further to 51.71 million in 2014.
- The growth trend continued in 2015 with 57.11 million meters, reaching 62.36 million in 2016.
- By 2017, the number of smart meters had risen to 69.47 million, and by 2018, it had grown to 76.5 million.
- The upward trajectory persisted, with 83.54 million meters in 2019 and 90.69 million in 2020.
- The trend continued through 2021, with 97.71 million meters installed, and by 2022. The number of residential advanced meters in the United States has reached 104.24 million.
- This consistent increase over the decade highlights the widespread adoption and integration of smart meter technology in residential areas across the United States.
(Source: Statista)
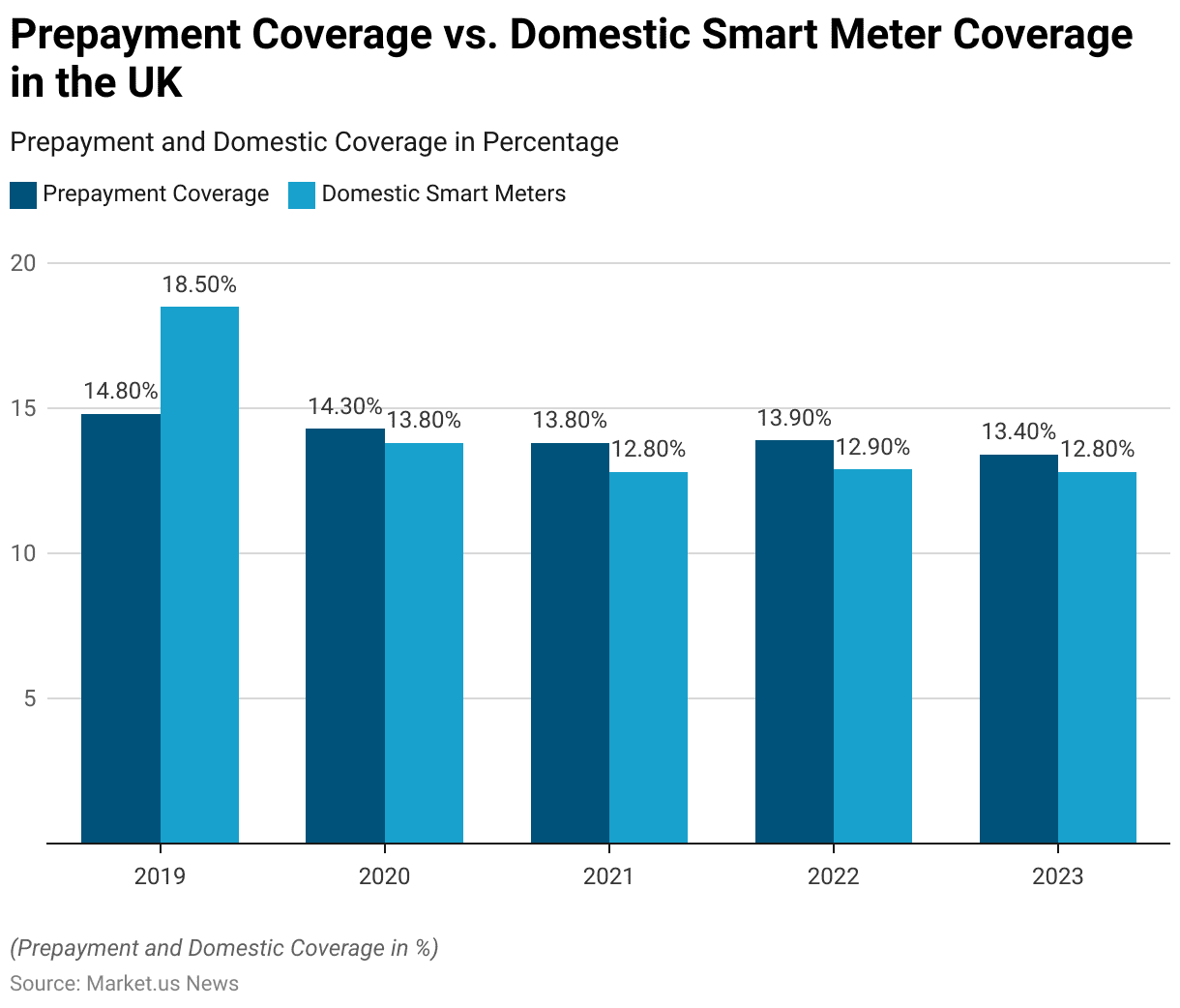
Smart Meter Coverage Trends
- Between 2019 and 2023, the UK experienced fluctuations in both prepayment coverage and domestic smart meter coverage.
