Table of Contents
Introduction
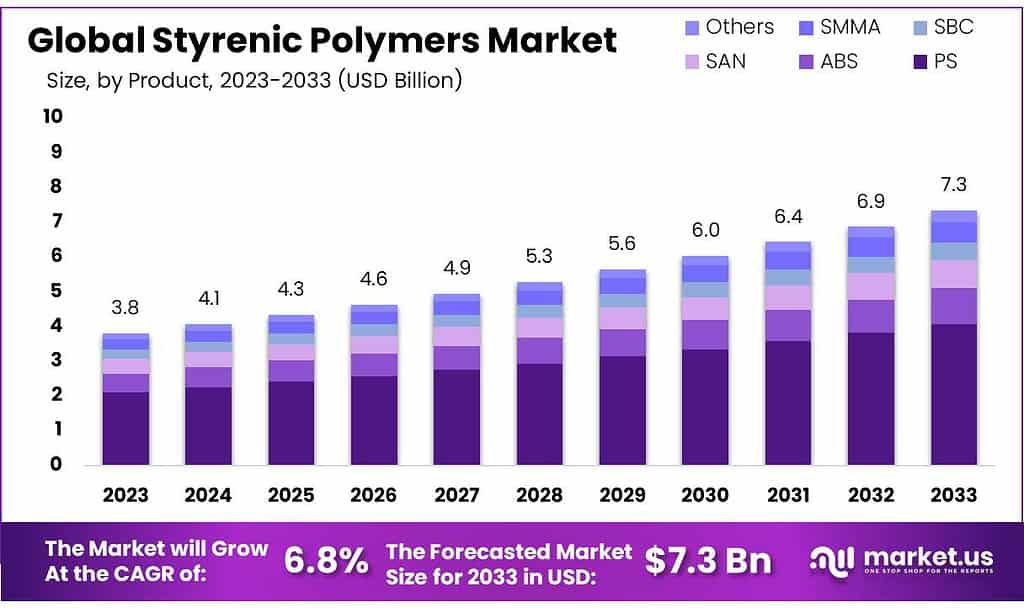
The global market for Styrenic Polymers is poised to expand from USD 3.8 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 7.3 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% over the forecast period. This growth is driven by increasing applications across various industries including automotive, building, and construction, and especially in packaging due to their superior molding capabilities and cost-effectiveness.
However, the market faces challenges such as the environmental concerns related to the biodegradability of certain styrenic polymers like polystyrene, which has prompted regulatory pressures for more sustainable alternatives. Additionally, the market is affected by the volatility of raw material prices, particularly due to fluctuations in crude oil prices, which are a primary raw material source for these polymers.
Recent developments in the market include advancements in the production of medical devices and the rising focus on sustainable and recycled polymers. Companies are investing in research and development to enhance the properties of styrenic polymers and to develop new, more environmentally friendly materials. There’s also a significant trend towards the customization of these polymers to meet specific industry needs, which is fostering innovation in polymer formulations and processing technologies.
TotalEnergies has been reshaping its portfolio and operations. The company sold its polystyrene segment in China to INEOS, focusing its activities on markets where it holds a stronger position like Europe and North America. Moreover, TotalEnergies and INEOS realigned their petrochemical assets in eastern France to enhance operational efficiencies in ethylene production and distribution.
SABIC, in collaboration with BASF and Linde, has begun constructing the world’s first large-scale electrically heated steam cracker furnaces at BASF’s Ludwigshafen site. This project is set to drastically reduce CO2 emissions by utilizing renewable electrical energy, marking a significant advancement towards sustainable production practices in the industry. Trinseo is advancing sustainability with its focus on recycling technologies. Together with INEOS Styrolution, Trinseo is developing the first European polystyrene recycling plant based on depolymerization in France, highlighting its commitment to circular economy principles.
Overall, while the market for styrenic polymers presents substantial growth opportunities, it must navigate environmental challenges and innovate continually to meet changing consumer and regulatory demands.
Key Takeaways
- The market is expected to grow from USD 3.8 billion in 2023 to USD 7.3 billion by 2033, at a 6.8% CAGR.
- Polystyrene (PS) dominated in 2023 with a 55.6% market share.
