Table of Contents
Introduction
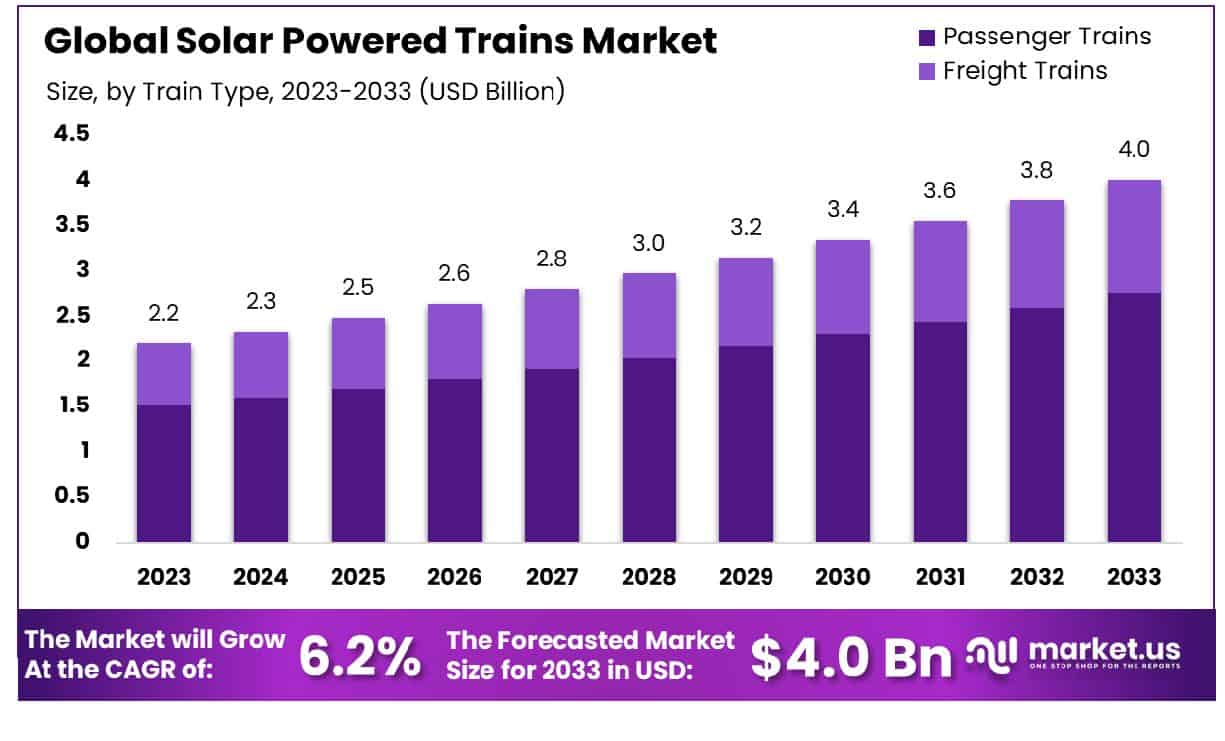
The Global Solar Powered Trains Market is projected to expand significantly, with the market size expected to rise from USD 2.2 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 4.0 billion by 2033, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% throughout the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. This growth is primarily fueled by the increasing global emphasis on sustainable transportation solutions and the integration of renewable energy technologies in the railway sector. However, the market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the technical complexities associated with retrofitting existing train systems with solar technology.
Recent developments have demonstrated substantial advancements in this area, including the introduction of innovative solar-powered train prototypes and governmental investments in greener public transport solutions. For instance, several European countries have increased their funding for sustainable transport projects by up to 30% in the past year alone, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and enhance energy efficiency in rail systems. These factors collectively contribute to the dynamic expansion and the complexities of the Solar Powered Trains Market.
Trina Solar, a leading provider of photovoltaic modules, has recently secured a significant contract to supply solar panels for a new solar-powered train project in Germany. This project aims to replace traditional diesel engines with photovoltaic systems, highlighting a major step towards sustainable rail solutions. The deal, valued at approximately USD 15 million, underscores Trina Solar’s commitment to innovating in the realm of eco-friendly transportation.
Riding Sunbeams is a pioneering enterprise focusing on integrating solar energy with railway networks. They have launched a new initiative in partnership with the UK government, receiving funding of around USD 10 million to develop and trial solar-powered rail systems in southeastern England. This initiative is particularly notable for its potential to set precedents for future solar applications in public transport.