- In 2019, prepayment coverage was at 14.80%, while domestic smart meter coverage was slightly higher at 18.50%.
- The following year, prepayment coverage saw a minor decline to 14.30%, and domestic smart meter coverage decreased more significantly to 13.80%.
- This downward trend continued in 2021, with prepayment coverage dropping to 13.80% and smart meter coverage to 12.80%.
- In 2022, there was a slight increase in prepayment coverage to 13.90%. While smart meter coverage showed a marginal rise to 12.90%.
- By 2023, prepayment coverage fell again to 13.40%, with domestic smart meter coverage stabilizing at 12.80%.
- These trends reflect the shifting dynamics in the UK’s energy market. Where technological adoption and consumer preferences are in constant flux. Impacting the penetration rates of both prepayment and smart metering systems.
(Source: Q4 2023 Smart Meters Statistics Report – Government of UK)
Storage Capacity of Smart Meter Statistics
- The storage capacity of smart meters varies significantly by company, reflecting differences in technological advancement and intended application.
- For example, Itron smart meters, are widely used in the United States. Typically offer storage capacities ranging from 30 to 60 days of data, depending on the model and configuration.
- In contrast, Genus Power Infrastructures, a leading provider in India, offers smart meters with storage capacities designed to support extensive data logging and advanced metering infrastructure, often storing up to 90 days of data.
- Meanwhile, Siemens smart meters, known for their reliability and precision, can store detailed consumption data for up to 180 days.
- These variations highlight the diverse capabilities and market adaptations of smart meters across different regions and companies.
(Sources: South-western Electric Power Company, MERCOM INDIA)
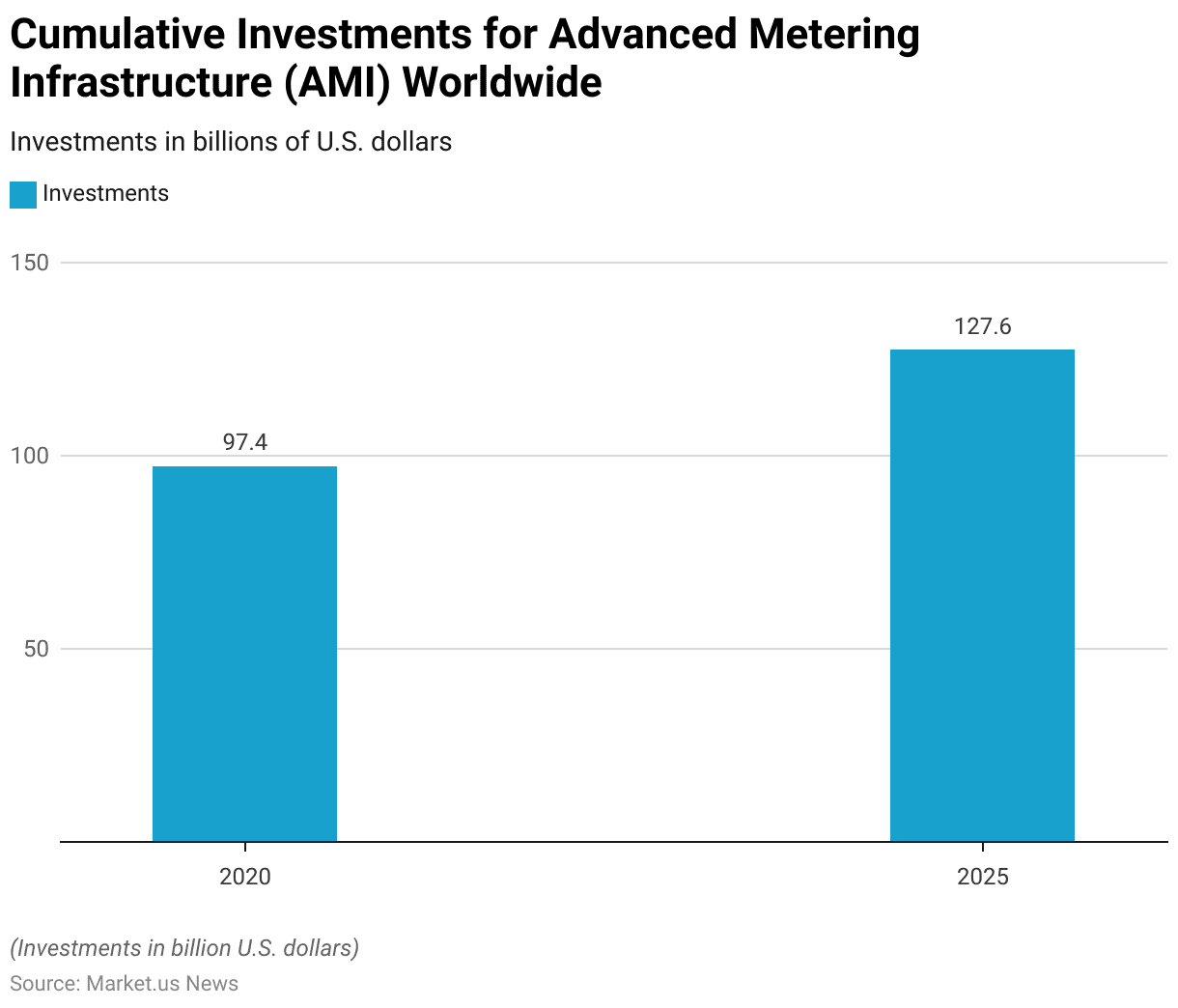
Key Smart Meter Investments Statistics
- Cumulative investments in advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) worldwide have demonstrated significant growth, reflecting the increasing commitment to modernizing energy grids.
