Table of Contents
Introduction
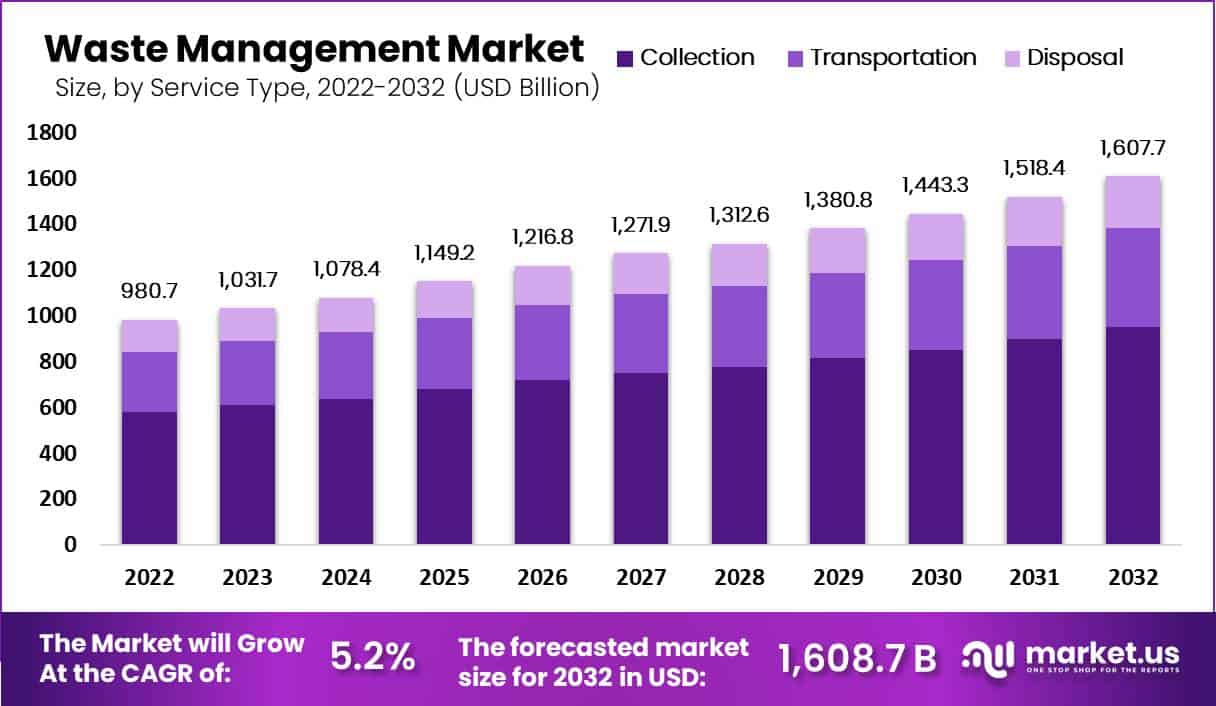
The global waste management market has shown substantial growth in recent years, with its size estimated at USD 980.7 billion in 2022. Projections indicate that this market will reach USD 1,607.6 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2032. This growth is driven by several key factors, including increasing urbanization, industrialization, and stringent government regulations aimed at ensuring proper waste management and environmental protection.
One of the significant drivers of market growth is the rise in waste generation, particularly in urban areas. As more people move to cities, the amount of municipal solid waste (MSW) generated continues to increase. In Asia-Pacific, for instance, rapid urbanization has led to an increase in waste production, necessitating enhanced waste management solutions. This region dominates the global waste management market, with substantial investments in infrastructure and technology to manage the growing volume of waste.
Government regulations are another critical factor influencing the market. Regulations such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States and the Waste Shipment Regulation in Europe are designed to ensure safe waste disposal, reduce environmental impact, and promote recycling. These regulations have led to increased investments in advanced waste management technologies, such as waste-to-energy and recycling, further propelling market growth.
Technological advancements, particularly in electronic waste management, are also contributing to market expansion. The rapid turnover of electronic devices due to technological obsolescence has resulted in a growing volume of e-waste, driving demand for specialized waste management services. The market is also seeing a shift towards circular economy practices, where waste is minimized, and resources are recovered and reused.