- Packaging industry leads with a 73.3% share due to versatility and cost-effectiveness.
- EU chemical imports in 2021 were €272 billion, and exports €458 billion.
- The U.S. produces over 2 million tons of polystyrene annually.
- Prices for GPPS and HIPS ranged from $1,000 to $1,500 per metric ton.
- Environmental regulations increase production costs by 10-20%.
Styrenic Polymers Statistics
polymers, and with 760 and 700 for SAN-based polymer. Differentiation between GPPS and
The chains of between 70 and 80% by weight styrene and 20 to 30% acrylonitrile.
The copolymer has a glass transition temperature greater than 100 °C owing to the acrylonitrile units in the chain
The rubber chains form separate phases which are 10-20 micrometers in diameter.
Rigid styrenic polymers are typically used at temperatures below 150°F.
These block copolymers generally have a very soft feel and excellent hysteresis, or elastic retention, properties when made as films. Some grades can perform up to 270°F.
COCs can also be used in various blended custom compounds in applications requiring thermal stability up to 300°F.
A general-purpose polyolefin that is harder and stiffer than polyethylene with a use temperature range of up to 265°F.
General-purpose materials that have good flexibility and excellent chemical and moisture resistance. Upper-level use temperature to 225°F.
Emerging Trends
- Sustainability Initiatives: There is a growing emphasis on enhancing the recyclability and biodegradability of styrenic polymers. The development of bio-based and recycled styrenic polymers aims to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and minimize environmental impact. This trend is partly driven by increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demands for more sustainable materials, especially concerning the environmental issues associated with polystyrene, which is not easily biodegradable.
- Technological Innovations: Advancements in technology are fostering improvements in the properties of styrenic polymers, such as enhanced heat resistance and flame retardancy. Innovations also include the customization of these polymers to meet specific industry requirements, which is crucial for applications across various sectors including automotive, packaging, and construction.
- Digitalization and Industry 4.0: In regions like South Korea, the styrenics market is being transformed by digitalization, AI, machine learning, and data analytics. These technologies are optimizing production processes, improving efficiency, and enhancing product quality, aligning with new Industry 4.0 initiatives that promote collaboration and information sharing among supply chain partners.
- Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing robust growth due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and an expanding middle-class. This growth is supported by the wide-ranging applications of styrenic polymers in industries such as automotive, packaging, and consumer goods.
Use Cases
- Packaging: Polystyrene is extensively used in packaging because of its lightweight, insulating, and shock-absorbing properties. It is commonly found in the form of food containers, disposable cups, and cushioning material for shipping fragile items.
- Construction: In the construction industry, styrenic polymers are valued for their insulation properties. Polystyrene, for example, is used in insulation panels, roofing materials, and wall cladding, helping to enhance energy efficiency in buildings.
- Automotive: ABS is prevalent in the automotive sector, where it is used for dashboard trim, body parts, and interior panels due to its strong impact resistance and aesthetic qualities. It helps in reducing vehicle weight, which can improve fuel efficiency and performance.
- Electronics: Styrenic polymers like ABS and HIPS are used in the electronics industry for manufacturing parts such as computer housings, electronic enclosures, and other components that require dimensional stability and aesthetic appeal.
- Medical Devices: Due to their purity and ease of sterilization, polystyrene and ABS are used in the medical field for products like petri dishes, diagnostic devices, and housing for medical equipment.
- Consumer Goods: These polymers are employed in a myriad of consumer products ranging from toys, household appliances to safety helmets due to their ease of processing and durability.
Key Players Analysis
INEOS Styrolution is a leading global supplier in the styrenic polymers sector, focusing on materials like styrene monomer, polystyrene, ABS, and advanced styrenic specialties. With more than 90 years of experience, the company operates across multiple industries, including automotive, healthcare, and packaging. They are recognized for their commitment to innovation and sustainability, developing materials that enhance circularity and reduce carbon emissions. Their work includes using recycled and renewable content in products and striving for solutions that support the shift towards a circular economy.