- In 2020, global investments in AMI totaled USD 97.4 billion. This substantial financial commitment underscores the widespread recognition of the benefits associated with advanced metering technologies, including enhanced energy efficiency, improved grid reliability, and better resource management.
- Looking ahead, investments are projected to continue their upward trajectory, with forecasts indicating that by 2025, cumulative investments will reach USD 127.6 billion.
- This anticipated increase highlights the ongoing global efforts to develop further and implement advanced metering infrastructure, driven by the need for more intelligent and responsive energy systems.
(Source: Statista)
Key Smart Meter Benefits Statistics
- Smart meters provide real-time data on energy use, enabling users to reduce consumption and lower their carbon footprint. Research by the Energy Saving Trust indicates that households with smart meters cut electricity use by 2.8% and gas by 2%, leading to decreased carbon dioxide emissions.
- In Uzbekistan, the World Bank has allocated $46.25 million under the Paris Agreement to cut greenhouse gas emissions and engage with international carbon markets, aiming to reduce emissions by 60 million tonnes of CO2 by 2028. Smart meters are a central part of this effort.
- A 2022 study highlights that smart meters reduce climate change potential by 21%, fossil resource scarcity by 19%, and land pollution by 11%, compared to traditional meters.
- They also support the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, contributing to an anticipated rise in global renewable energy share from 29% to 35% by 2025, as reported by the International Energy Agency (IEA). This shift results in cleaner air and resource conservation.
- Additionally, smart meters cut transport costs and improve network problem detection. For instance, Terranova observed a 90% increase in cash flow following the installation of electronic gas meters.
- Smart meters help households manage energy use and reduce bills. The latest estimates suggest that installing a smart meter can save an average of 3.0% on electricity and 2.2% on gas (or 0.5% for gas with prepay meters). Governments aim to maximize the number of households benefiting from these savings.