Despite these growth factors, the market faces challenges, including the high cost of advanced waste management technologies and the complex regulatory environment, which can act as barriers to entry for new players. Established companies like Veolia, Waste Management Inc., and Suez continue to dominate the market, leveraging their scale and expertise to maintain a competitive edge.
Valicor Environmental Services: Valicor continued its expansion by acquiring multiple companies in 2023, such as EnviroServe, which specializes in environmental remediation and hazardous waste management. This move is part of Valicor’s strategy to enhance its service offerings and expand its market presence across the United States.
Strategic Partnerships: Veolia has been focusing on partnerships to advance its capabilities in waste management. In 2023, Veolia entered a significant partnership with Groupe Renault and Solvay to develop closed-loop recycling for electric vehicle batteries in Europe. This collaboration aims to reinforce Veolia’s leadership in sustainable waste management and recycling technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The global waste management market witnessed substantial expansion between 2023-2032, reaching USD 980.7 billion at an impressive compound annual growth rate of 5.2% annually from 2023-2032. Projections indicate a remarkable surge to approximately USD 1607.6 billion
- Analysis by Service Types: Waste collection remains the top service market segment with 59% waste management market share, followed by transportation (31% market share), collection, and disposal. Waste collection represents 59% market share overall.
- Based on End User Analysis: About end-user analysis, the residential segment is by far the dominant in this market capturing 47%.
Waste Management Statistics
- According to World Bank data, at least 2.01 billion tons of municipal solid waste appear globally every year, which may increase by 70% in 2050 and reach 3.40 billion tons.
- As if it wasn’t enough, 33% are not correctly managed. Consider adding the amount of unregistered waste disposal!
- The annual value of food wasted globally is 1 trillion dollars. Up to 10% of global greenhouse gases come from wasted food. If it was a country, it would be the
- 28 percent of the world’s agricultural area is used annually to produce lost or wasted food, larger than China.
- 2.3 billion people are joining the planet by 2050 – this will require a 60-70% increase in global food production.
- we produce 400 million tons of hazardous waste annually – almost 13 tons a second! But the dumping of waste in large amounts and risks creates another global problem.
- The US creates over 624,000 metric tons of waste per day.
- Nevada generates the highest amount of waste per person: 38.4 tons.
- The US threw out over 292 million tons of trash in 2018.
- The US spends about $200 billion a year on solid waste management and lost energy resources from trash disposal.
- Landfilling accounts for approximately 50% of all municipal solid waste. Recycling constitutes 25% of waste while composting only accounts for 9%.
- In 2017, landfilling was the most prominent form of waste removal, accounting for over 60% of the total waste management market.
- Global e-waste volumes grew by 21% between 2104 and 2019, according to the United Nations, a pace that will lead to a doubling of e-waste in just 16 years. The world discarded 53.6 million tons of e-waste in 2019.
- Only 17.4% of e-waste discarded in 2019 was recycled, the United Nations reports.
- Europe leads the world in e-waste recycling, collecting, and processing 42.5% of its 2019 e-waste, according to the International Telecommunications Union.
- Asia, with 24.9 million tons of e-waste, now accounts for almost twice the e-waste volume the Americas (13.13.1 million tons) produce each year. Asia also recycles more of its e-waste, at 11.7% in 2019, than the Americas do at 9.4%.
- The EPA reported that the United States generated 6.92 million tons of e-waste, about 46 pounds per person, in 2019. It recycled only 15% of the material.
- According to Allen, if the recycling rates for gold (15%), silver (15%), and platinum (5%) all increased to 100%, the electronics sector could realize $12 billion in financial and natural capital benefits.
- Americans throw out approximately 416,000 mobile phones each day, according to 2014 figures from the EPA. That equates to more than 151 million phones thrown away in one year.
- Globally, about 37% of waste is disposed of in some type of landfill, 33% is openly dumped, 19% undergoes materials recovery through recycling and composting, and 11% is treated through modern incineration.
- In 2018, the UK generated 67.8 million tonnes of non-hazardous C&D waste (excluding excavation waste).
- Recycling and other recovery’ was the most common final waste treatment type in the UK, accounting for 108.4 million tonnes (50.4%) in 2018.
- Landfill is the second most used waste treatment in the UK, with 23.6% (50.8 million tonnes) of waste disposed of at landfills in 2018.
- 4.8 tonnes of waste were generated per EU inhabitant in 2020.
- 39.2 % of waste was recycled and 32.2 % was landfilled in the EU in 2020.