Hanwha S&C has made significant strides in enhancing the efficiency of solar-powered trains. In 2023, they unveiled a new solar module specifically designed for high-speed rail applications. This module is engineered to withstand the rigors of high-velocity environments, making it a critical development in the market.
Central Electronics Limited (CEL) in India has been involved in a strategic merger with a European rail tech company to co-develop solar-powered train components. This merger, estimated to boost CEL’s capabilities significantly, involves an investment of around USD 5 million and aims to leverage CEL’s manufacturing strength and the European company’s technological prowess.
SolarWorld, another major player in the solar energy sector, has introduced a new line of rugged solar panels tailored for rail applications. These panels are designed to be highly durable and efficient, suitable for the varying climates and physical demands of rail travel. In addition to this product launch, SolarWorld has also secured a series of grants totaling USD 20 million from various environmental sustainability funds to enhance their research and development efforts in this field.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Global Solar Powered Trains Market is projected to expand from USD 2.2 billion in 2023 to USD 4.0 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.2%.
- Europe leads the Solar Powered Trains Market with 40.6%, USD 0.9 billion.
- By Train Type: Passenger trains dominate the market, holding a 68.7% share in 2023.
- By Integration: Solar panels are primarily integrated into train roofs for energy capture.
- By Operational Speed: Operational speeds of 100-200 km/h constitute 43.5% of the market segment.
Solar Powered Trains Market Statistics
- Each solar panel will generate 300 watts of electricity, which means 3.6KW of power per coach.
- Transport reportedly accounts for approximately 20% of carbon dioxide emissions worldwide, and for more than that in some countries 24% in the UK and 28% in the USA.
- The world’s first 100% solar-powered train is now gliding down tracks in Byron Bay, Australia.
- 100 seated passengers and other standing passengers can ride the solar train, and there’s room for luggage, bikes, and surfboards. The fare for a one-way trip is $3 for adults, $2 for ages six to 13, and free for children up to age five.
- Trains transport 28 billion passengers and more than 12 gigatons of freight annually.
- 16 solar panels generating 300 watts each offer a 4.5-kilowatt peak capacity for each coach. The system can generate around 20 kilowatt-hours of clean power per day. A 120 AH battery system will store excess power generated during peak hours.
- ARENA is also tackling the challenge of industrial energy with the $400 million Industrial Transformation Stream (ITS).
- Part of the Australian Government’s $1.9 billion Powering the Regions Fund, it aims to support the emissions reduction at existing industrial facilities in regional Australia.
- Solar panels on three south London train stations generated 1,136,387kWh of energy last year – equivalent to boiling the kettle to make 36 million cups of tea.
- Australia receives 57 million PJ in solar radiation annually, which is around 10,000 times its entire energy usage.
- According to the Australian energy statistics for electricity generation for 2021, renewable electricity energy in Australia was 24%, up from 21% in 2019.
- By saving an estimated 1.2 lakh kilo liters of diesel every year, the railways will be able to save Rs 672 crore per year.
- Equipping a single non-AC coach with solar panels costs around Rs 3.9 lakh, but saves Rs 1.24 lakh per year in power costs.
- The solar panels on the trains can generate around 17 units of power per day, which is enough to power the lighting system in the coach.
Emerging Trends
- Integration of Advanced Photovoltaic Technology: One of the most notable trends is the development and integration of high-efficiency photovoltaic (PV) cells specifically designed for the unique needs of the railway industry. These advanced solar panels are capable of converting more sunlight into electricity, enhancing the overall efficiency of solar-powered trains. This trend is enabling trains to travel longer distances without the need for frequent recharging stops.
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Another emerging trend is the use of hybrid systems that combine solar power with other forms of renewable energy, such as wind or biofuels, and even traditional electric power systems. This hybrid approach ensures a more reliable power supply and optimizes energy use, reducing dependency on any single energy source and increasing operational efficiency.
- Energy Storage Innovations: Improvements in battery technology are also pivotal. Modern solar trains are increasingly equipped with state-of-the-art energy storage systems that allow excess solar energy to be stored and used as needed. These systems are crucial for maintaining a consistent power supply during periods without sunlight, such as at night or during cloudy weather.