(Sources: Energy Saving Trust, World Bank, Gazeta, Science Direct, Smart Energy)
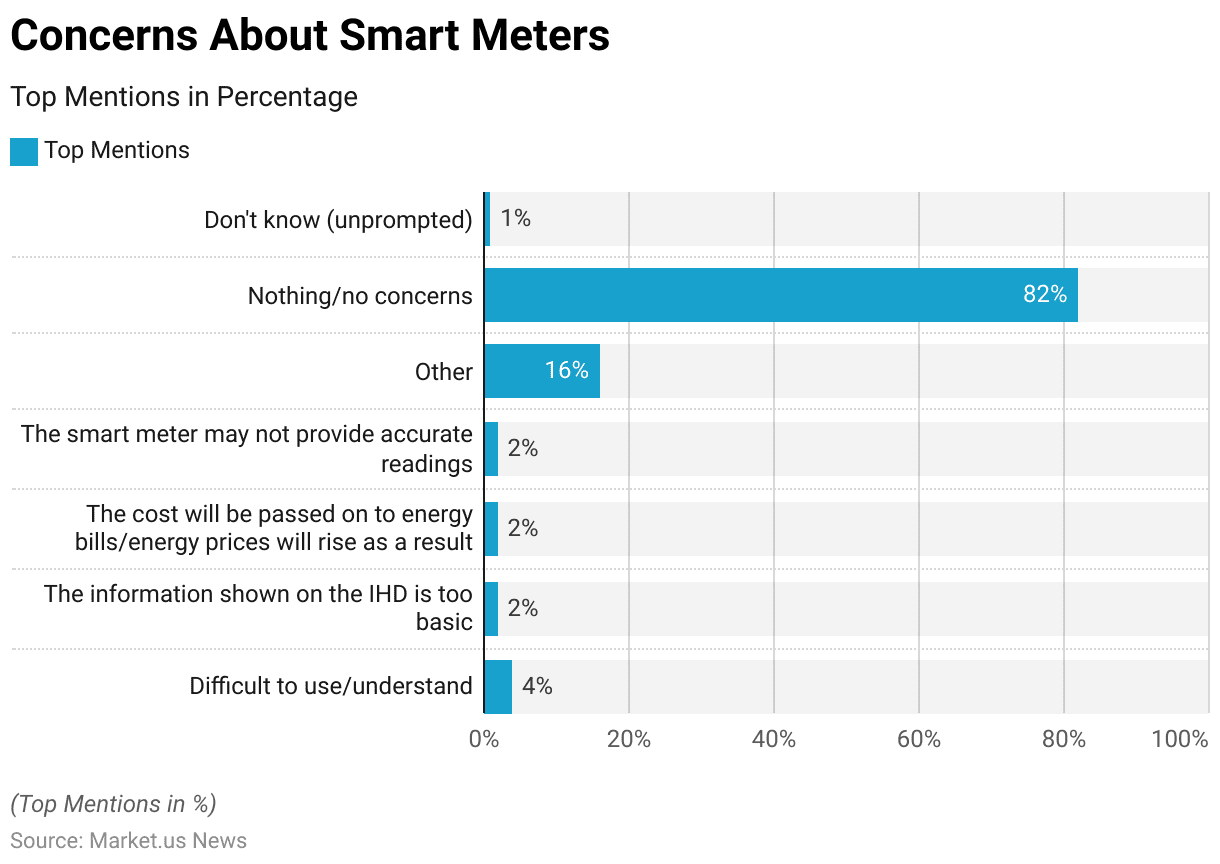
Concerns About Smart Meters
- In a recent survey regarding concerns about smart or new meters, the majority of respondents expressed minimal apprehension. Notably, 82% reported having no concerns at all.
- Among those who had voice issues, the top concern mentioned by 4% of respondents was the difficulty in using or understanding the meters.
- Additionally, 2% of participants felt that the information displayed on the In-Home Display (IHD) was too basic.
- In comparison, another 2% were worried that the cost of the meters might be passed on to their energy bills or that energy prices could rise as a result.
- An equal percentage, 2%, expressed doubts about the accuracy of the smart meter readings.
- A diverse array of other concerns was mentioned by 16% of respondents, and 1% indicated they were unsure about any potential issues.
- Overall, the survey indicates a high level of satisfaction and confidence in smart meter technology among users.