Emerging Trends
- Circular Economy Initiatives: The shift towards a circular economy is gaining momentum in waste management. Companies and governments are increasingly focusing on recycling and reusing materials to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. For instance, businesses are implementing closed-loop systems where waste products are reprocessed into new raw materials, promoting sustainability and reducing reliance on virgin resources.
- Advancements in Recycling Technologies: Innovative recycling technologies are transforming waste management. New sorting technologies, such as automated systems using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, are improving the efficiency of recycling processes. These technologies enable better separation of recyclable materials from non-recyclables, enhancing the quality and quantity of recycled output.
- Waste-to-Energy Solutions: Waste-to-energy (WtE) technologies are becoming more prevalent. These technologies convert waste materials into usable energy, such as electricity or heat. Modern WtE plants are designed to reduce emissions and improve energy efficiency, making them a viable solution for managing municipal solid waste while generating renewable energy.
- Smart Waste Management Systems: The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices into waste management systems is on the rise. Smart waste bins equipped with sensors can monitor fill levels and optimize collection routes, reducing operational costs and improving service efficiency. This technology also helps in tracking and managing waste more effectively.
- Bio-waste Management: There is increasing attention on the management of bio-waste, including organic waste from food and agriculture. Composting and anaerobic digestion are being promoted as sustainable methods to handle bio-waste. These processes convert organic waste into valuable compost or biogas, contributing to waste reduction and renewable energy production.
- Regulatory and Policy Changes: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations and policies to address waste management challenges. Legislation focusing on reducing single-use plastics, promoting recycling, and encouraging waste reduction is becoming more common. These policies are driving the adoption of sustainable waste management practices across various sectors.
- Consumer Awareness and Behavior: Growing consumer awareness about environmental issues is influencing waste management practices. More individuals are adopting sustainable habits, such as reducing waste, recycling, and supporting companies with eco-friendly practices. This shift in consumer behavior is encouraging businesses to enhance their waste management strategies and sustainability efforts.
- Digital Platforms for Waste Management: Digital platforms and mobile applications are emerging as tools for improving waste management. These platforms provide information on local recycling programs, waste disposal guidelines, and collection schedules. They also enable users to report issues, schedule pickups, and track waste management services, increasing transparency and engagement.
Use Cases
- Smart Waste Bins in Urban Areas: In many cities, smart waste bins equipped with sensors are being deployed to optimize waste collection. These bins monitor fill levels in real time and send data to waste management teams, allowing them to plan efficient collection routes and reduce unnecessary pickups. For example, in the city of San Francisco, the introduction of smart bins reduced waste collection costs by 20% and decreased carbon emissions from waste trucks.
- Waste-to-Energy Plants: Waste-to-energy (WtE) plants are increasingly being used to convert municipal solid waste into energy. These plants burn waste to produce electricity or heat, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills. In Sweden, 99% of household waste is reused, recycled, or used for energy recovery. The country generates about 20% of its district heating and electricity needs through WtE, significantly reducing landfill use.
- Plastic Waste Recycling Initiatives: Several companies and municipalities are focusing on recycling plastic waste to combat environmental pollution. For instance, the Netherlands has implemented advanced plastic sorting and recycling facilities that process over 50% of the country’s plastic waste. This initiative has helped reduce plastic pollution and supported the creation of a circular economy where plastics are continuously recycled.
- E-Waste Recycling Programs: Electronic waste (e-waste) is a growing concern due to the rapid turnover of electronic devices. Japan has implemented comprehensive e-waste recycling programs that recover valuable metals such as gold, silver, and copper from discarded electronics. During the 2020 Tokyo Olympics, medals were made from recycled metals, a project that collected 78,985 tons of e-waste, including 6.21 million mobile phones.
- Organic Waste Composting in Agriculture: Organic waste composting is being increasingly used in agriculture to improve soil health and reduce chemical fertilizer use. In the United States, the state of California has implemented large-scale composting programs that divert organic waste from landfills. These programs help produce compost used by farmers to enhance soil quality, supporting sustainable agricultural practices and reducing greenhouse gas emissions from organic waste decomposition.
- Hazardous Waste Management in Industries: Industries producing hazardous waste, such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals, are adopting specialized waste management practices to safely dispose of toxic materials. In Germany, the hazardous waste treatment facility operated by REMONDIS processes over 1 million tons of hazardous waste annually, using advanced techniques to neutralize or recycle dangerous substances, thus preventing environmental contamination.