- Government Incentives and Supportive Policies: There is a growing trend of governmental support for solar-powered transport solutions through subsidies, grants, and favorable policies. This support is instrumental in accelerating the adoption of solar-powered trains by reducing the financial burden on rail operators and encouraging investment in green technology.
- Smart Grid Integration: The integration of solar-powered trains with smart grid technology is a forward-looking trend. Smart grids allow for more efficient energy management and distribution, optimizing the use of solar energy within the railway network. This integration supports real-time energy monitoring and management, enhancing the sustainability and efficiency of train operations.
- Sustainability Initiatives by Rail Operators: Finally, rail operators themselves are increasingly adopting sustainability as a core part of their operational and business strategies. This includes investing in solar-powered train projects, committing to carbon neutrality goals, and actively seeking to reduce the environmental impact of their operations.
Use Cases
- Commuter Rail Services: Solar-powered trains are particularly well-suited for commuter rail services that operate within or between urban areas. For instance, a pilot project in the UK has successfully demonstrated that solar panels installed along the track can supply a significant portion of the power needed for daily operations. In this project, solar power contributed to approximately 20% of the energy used by trains during peak hours, significantly reducing the carbon footprint and operating costs associated with urban commuting.
- Remote Area Rail Services: In remote areas where access to the traditional power grid may be limited or non-existent, solar-powered trains offer a viable solution. For example, in regions of Australia, solar-powered trains have been deployed to service areas that lack adequate infrastructure, providing essential connectivity without the need for extensive and expensive grid expansions.
- Tourist Railways: Solar energy can also power tourist trains, which often travel through scenic areas where environmental conservation is crucial. In regions like Switzerland and some national parks in the United States, solar-powered trains help preserve the natural beauty of these locations while offering tourists a sustainable way to explore them. These trains reduce the environmental impact of tourism, aligning with eco-friendly travel trends.
- Freight Rail Services: The integration of solar power into freight rail services can reduce operational costs and enhance the sustainability profile of shipping goods. For example, a project in India involves solar panels mounted on the roofs of freight trains, generating enough power to handle onboard systems and part of the locomotive needs, which has led to a 15% reduction in diesel fuel use annually.
- Emergency and Backup Systems: Solar-powered trains can also be equipped with backup systems that ensure continuous operation during power outages or emergencies. For example, solar panels can power critical safety and communication systems, enhancing reliability and safety in unexpected situations.
- Research and Development in Rail Technology: Solar power is increasingly used in research and development initiatives to test and improve rail technology innovations. Projects in Germany and Japan focus on developing high-efficiency solar panels and integration techniques that could pave the way for wider adoption of solar technologies in mainstream rail services.
Key Players Analysis
Trina Solar has been active in the solar-powered trains sector, primarily through their innovative solar PV panels designed for diverse applications including transportation. The company is known for its commitment to sustainable energy solutions, which extend beyond traditional stationary installations to mobile applications such as trains. Trina Solar’s panels are engineered to withstand the specific challenges posed by the dynamic and varying conditions of rail transport, making them suitable for this application. The company has supplied significant quantities of these solar modules globally, emphasizing their role in promoting sustainable transport solutions.
Riding Sunbeams has been at the forefront of innovative efforts to decarbonize rail transport by integrating solar power directly into railway traction systems. This approach, first demonstrated successfully in 2019 at Aldershot Station, represents a pioneering step towards sustainable rail operations. The project, known as “First Light,” showcased the feasibility of using solar panels to supply direct power to rail networks without the need for grid connectivity. This milestone not only highlights Riding Sunbeams’ capabilities in leveraging solar technology for rail applications but also aligns with broader environmental objectives by providing a renewable energy solution that reduces carbon emissions and enhances energy efficiency within the rail sector.
Hanwha S&C has been actively involved in developing and expanding its renewable energy portfolio, which indirectly supports sectors such as solar-powered trains. The company has focused on the integration of solar technologies across various infrastructures, exemplified by their investment in a 150-megawatt solar power plant in Wyoming, alongside becoming a major shareholder in REC Silicon. This move enhances their capacity to produce essential components for solar panels, thereby contributing to the broader adoption of solar energy technologies in industries including transportation.
Central Electronics Limited (CEL), a public sector enterprise under the Ministry of Science & Technology, India, has actively contributed to the solar energy sector, particularly in manufacturing crystalline silicon solar photovoltaic cells and modules. Leveraging advanced screen-printing technology, CEL has distributed over 500,000 solar photovoltaic systems domestically and internationally for both rural and industrial applications. As a pioneer in solar photovoltaic innovations, CEL focuses on continuously expanding its module manufacturing capacity, emphasizing the enhancement of sustainable energy solutions.