TotalEnergies, although traditionally known for its energy and petrochemical products, has been active in the styrenic polymers market through strategic asset alignments and divestitures. They have previously managed a significant polystyrene business in China, though recent strategic shifts have seen them divest these assets to focus on markets where they hold stronger positions. Their actions in the styrenics sector align with broader company strategies focusing on core operational efficiencies and market concentration.
SABIC is actively involved in the styrenic polymers market, primarily focusing on the development and production of high-performance materials such as Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN). These materials are highly valued for their durability, impact resistance, and aesthetic qualities, making them ideal for a range of applications including automotive components, consumer electronics, and medical devices. SABIC’s commitment to innovation is evident in its continuous efforts to enhance the properties of these polymers to meet the demanding requirements of these industries.
Dow, Inc., another significant player in the styrenic polymers sector, specializes in producing a variety of styrene-based materials, including polystyrene and ABS. Dow focuses on leveraging these materials for applications across multiple sectors such as packaging, building and construction, and consumer products. Their extensive research and development efforts aim to improve product performance and environmental sustainability, addressing the needs of an evolving global market
BASF SE is a prominent player in the styrenic polymers sector, particularly known for its innovative styrenic foams like Neopor® and Styrodur®. These products are crucial in the construction industry for providing efficient insulation solutions that significantly contribute to reducing CO2 emissions. BASF’s commitment to sustainability is evident in its development of products designed to minimize environmental impact while enhancing energy efficiency in building applications.
Trinseo, another key industry player, focuses on offering a variety of styrenic polymers, including polystyrene and ABS. They emphasize sustainability and have invested in circular solutions like recycling technologies. Trinseo’s approach includes not only the development of new materials but also collaboration on recycling initiatives, demonstrating their commitment to environmental responsibility and innovation in the use of styrenic polymers.
LG Chem actively participates in the styrenic polymers market, emphasizing sustainable and innovative material solutions. They focus on eco-friendly biomaterials, developing biodegradable plastics that serve as alternatives to traditional polymers. LG Chem’s initiatives often center around using plant-derived materials for production, contributing significantly to environmental sustainability. Their strategic partnerships aim to enhance the development and commercialization of these green materials, reflecting their commitment to reducing carbon emissions and advancing circular economy principles.
Chi Mei Corporation is a major player in the global styrenic polymers market, particularly noted for its production of ABS, SAN, and other styrenic resins. The company is renowned for its extensive portfolio of high-performance materials used across various industries including automotive, electronics, and healthcare. Chi Mei’s focus on innovation and quality has positioned it as a key supplier in the styrenic market, with a strong emphasis on technological advancement and customer-oriented solutions.
Covestro is intensively engaged in advancing the styrenic polymers sector through its commitment to sustainability and innovation. The company has pioneered in integrating recycled materials into its product lines, notably introducing polycarbonates derived from chemically recycled plastics. This effort is part of Covestro’s broader strategy to achieve a circular economy within their operations. Additionally, Covestro is expanding its production capabilities, recently initiating new facilities in Shanghai to meet the rising demand for polyurethane dispersions and elastomers, thereby reinforcing its market position in high-performance polymers.
Versalis is actively involved in the styrenic polymers market, focusing on the development and commercialization of styrenic products, including polystyrene and ABS. Their operations emphasize not only the production of these polymers but also the development of new technologies and formulations to improve product performance and environmental sustainability. Versalis’ approach aligns with the broader trends in the industry towards more sustainable and advanced material solutions.
Conclusion
Styrenic polymers, encompassing materials like polystyrene, ABS, and SAN, play a crucial role across a broad spectrum of industries due to their versatile properties and economic viability. These polymers are integral to sectors ranging from packaging and construction to automotive and electronics, offering benefits such as lightweight, insulation, impact resistance, and aesthetic flexibility.
The ongoing advancements in polymer technology, coupled with a growing emphasis on sustainability, are driving innovations such as enhanced recyclability and the development of bio-based alternatives. As the industry navigates regulatory pressures and environmental concerns, the adaptability and continuous improvement of styrenic polymers are likely to keep them at the forefront of materials technology, ensuring their relevance and expanding their application scope even further. Thus, styrenic polymers are not only fundamental to current manufacturing processes but are also pivotal in shaping the future landscape of material science.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