Major Challenges
- Increasing Waste Volumes: The global rise in waste production is one of the most pressing challenges. Rapid urbanization, industrial growth, and increased consumerism contribute to higher waste volumes. For instance, municipal solid waste generation is expected to reach 3.4 billion tons by 2050, posing significant challenges for waste management infrastructure and capacity.
- Inefficient Recycling Systems: Many recycling systems worldwide are inefficient and face obstacles such as contamination of recyclable materials and inadequate sorting technologies. According to recent data, the global recycling rate is only around 20%, with significant quantities of recyclable materials ending up in landfills. Improving sorting technologies and recycling processes is essential for increasing efficiency.
- Environmental Impact of Landfills: Landfills continue to be a major environmental concern due to their potential to leach hazardous chemicals into soil and water. Methane emissions from landfills also contribute to greenhouse gas effects. As of 2023, landfills are responsible for approximately 20% of global methane emissions, highlighting the need for better waste management practices.
- Cost of Waste Management Technologies: Advanced waste management technologies, such as waste-to-energy plants and automated sorting systems, often involve high capital costs. This financial barrier can be particularly challenging for municipalities and organizations with limited budgets, limiting the adoption of these technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with increasingly stringent waste management regulations presents a challenge for many organizations. Regulations around hazardous waste, recycling mandates, and landfill diversion require significant investment in systems and processes, which can be difficult for smaller entities to manage.
- Public Engagement and Education: Effective waste management also depends on public participation. Many communities struggle with low awareness and engagement regarding proper waste disposal and recycling practices. Increasing public education and fostering a culture of sustainability are crucial for improving waste management outcomes.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Expansion of Recycling Infrastructure: The growing global emphasis on recycling presents significant opportunities for expanding recycling infrastructure. As more countries implement regulations to reduce landfill use and promote recycling, there is a rising demand for advanced recycling facilities. For example, the European Union has set a target to recycle 65% of municipal waste by 2035, creating opportunities for companies to invest in new recycling technologies and facilities.
- Growth in Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Waste-to-energy (WtE) technologies are becoming increasingly important as a solution to both waste management and energy production. With the global push towards renewable energy sources, there is a substantial opportunity for WtE projects. Countries like China, which already has over 300 WtE plants, are expanding these facilities to manage waste and generate electricity, indicating a growing market for such technologies.
- E-Waste Management and Recycling: The rapid turnover of electronic devices is leading to an increase in electronic waste (e-waste), which is rich in valuable materials like gold, silver, and rare earth metals. The global e-waste recycling market is expected to grow as more countries implement regulations for proper e-waste disposal and recycling. For instance, in 2021, India introduced stringent e-waste management rules, creating opportunities for companies to establish or expand e-waste recycling operations in the region.
- Sustainable Waste Management Solutions in Emerging Markets: Emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, are experiencing rapid urbanization and industrialization, leading to increased waste generation. These regions offer substantial growth opportunities for companies providing sustainable waste management solutions. As governments in these areas seek to address waste management challenges, there is a growing demand for services such as municipal waste management, hazardous waste treatment, and recycling.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: The global shift towards a circular economy, where waste is minimized, and resources are reused, offers significant growth opportunities. Companies that can provide innovative solutions for resource recovery, recycling, and waste reduction will find opportunities in various sectors, including manufacturing, packaging, and consumer goods. For example, the global packaging industry is increasingly adopting circular economy principles, driving demand for recyclable and biodegradable materials.
Key Players Analysis
Suez is a global leader in waste management, providing innovative solutions for waste collection, recycling, and resource recovery. The company operates extensive waste treatment facilities across Europe, Asia, and the Americas. Suez is committed to advancing the circular economy by turning waste into valuable resources and reducing environmental impact. In 2022, Suez further strengthened its market position by acquiring the UK-based recycling and recovery business, Suez R&R, which has enhanced its capabilities in waste-to-energy and material recovery sectors.
Valicor Environmental Services specializes in providing comprehensive waste management solutions, particularly in the treatment of industrial wastewater and hazardous waste. The company operates a network of treatment facilities across the United States, offering services such as waste minimization, resource recovery, and safe disposal of hazardous materials. Valicor focuses on helping industries meet environmental regulations and reduce their environmental impact. Through strategic acquisitions, Valicor has expanded its capabilities and geographic reach, becoming a key player in industrial waste management.