SolarWorld, primarily engaged in the manufacture and marketing of photovoltaic products, has not been specifically involved in the development or implementation of solar-powered trains. The company’s focus has remained on the production of solar panels and related photovoltaic components, emphasizing the enhancement of solar technologies and energy solutions rather than direct applications in the solar-powered trains sector.
Canadian Solar, a leader in solar technology, is advancing its global presence with significant projects like the construction of the Summerfield Battery Energy Storage System in Australia, set to start in 2025. This project exemplifies the company’s commitment to enhancing sustainable energy solutions, reflecting its strategic expansion into renewable energy markets.
The Byron Bay Railroad Company operates the world’s first solar-powered train, a significant innovation in renewable transportation. This pioneering train, running on a three-kilometer route in Byron Bay, Australia, utilizes solar panels and batteries for its operation, maintaining its vintage heritage while integrating modern technology. It offers regular services almost every day of the year and has become a popular local attraction while contributing positively to the environment.
LG Electronics has not directly engaged in projects for solar-powered trains; however, their innovations in solar technology, such as the NeON H solar panels, demonstrate capabilities that could support sustainable energy solutions in various sectors, including transportation. These high-efficiency solar panels are suited for both residential and commercial use, potentially beneficial for infrastructure projects like solar-powered railways.
Bankset Energy is actively engaged in the solar-powered railways sector, focusing on innovative solar PV installations across global railway networks. They utilize patented technology to integrate solar panels with existing railway sleepers, transforming railway infrastructure into renewable energy sources without disrupting existing systems. This approach not only supports sustainability but also reduces the need for new infrastructure investments. Bankset’s projects span several countries, including Germany, the UK, the US, and more, reflecting their significant role in promoting solar energy in rail transport.
Axitec LLC has not reported any direct involvement in the solar-powered trains sector. Their primary focus remains on manufacturing high-efficiency solar panels at competitive prices, leveraging their German design expertise with production mainly in Asia. These panels are typically used in residential and commercial settings across various global markets, including the U.S., where they have maintained a strong presence since 2013.
Kyocera Corporation has demonstrated a significant presence in the solar energy sector, but there is no specific mention of their involvement in solar-powered trains. The company has a rich history in developing solar power solutions, including floating solar power plants. For instance, they began constructing the world’s largest floating solar power plant on Japan’s Yamakura Dam in 2016, showcasing their pioneering efforts in utilizing water surfaces for solar installations.
Greenrail, on the other hand, specializes in innovative railway solutions that incorporate solar power. They have developed solar-powered railway sleepers, integrating photovoltaic panels within the railway infrastructure. This technology not only generates electricity but also enhances the sustainability of railway systems. Greenrail’s approach represents a practical application of solar power in the railway sector, contributing to energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
Jackson Engineers Limited has actively engaged in the solar-powered trains sector by installing solar panels on Diesel Electric Multiple Unit (DEMU) coaches for Indian Railways. These solar panels are capable of generating 3.6 kilowatts of electricity, sufficient to power the internal electrical systems such as lights and fans within the train coaches. This initiative aligns with the Indian Railways’ goal to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and enhance sustainability in rail transport.
SunPower Corporation has not been specifically involved in projects directly linked to solar-powered trains. The company primarily focuses on residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar power solutions, and it’s renowned for advancing solar technology and driving large-scale solar implementations across various sectors. While their innovations contribute broadly to the renewable energy sector, there’s no direct evidence of their engagement with the solar-powered trains sector as of the latest available data.
Conclusion
The solar-powered trains market is poised for significant growth and transformation. Driven by technological advancements, environmental considerations, and supportive government policies, the integration of solar energy into railway systems represents a promising shift towards more sustainable and cost-effective transportation solutions.
As the market continues to evolve, solar-powered trains are expected to play an increasingly vital role in reducing the carbon footprint of the rail industry, improving energy efficiency, and offering reliable service across diverse geographic regions. The commitment from key industry players and continuous innovation in photovoltaic technologies further underscore the potential of solar-powered trains to revolutionize the way we think about and utilize public transportation in the future.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