(Source: Smart Meter Early Assessment Survey – Government of UK)
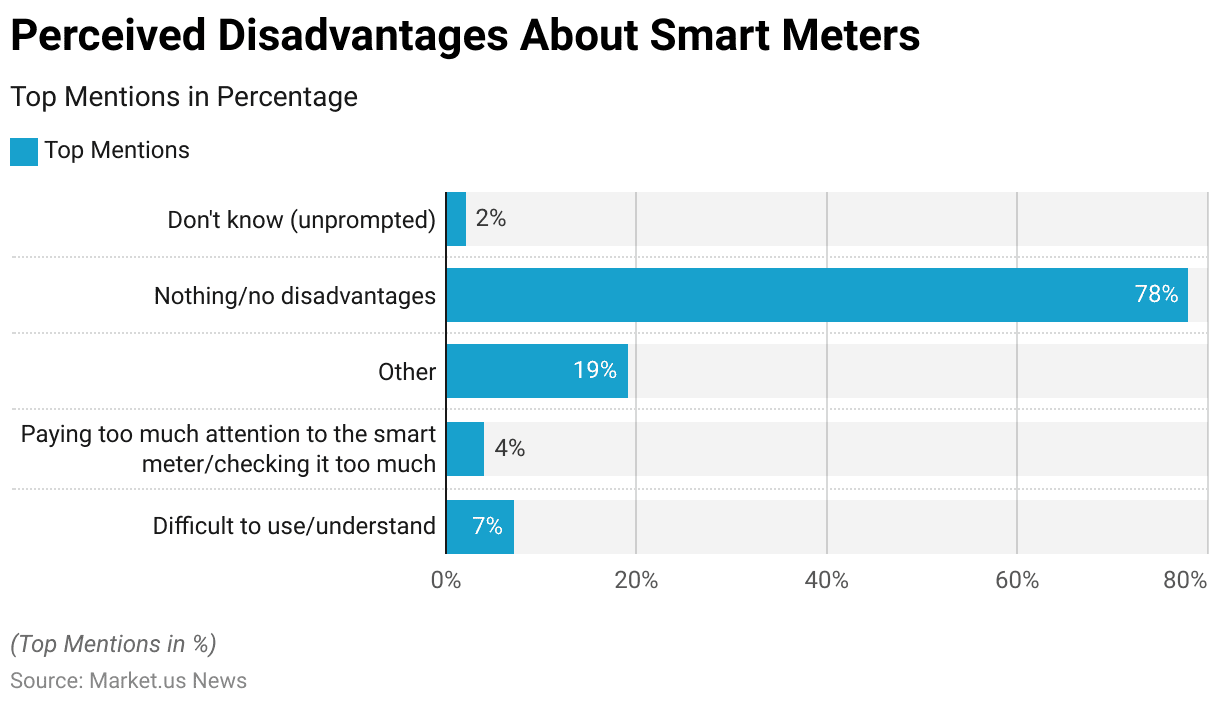
Perceived Disadvantages About Smart Meters
- A recent survey on the perceived disadvantages of smart meters revealed that the vast majority of respondents do not see significant drawbacks.
- Specifically, 78% of participants reported no disadvantages associated with using smart meters.
- Among those who did identify issues, 7% found smart meters difficult to use or understand.
- Additionally, 4% of respondents mentioned that they tend to pay too much attention to the smart meter or check it excessively.
- A variety of other concerns were cited by 19% of respondents, while 2% were unsure about any potential disadvantages.
- Overall, these findings suggest that most users are satisfied with their smart meters and do not perceive major disadvantages.
(Source: Smart Meter Early Assessment Survey – Government of UK)
Regulations for Smart Meters
- Regulations for smart meters vary significantly across countries, reflecting diverse national policies and rollout strategies aimed at modernizing energy infrastructure and improving energy efficiency.
- In the European Union, directives such as the Third Energy Package and the Clean Energy Package have mandated that member states ensure at least 80% of consumers have smart meters by 2020, with many countries exceeding this target.
- For instance, Estonia and Denmark have achieved near-universal coverage, while France and Portugal have implemented large-scale deployments despite some delays.
- In the United Kingdom, the government has set ambitious targets to reach full smart meter coverage by 2025, supported by specific annual installation goals.
- After initial hesitations, Germany has committed to a full rollout by 2030.
- Outside Europe, India‘s Ministry of Power aims to replace all traditional meters with smart meters by 2025.
- These regulations underscore a global trend toward digitalization in energy systems aimed at enhancing efficiency, consumer engagement, and grid resilience.
(Sources: European Commission, Tripica, MDPI, Springer Link, Government of UK)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- Itron acquires SmartSynch: In mid-2023, Itron acquired SmartSynch, a company specializing in smart grid solutions, for $100 million. This acquisition aims to enhance Itron’s smart meter offerings by integrating SmartSynch’s advanced communication technologies.