Veolia is a global leader in waste management, providing comprehensive services including waste collection, recycling, hazardous waste treatment, and waste-to-energy solutions. The company focuses on driving the circular economy by turning waste into resources, such as converting waste into energy and recycling materials. Veolia is also heavily involved in industrial waste management and has expanded its operations in emerging markets like Asia-Pacific. The company’s innovative approach includes partnerships for closed-loop recycling, especially in the automotive and electronics sectors.
Waste Connections is a prominent waste management company in North America, offering a wide range of services including solid waste collection, recycling, and landfill operations. The company primarily serves smaller, underserved markets across the United States and Canada, focusing on residential, commercial, and industrial waste management. Waste Connections emphasizes efficient and sustainable waste practices, including expanding its recycling and landfill gas-to-energy projects. Through strategic acquisitions, Waste Connections has grown its market presence, becoming one of the largest waste management firms in the region.
Republic Services, Inc. is a leading waste management company in the United States, offering a full spectrum of services including waste collection, recycling, and landfill operations. The company serves residential, commercial, and industrial customers across the country. Republic Services is committed to sustainability, focusing on landfill diversion, recycling innovation, and renewable energy projects. The company is also expanding its capabilities in waste-to-energy and landfill gas-to-energy initiatives, aiming to reduce environmental impact and support a circular economy.
Biffa is a leading waste management company in the United Kingdom, providing waste collection, recycling, and resource recovery services. The company focuses on helping businesses and communities reduce waste and increase recycling rates. Biffa operates an extensive network of recycling facilities and is a key player in the UK’s waste-to-energy sector. The company is committed to sustainability, with initiatives to reduce landfill use and enhance the recycling of plastics, food waste, and other materials, contributing to the circular economy in the UK.
Clean Harbors, Inc. is a leading provider of environmental, energy, and industrial services, specializing in hazardous waste management. The company operates the largest network of hazardous waste disposal sites in North America, offering services such as waste collection, treatment, and safe disposal. Clean Harbors also provides emergency response and industrial cleaning services. Its focus on managing complex and hazardous waste streams makes it a critical player in maintaining environmental safety and compliance across various industries.
Covanta Holding Corporation specializes in waste-to-energy (WtE) services, converting municipal solid waste into renewable energy. The company operates WtE plants primarily in North America, where it processes millions of tons of waste annually, generating electricity and reducing landfill use. Covanta is committed to sustainable waste management practices, focusing on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy recovery. The company’s operations play a crucial role in supporting circular economy initiatives by turning waste into a valuable energy resource.
Hitachi Zosen Co. is a Japanese engineering company that plays a significant role in the waste management sector, particularly through its waste-to-energy (WtE) technologies. The company designs and constructs WtE plants globally, helping municipalities convert waste into electricity and reduce landfill dependency. Hitachi Zosen is known for its advanced incineration technology, which is designed to minimize environmental impact while maximizing energy recovery. Their solutions are integral in managing waste sustainably and supporting the circular economy in various regions.
Remondis Se & Co. Kg is one of Europe’s largest waste management companies, providing comprehensive services including waste collection, recycling, and water management. The company operates in over 30 countries, focusing on transforming waste into valuable resources. Remondis is a leader in recycling, processing millions of tons of waste annually, and contributing significantly to resource recovery. Their commitment to sustainability is evident in their extensive recycling operations and innovative approaches to reducing waste and promoting the circular economy across Europe.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the waste management sector plays a crucial role in promoting environmental sustainability and resource efficiency. As global waste generation continues to rise, driven by urbanization and industrial activities, the importance of effective waste management systems cannot be overstated. Innovations such as waste-to-energy technologies, advanced recycling methods, and smart waste management solutions are key to addressing the challenges of waste accumulation and environmental degradation.
Additionally, the shift towards a circular economy model emphasizes the need for reducing waste generation and enhancing recycling rates. Stakeholders in the waste management industry, including governments, businesses, and communities, must continue to collaborate and innovate to develop systems that not only manage waste effectively but also contribute to the conservation of natural resources and the protection of our planet for future generations.
Discuss Your Needs With Our Analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