- Landis+Gyr acquires Rhebo: In late 2023, Landis+Gyr acquired Rhebo, a cybersecurity firm focused on operational technology. This merger is expected to strengthen Landis+Gyr’s smart meter security by incorporating Rhebo’s real-time monitoring and anomaly detection capabilities.
New Product Launches:
- Siemens’ Advanced Smart Meter: Siemens launched a new advanced smart meter in early 2024, featuring enhanced data analytics, real-time energy usage monitoring, and improved connectivity options. This product aims to provide more accurate and efficient energy management for both utilities and consumers.
- Honeywell’s Residential Smart Meter: In mid-2023, Honeywell introduced a new residential smart meter designed for easy installation and user-friendly interfaces. This meter offers real-time energy consumption data and integration with home automation systems.
Funding:
- Aclara secures $150 million: Aclara, a leading supplier of smart infrastructure solutions, raised $150 million in a funding round in 2023 to expand its smart meter product line and enhance its R&D efforts, focusing on next-generation smart grid technologies.
- Sensus raises $100 million: In early 2024, Sensus, a provider of smart meters and communication networks, secured $100 million to accelerate the development of its advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and expand its market reach.
Technological Advancements:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Smart meters are increasingly integrating AI and machine learning to provide predictive analytics. Optimize energy usage, and detect anomalies, leading to more efficient and intelligent energy management systems.
- Enhanced Connectivity Solutions: Advances in IoT and communication technologies are enabling smart meters to offer enhanced connectivity. Supporting real-time data transmission, remote monitoring, and seamless integration with smart grids.
Market Dynamics:
- Growth in Smart Meter Market: The global smart meter market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2023 to 2028. Driven by increasing demand for energy efficiency, regulatory mandates, and the transition to smart grids.
- Rising Adoption in Residential Sector: The residential sector is seeing significant adoption of smart meters due to the growing awareness of energy conservation and the benefits of real-time energy usage monitoring, contributing to market growth.
Regulatory and Strategic Developments:
- EU’s Clean Energy Package: The European Union’s Clean Energy Package, implemented in early 2024, mandates the deployment of smart meters across member states to enhance energy efficiency. Support renewable energy integration, and provide consumers with better control over their energy usage.
- US Smart Grid Investment Grant Program: The US Department of Energy continued its Smart Grid Investment Grant Program in 2023. Providing funding to utilities for the deployment of smart meters and other smart grid technologies to modernize the nation’s energy infrastructure.
Research and Development:
- Next-Generation Smart Meters: R&D efforts are focusing on developing next-generation smart meters that offer higher accuracy, better security, and more advanced features such as multi-utility metering and enhanced data analytics capabilities.
- Blockchain for Energy Transactions: Researchers are exploring the use of blockchain technology in smart meters to enable secure and transparent energy transactions, improve data integrity, and facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading.
Conclusion
Smart Meter Statistics – The increasing acceptance and integration of smart meters globally reflect significant investments in advanced metering infrastructure aimed at modernizing energy systems.
Despite some concerns about usage difficulty and cost implications, the majority of users report no major issues.
High penetration rates in countries like China and Japan and the steady increase in installations in the United States highlight the growing recognition of smart meters’ benefits, such as enhanced energy efficiency and resource management.
Overall, the positive outlook for smart meter technology suggests it will play a crucial role in future global energy strategies. Continued investments are likely to address and diminish existing concerns.
FAQs
A smart meter is an advanced energy meter that measures electricity, gas, or water usage in real-time. It provides detailed information on consumption patterns and communicates directly with the energy supplier for automated readings and efficient energy management.
Smart meters use wireless technology to send real-time usage data to energy suppliers. They also display energy consumption information on an In-Home Display (IHD) unit, allowing users to monitor their usage and costs.
Smart meters offer several benefits, including accurate billing, real-time monitoring of energy usage, enhanced energy efficiency, and improved resource management. They help consumers make informed decisions about their energy consumption and can lead to cost savings.
Some users may find smart meters difficult to use or understand. Concerns have also been raised about the potential for increased energy bills and the accuracy of readings. However, the majority of users report no significant issues.
In many regions, installing a smart meter is not mandatory, but it is encouraged. Energy suppliers may offer incentives for switching to a smart meter, and future energy policies might increasingly favor smart meter adoption.



